Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 27, December 2020
This paper provides an overview of nutrition recommendations for dietary intakes necessary to support normal growth and development of children from birth to 18 years and to promote long-term health and quality of life. Key nutrients and food-based dietary recommendations have been examined from international evidence-based child dietary and feeding guidelines from the World Health Organization and a convenience sample of countries. The paper also reviews key issues relating to the environmental impacts of child diets.
Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 27, December 2020
Current food systems are failing to guide children towards healthy diets. This paper presents a tool to identify the actions needed to reorient food systems to become more child-centred from a nutrition perspective. To connect the dots between children's lives, their food environments and food supply systems, the tool takes a child-centred, food systems approach.
Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 27, December 2020
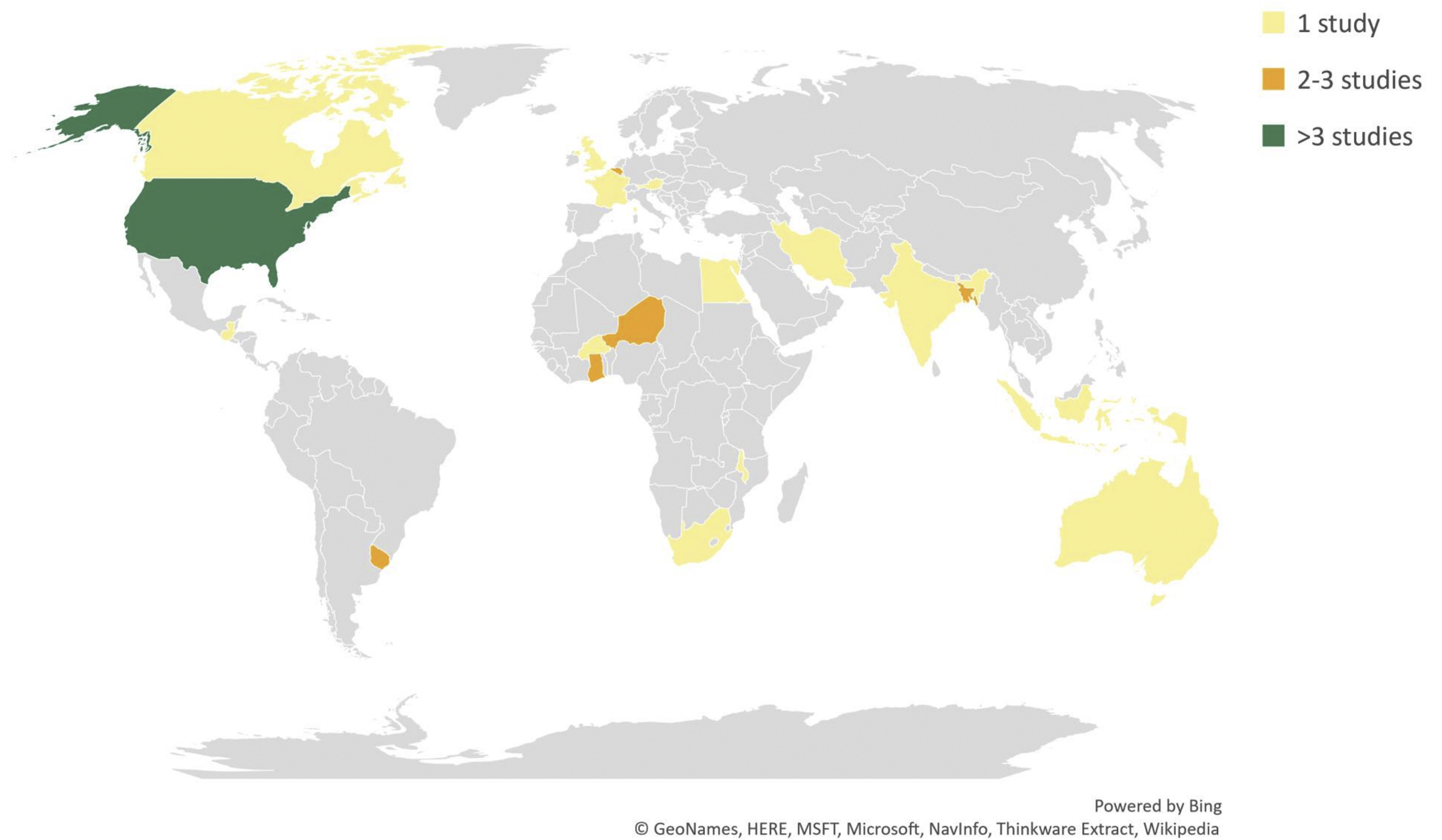
Intervening in the food environment is critical to improve the diets and nutrition of children and adolescents. Little is known about the most effective interventions targeting children and adolescents, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). We conducted a scoping review of the literature to examine influence of external and personal food environment interventions on the diets and nutrition of children and adolescents. Most of the included studies examined interventions in school settings in the United States, with few studies from LMICs.
Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 27, December 2020
This paper focuses on the most proximate determinants of dietary intake: food behaviors of caregivers, children and adolescents. Utilizing a case study approach, we explored cultural-ecological factors that have been shown to affect behavioral interventions aimed improving diet quality. The results provide insights about facilitators and barriers to uptake of interventions aimed at improving dietary behaviors in children and adolescents and highlight their implications for planning and monitoring future interventions.
Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 27, December 2020
Unhealthy food marketing has long been identified as a systems factor with negative health effects on children. The data-driven, personal data extraction and behavioural design practices of 21st century media advertising in digital technology systems mean that food marketing now sits at the intersection of multiple harms, infringing not only children's rights to health and to food, but also their rights to privacy and to be free from exploitation. This further sharpens the need for State regulation to protect children and their rights effectively.
Elsevier, Clinical Imaging, Volume 68, December 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically altered the professional and personal lives of radiologists and radiation oncologists. This article summarizes the 2020 American Association for Women in Radiology (AAWR) Women's Caucus at the American College of Radiology (ACR) Annual Meeting. The caucus focused on the major challenges that women in radiology have faced during the pandemic.
Elsevier, Leadership Quarterly, Volume 31, December 2020
Managerial oversight is strengthened and firms' strategic performance improved when boards are gender-diverse. Yet the rate of women's appointment to corporate boards is decelerating. This study proposes an explanation for the unexpected attenuation rooted in social movement dynamics, particularly cross-movement influences originating from the contemporary governance reform movement. Seeking to alleviate managerialist tendencies, the governance reform movement has compelled major changes to board structure, composition, and activity, as well as the broader logic surrounding corporate boards.
Elsevier, Computers and Security, Volume 99, December 2020
With regard to computer abuse, the term "malicious insider" tends to be associated with male employees, likely because men commit more crimes relative to women. We draw on the chivalry hypothesis to inform our study and explore whether managers demonstrate gender bias in decision-making regarding insider threats posed by subordinate employees. We recruited managers as participants in our study and randomly assigned them to an "employee gender" condition, wherein half the participants read a scenario with a female offender and half the participants read a scenario with a male offender.
Elsevier, EClinicalMedicine, Volume 29-30, December 2020
Background: Patients from ethnic minority groups are disproportionately affected by Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to explore the relationship between ethnicity and clinical outcomes in COVID-19. Methods: Databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, PROSPERO, Cochrane library and MedRxiv) were searched up to 31st August 2020, for studies reporting COVID-19 data disaggregated by ethnicity. Outcomes were: risk of infection; intensive therapy unit (ITU) admission and death. PROSPERO ID: 180654.
Elsevier, International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection, Volume 31, December 2020
Early and accurate anomaly detection in critical infrastructure (CI), such as water treatment plants and electric power grid, is necessary to avoid plant damage and service disruption. Several machine learning techniques have been employed for the design of an effective anomaly detector in such systems. However, threats such as from insiders and state actors, introduce challenges in the design of an effective anomaly detector. This work presents a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) based anomaly detector that uses an unsupervised approach to safeguard CI from the adverse impacts of cyber-attacks.