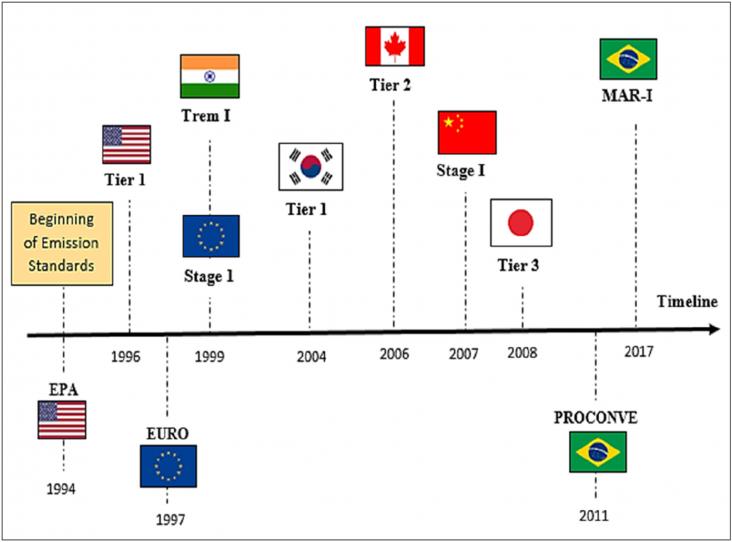
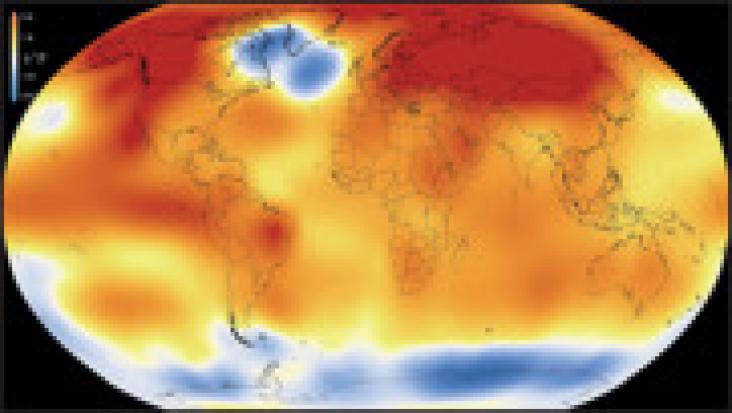
COP26 is the 2021 United Nations annual climate change conference. COP stands for Conference of the Parties. Parties are the signatories of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) - a treaty agreed in 1994 which has 197 Parties (196 countries and the EU). The 2021 conference, hosted by the UK, together with our partners Italy, in Glasgow, will be the 26th meeting of the Parties, which is why it's called COP26.
United Nations climate change conferences are among the largest international meetings in the world. The negotiations between governments are complex and involve officials from every country in the world as well as representatives from civil society and the global news media.
To build momentum for this pivotal event, we're sharing a curated list of impactful book chapters and journal articles that will drive research and deliver meaningful ways to take positive environmental action.
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 30, August 2021
Since the launch of the United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, the SDGs have been widely adopted by governments and corporations in an effort to improve their sustainability. There are 17 SDGs, comprising 169 targets, which are measurable against 247 unique indicators. Despite pervasive global pollution from (micro)plastics, there is only one indicator (14.1.1b) under Goal 14, specifically related to reducing impacts from (micro)plastics.
