If moral concern for nonhuman nature underpins conservation, it is essential to understand how individuals populate their “moral communities,” a core concept from environmental ethics, with various el
Most of the terrestrial world is experiencing high rates of land conversion despite growth of the global protected area (PA) network.
Refuges and refugia are important to conservation management because of their potential to protect species from difficult-to-manage threats such as changing climate, extreme events (e.g., drought, fir
Forests are key components of the global carbon cycle and dominate mitigation strategies for climate change and biodiversity loss.
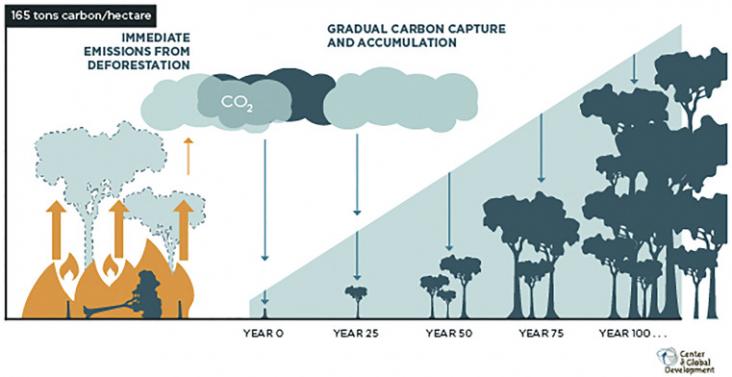
Largely driven by the corporate sector, the recent surge of interest in trees as a solution to climate change has a distinct emphasis on planting trees.
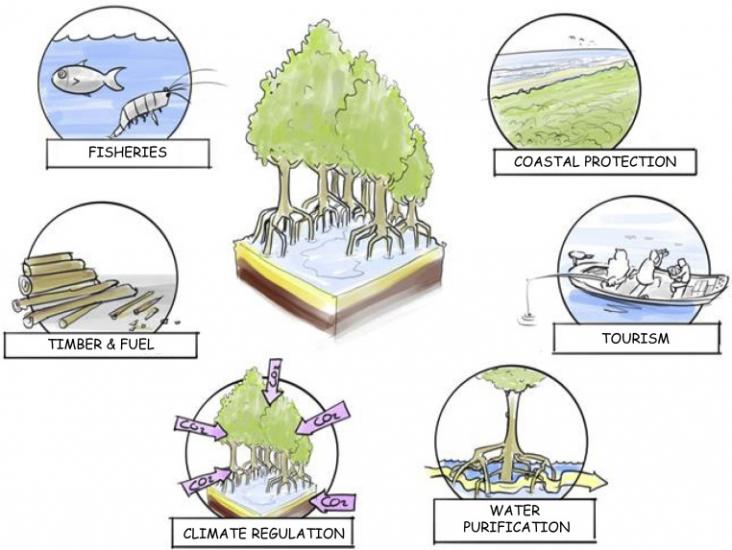
Mangrove forests are found on sheltered coastlines in tropical, subtropical, and some warm temperate regions.
The IUCN (the International Union for Conservation of Nature) World Conservation Congress called for the full protection of 30% of each marine habitat globally and at least 30% of all the ocean.
Ocean health is critical for human well-being but is threatened by multiple stressors. Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to protect 10% of their waters by 2020.
The planetary boundaries framework proposes quantified guardrails to human modification of global environmental processes that regulate the stability of the planet and has been considered in sustainab
