This Editorial highlights the relationship between climate change, fires, floods and infectious diseases.
UK mechanisms touching on sustainable development are generally based on, and have as their over-arching objective, some variation of the so-called “Brundtland definition”. These mechanisms also widely reference the three interconnected ‘pillars’ of sustainable development, also known as the ‘triple bottom line’ of sustainable development. The UK approach has a bearing on all SDGs and in particular, SDGs 9, 10 and 13.
Educating the leaders of tomorrow is an essential part of a sustainable future.
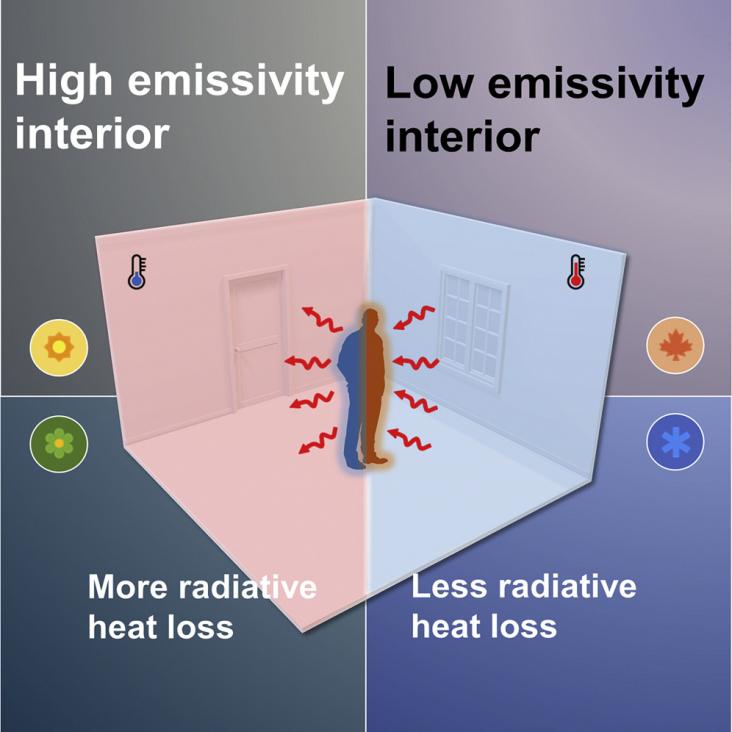
An assessment of personal heat exposure measures and strategies to reduce heat risk.
Advocating for green and sustainable conferences.
A Personal View in support of SDGs 13 and 16, discussing the promise and limitations of framing climate change as a human health issue to create greater impact on policy makers and to accelerate the shift from evidence to policy action.
This article supports SDG 2, SDG 3, and SDG 13 by demonstrating the economic benefits of wind energy development to the local individuals and communities.
Background: Associations between high and low temperatures and increases in mortality and morbidity have been previously reported, yet no comprehensive assessment of disease burden has been done.
This chapter advances UN SDG goals 11 and 13 by examining how the development of clean technologies can reduce potential environmental and human health hazards associated with the production of nanotechnology products.