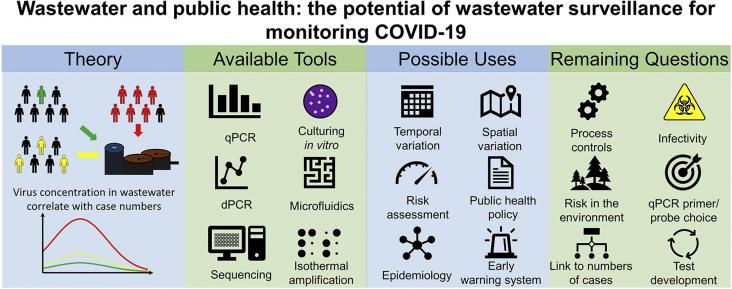
Global Groundwater. Source, Scarcity, Sustainability, Security, and Solutions, 2021, Pages 503-517
Global Groundwater. Source, Scarcity, Sustainability, Security, and Solutions, 2021, Pages 577-583
Advances in Chemical Pollution, Environmental Management and Protection, Volume 6, 2020, Pages 1-31
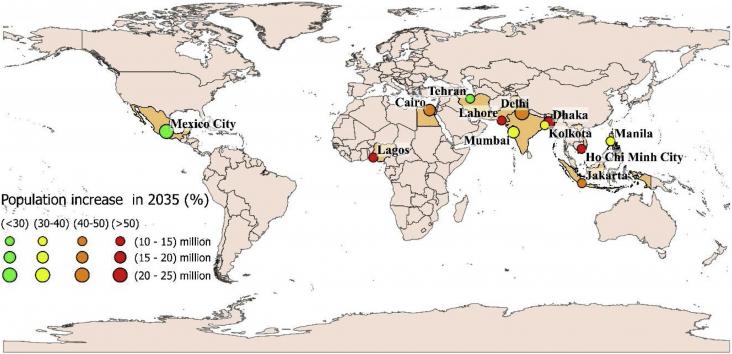
Urbanisation is increasing in many countries, leading to the establishment of 33 megacities, representing huge water demand which is increasingly difficult to supply, exemplified by the recently av
Aquananotechnology: Applications of Nanomaterials for Water Purification, 2021, Pages xv-xxiv