Design and Operation of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: The Systems Engineering Vision for Industrial Application, Volume , 1 January 2019
Climate Risk Management, Volume 34, January 2021
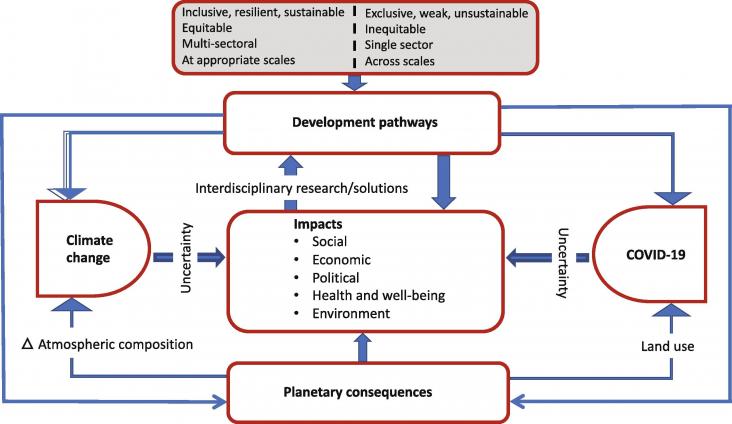
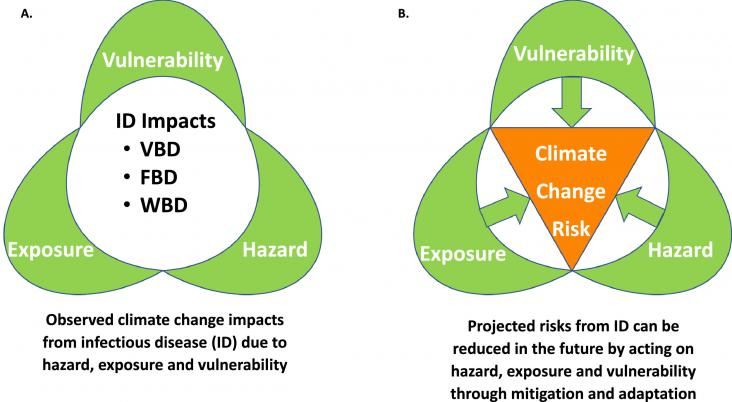
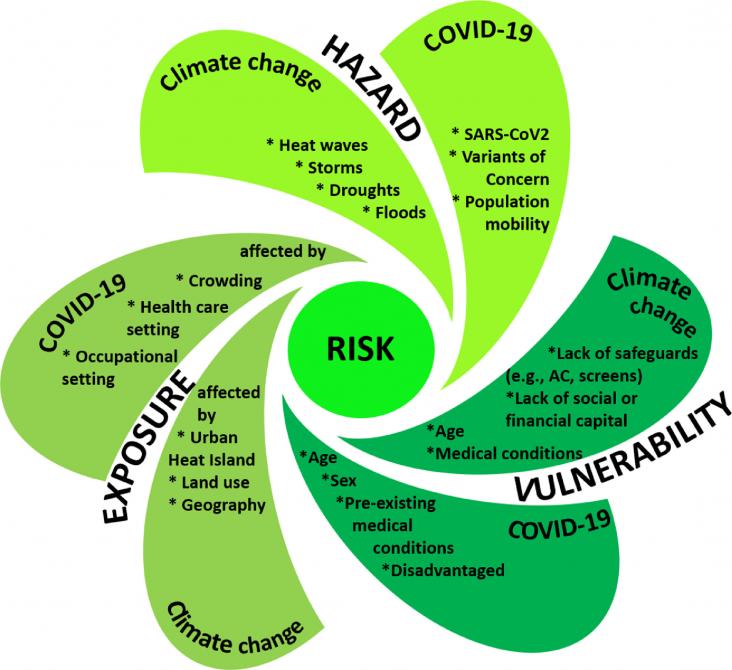
The COVID-19 pandemic and climate change are complex existential threats, unpredictable in many ways and unprecedented in modern times. There are parallels between the scale and scope of their impacts and responses. Understanding shared drivers, coupled vulnerabilities, and criteria for effective responses will help societies worldwide prepare for the simultaneous threats of climate change and future pandemics. We summarize some shared characteristics of COVID-19 and climate change impacts and interventions and discuss key policy implications and recommendations.
Green Ports: Inland and Seaside Sustainable Transportation Strategies, Volume , 20 September 2018
Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies, Volume , 4 July 2017
Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies, Volume , 4 July 2017
Hybrid Nuclear Energy Systems, A Sustainable Solution for the 21st Century, Hybrid Energy Systems, 2021, Pages 23-41
Nuclear Decommissioning Case Studies, Volume Two - Policies, Strategies, Planning and Knowledge Management, 2021, Pages 3-7
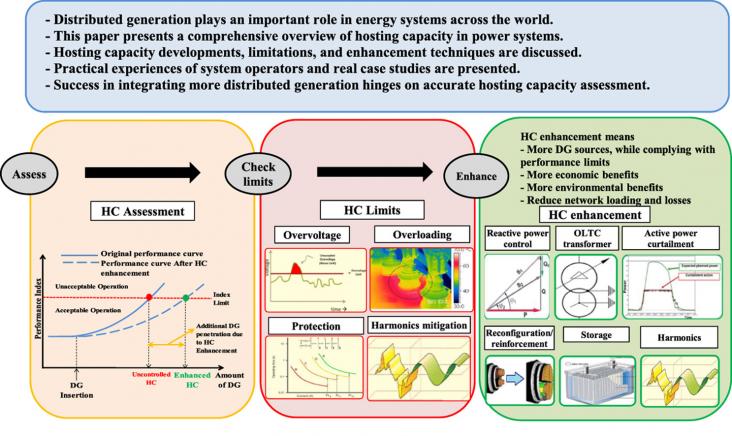
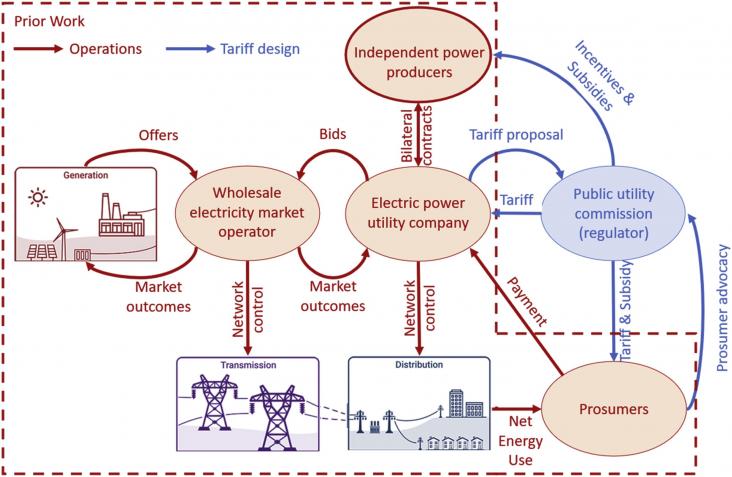
Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, Volume 28, December 2021
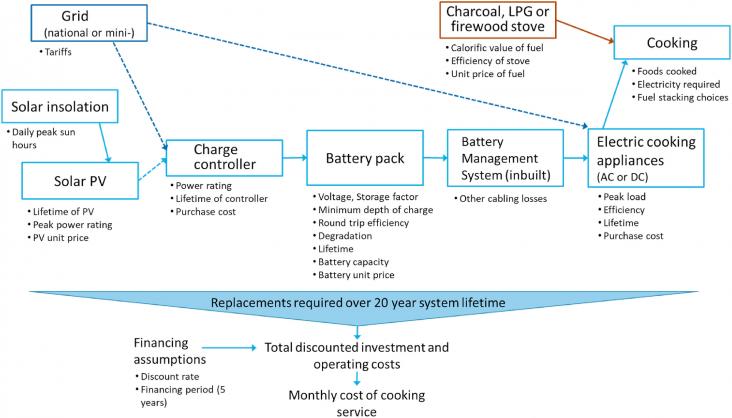
By the year 2019, the number of people without access to electricity was 770 million, most of which lived in rural areas. The currently models for rural electrification are often limited in their electrical analysis, or focus on a idealistic optimal solution whilst ignoring the real hierarchical topology of power systems. This work proposes a rural electrification strategy that makes use of Geographic Information System (GIS), graph theory and terrain analysis to create the best electric network topology.
Animal Behaviour, Volume 178, August 2021
Why is polyandry such a common mating behaviour when it exposes females to a range of significant fitness costs? Here, we investigated whether polyandry protects females against reduced male fertility caused by thermal stress from heatwave conditions. Sperm production and function are vulnerable to heat, and heatwave conditions are forecast to increase as our climate warms, so we examined these effects on female reproduction and mating behaviour in the flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum, a promiscuous ectotherm model in which fertility is damaged by environmental warming.
Energy for Sustainable Development, Volume 61, April 2021
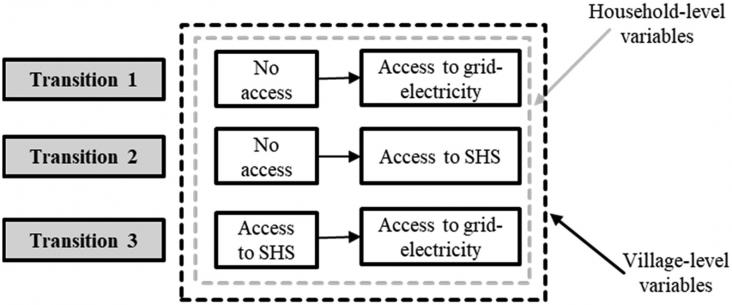
This paper presents an analysis of the path towards a clean energy transition in rural areas, from the time that households do not have electricity access from any source, to when they get access to the national electricity; considering the intermediate access to an off-grid renewable technology, as well as the post-electrification years. For this, field household-level data are collected through surveys and electricity consumption measurements in rural Kenya.
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, Volume 519, 1 January 2021
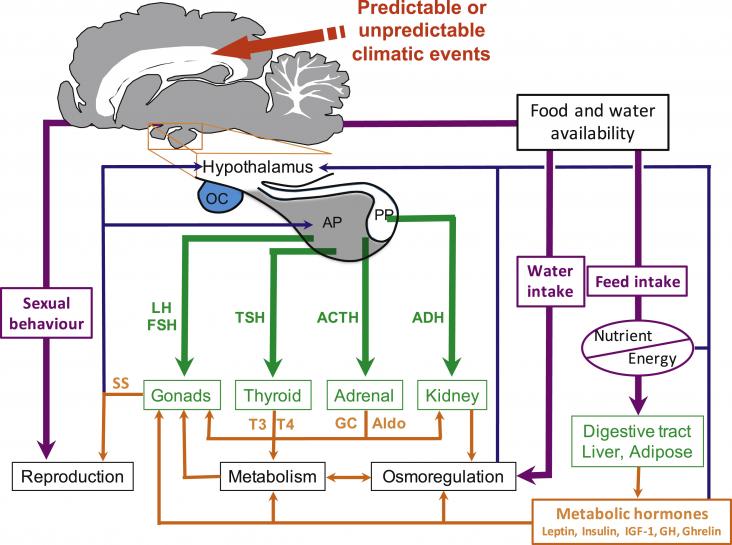
The ability to maintain a (relatively) stable body temperature in a wide range of thermal environments by use of endogenous heat production is a unique feature of endotherms such as birds. Endothermy is acquired and regulated via various endocrine and molecular pathways, and ultimately allows wide aerial, aquatic, and terrestrial distribution in variable environments. However, due to our changing climate, birds are faced with potential new challenges for thermoregulation, such as more frequent extreme weather events, lower predictability of climate, and increasing mean temperature.
Journal of the Energy Institute, Volume 92, December 2019
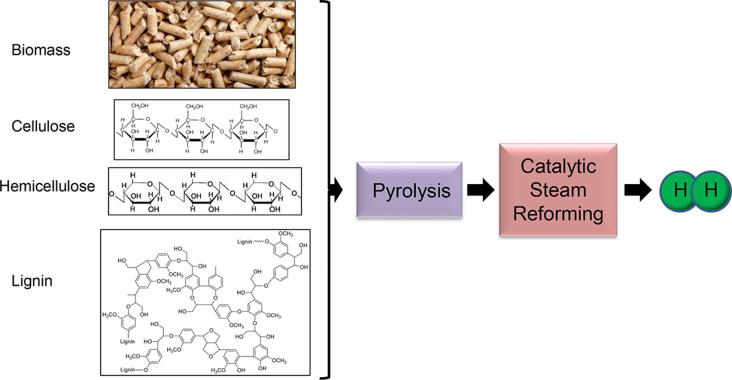
The pyrolysis-catalytic steam reforming of six agricultural biomass waste samples as well as the three main components of biomass was investigated in a two stage fixed bed reactor. Pyrolysis of the biomass took place in the first stage followed by catalytic steam reforming of the evolved pyrolysis gases in the second stage catalytic reactor. The waste biomass samples were, rice husk, coconut shell, sugarcane bagasse, palm kernel shell, cotton stalk and wheat straw and the biomass components were, cellulose, hemicellulose (xylan) and lignin.
Heliyon, Volume 7, July 2021
Despite the improvement in technologies for the production of alternative fuels (AFs), and the needs for using more AFs for motor vehicles for the reductions in air pollution and greenhouse gases, the number of alternative fuel vehicles (AFVs) in the global transportation sector has not been increasing significantly (there are even small drops for adapting some AFs through the projections) in recent years and even in the near future with projections to 2050. And gasoline and diesel fuels will remain as the main energy sources for motor vehicles.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 101, March 2019
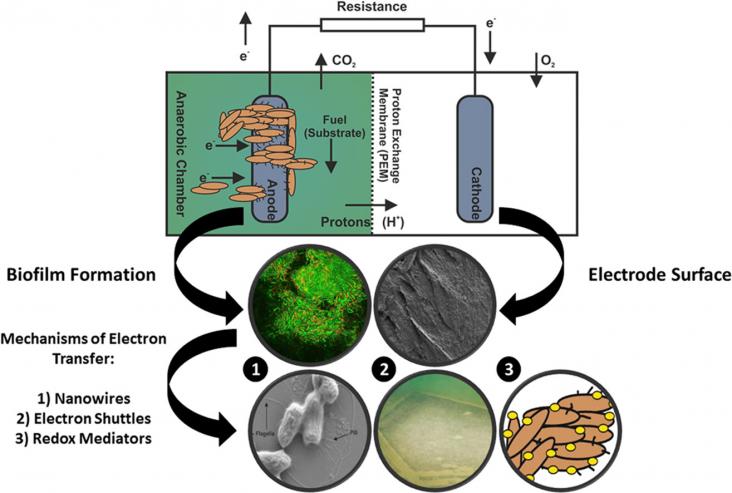
Research into alternative renewable energy generation is a priority, due to the ever-increasing concern of climate change. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are one potential avenue to be explored, as a partial solution towards combating the over-reliance on fossil fuel based electricity. Limitations have slowed the advancement of MFC development, including low power generation, expensive electrode materials and the inability to scale up MFCs to industrially relevant capacities. However, utilisation of new advanced electrode-materials (i.e.
Signal Processing, Volume 190, January 2022
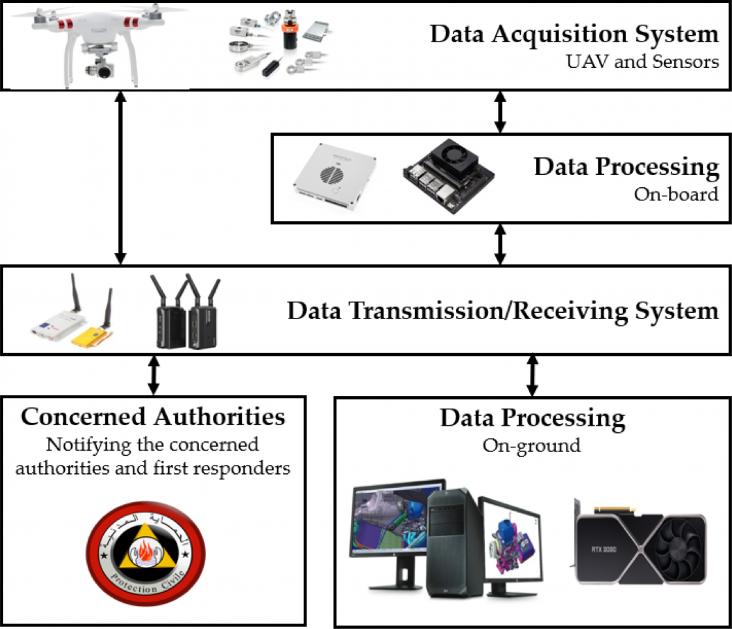
Wildfire is one of the most critical natural disasters that threaten wildlands and forest resources. Traditional firefighting systems, which are based on ground crew inspection, have several limits and can expose firefighters’ lives to danger. Thus, remote sensing technologies have become one of the most demanded strategies to fight against wildfires, especially UAV-based remote sensing technologies. They have been adopted to detect forest fires at their early stages, before becoming uncontrollable.
