Future Foods, Volume 3, June 2021
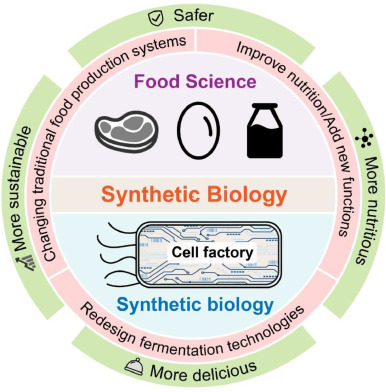
Food is essential to provide energy for human cellular metabolism, and is usually made from plants or animals. Beside plants and animals, other important food sources are made by microorganisms, typically products of fermentation (e.g bread, wine, beer, soy sauce, etc). Nowadays, because of the increasing environmental pollution, climate change and population growth, is becoming challenging to keep the food supply safe, nutritious and sustainable. Importantly, the development of the synthetic biology field enable the engineering of cells that can be used in food manufacturing.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Sea-level rise poses a significant threat to Small Island Developing States (SIDS) due to the concentration of people, assets, and infrastructure in coastal zones. This review assesses literature on key emerging topics in sea level rise including: the lasting impact of near-term mitigation on long-term sea-level rise; new global coastal vertical elevation data and their impact on existing sea-level rise projections; and the interaction of sea-level rise with other hazards, including salinization, tropical cyclones and extreme precipitation.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Sea level rise and land subsidence — induced flooding are projected to have severe impacts on highly populated Asian deltaic cities. These cities are already suffering from frequent floods, though few comparative analyses have been conducted on the similarities and differences of their adaptation approaches. Thus, this study aims to investigate the current adaptation pathways of Asian deltaic cities to flooding induced by slow onset events such as urbanization-induced land subsidence and sea level rise, by looking at Tokyo, Jakarta, Manila, and Ho Chi Minh City as case studies.
JAAD International, Volume 3, June 2021
Background: Skin diseases that cause chronic pruritus can have negative effects on a patient's quality of life. Objective: We evaluated the associations between chronic pruritus and psychological conditions including insomnia and depression. Methods: This study included responses from 91 participants with chronic pruritus (response rate: 74.6%).
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
As sea level rise drives saltwater farther inland, drinking water supplies of some coastal cities will be contaminated. This paper evaluates how climate change is shifting the location of ‘salt lines,’ the zone where coastal fresh water meets the ocean, and implications for drinking water management. It focuses on changes from climate, as opposed to water overuse or water quality mismanagement, and reviews recent literature along three dimensions. Firstly, the paper reviews regulations on salinity in drinking water.
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 29, June 2021
Microplastic pollution has sparked interest from researchers, public, industries, and regulators owing to reports of extensive presence of microplastics in the environment, household dust, drinking water, and food, which indicates chronic exposure to organisms within ecosystems and in human living spaces. Although exposure to microplastics is evident, negative effects from microplastics appear to be minimal in most studies on biota, and no risk assessments have been completed for microplastics on human health.