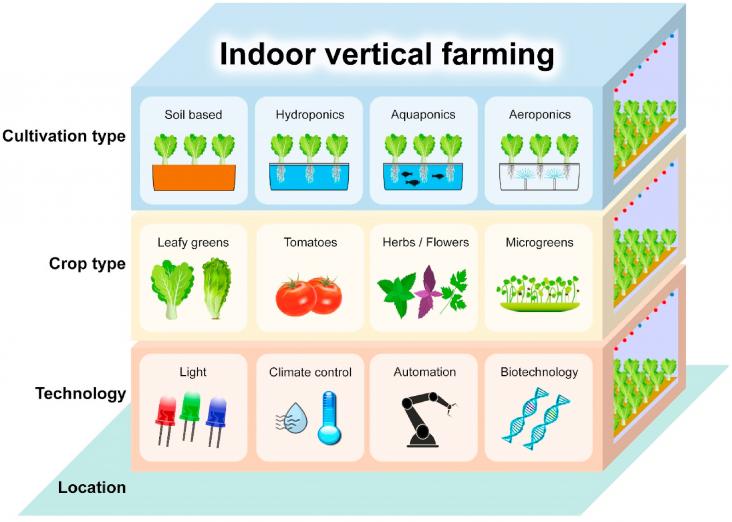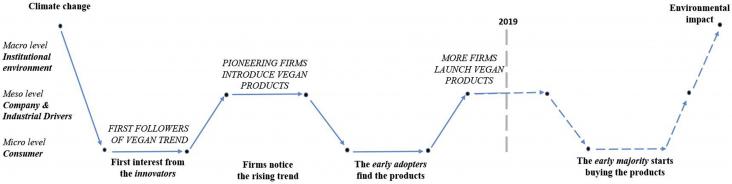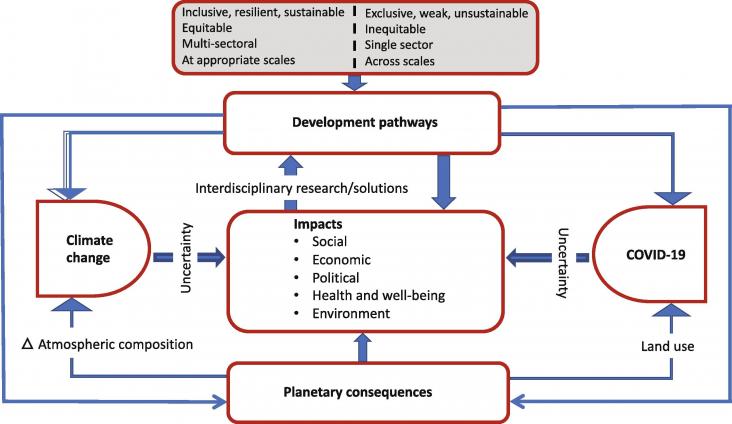
The COVID-19 pandemic and climate change are complex existential threats, unpredictable in many ways and unprecedented in modern times.
Climate change is the most critical public health crisis of the 21st century.
The ability to maintain a (relatively) stable body temperature in a wide range of thermal environments by use of endogenous heat production is a unique feature of endotherms such as birds.
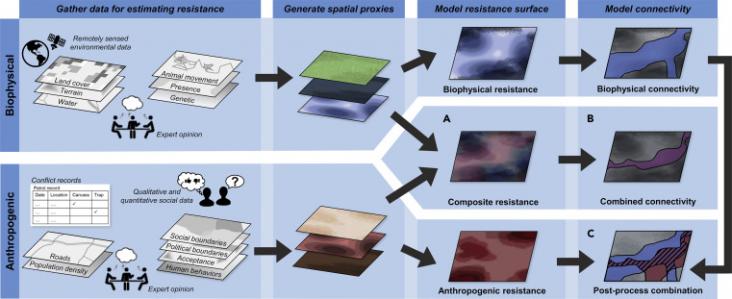
Maintaining or restoring connectivity among wildlife populations is a primary strategy to overcome the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation.