
This article examines how improved water security affects the success of other SDGs, when all the goals are examined simultaneously.
Elsevier,
Handbook of Advanced Approaches Towards Pollution Prevention and Control, 2021, Pages 281-305
This book chapter advances SDGs 3 and 6 by explaining why SDG goals toward clean water are so essential to those targeting good health.
Elsevier,
Gemma C. Cotton, Natalie R. Lagesse, Liam S. Parke, Carla J. Meledandri, 3.04 - Antibacterial Nanoparticles, Editor(s): David L. Andrews, Robert H. Lipson, Thomas Nann, Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Second Edition), Academic Press, 2019, Pages 65-82
This chapter advances SDGs 3 and 6 by showing how increasing bacterial resistance to commonly used antibiotics is a pressing threat to the human population on a global scale. As the development of new combative drugs is complex, expensive, time consuming and risky, there has been a strong focus in recent years to develop alternative strategies for the treatment of bacterial infections, and nanoscale materials have emerged a strong contender for this purpose.
In this study, the authors investigate the effect of phosphate functionalisation on the removal of uranyl ions from mine-drainage contaminated water.
This study analyzes the effects of a local water market formation on the efficiency of groundwater use productivity. These results demonstrate the role of a market-based groundwater allocation approach under water scarcity conditions.
The reported number of cases of Acanthamoeba amebic keratitis (AK) is continually increasing.
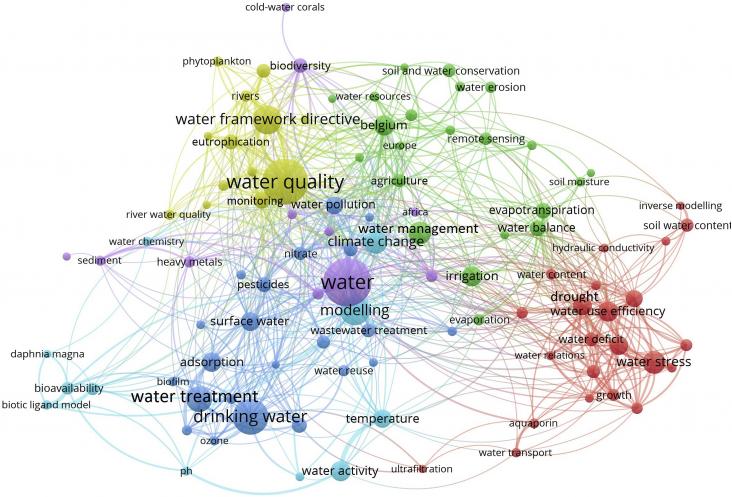
Reaching the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 on water and sanitation is fundamentally important and conditional to the achievement of all the other SDGs.

Recent policy developments in Europe consider the importance of water ecosystems to human wellbeing and the detrimental effects that multiple pressures may have on them.

Agricultural pesticides represent a significant class of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) to which non-target organisms around the world are constantly exposed.
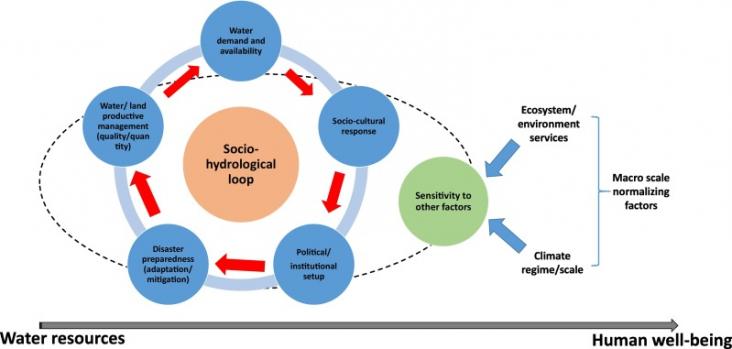
This paper presents challenges for water security in the three largest riverine islands in Asia, a socio-hydrology approach to manage water scarcity and human well-being, and an adaptive management cycle to implement socio-hydrology in the field.