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, Volume 42, December 2021
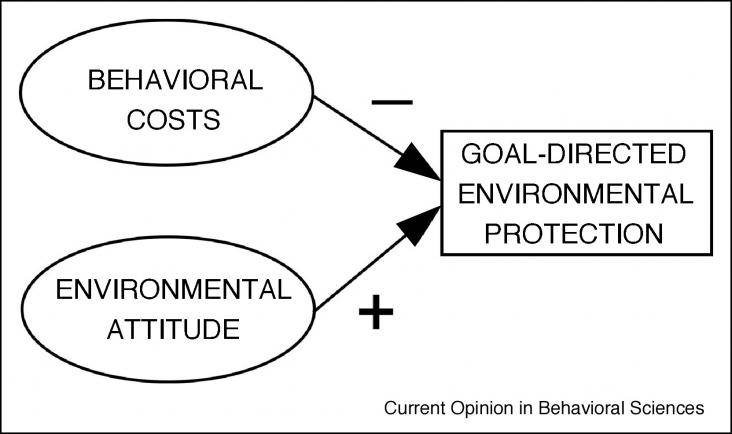
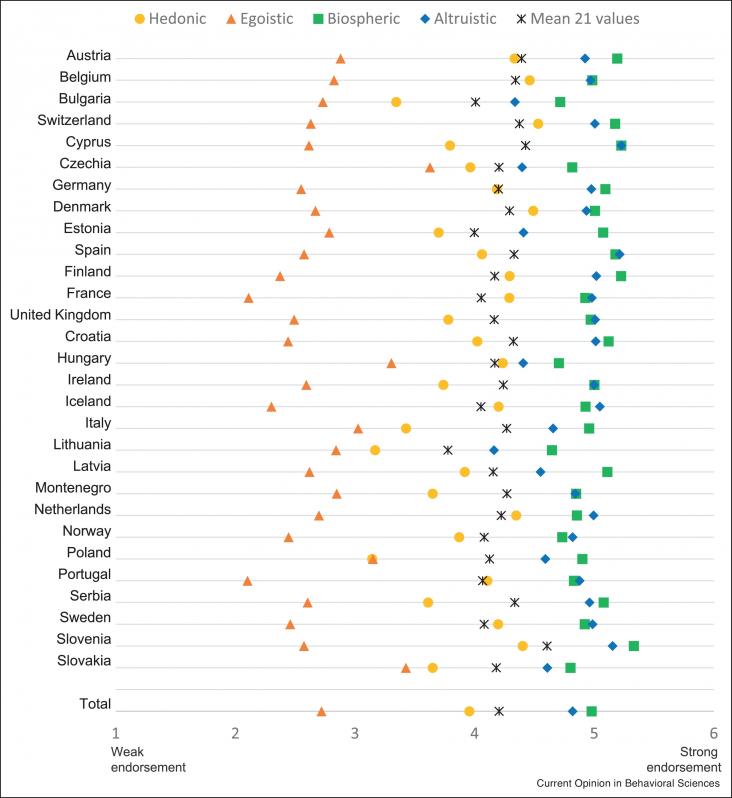
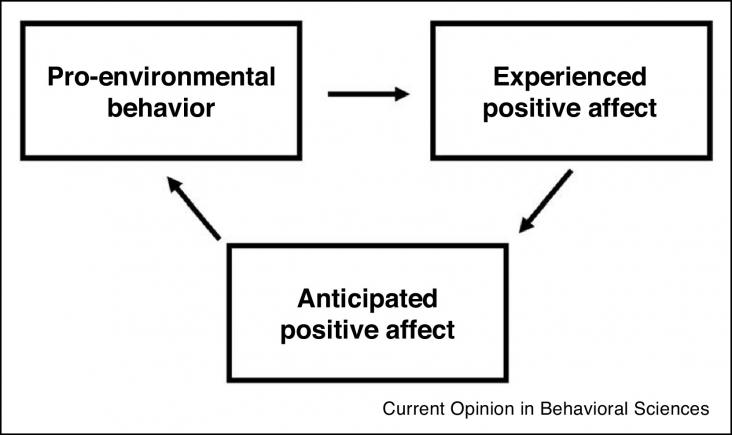
The mounting research on consumer behavior and climate change is gradually improving our understanding of effective ways to mobilize consumers to mitigate climate change. The relationship between consumer behavior and climate change is complex and most consumers are not capable of determining which behavior changes are worth doing. Research has come a long way identifying the most impactful behavior changes, but more research is needed to refine and situate these insights.
Public Health in Practice, Volume 2, November 2021
Cyclones and tropical storms are important threats to public health faced by countries worldwide as they are associated with infectious disease outbreaks, unsafe food and water to mention a few. To help meet these challenges, the World Health Organization encourages countries to strengthen their capacities for health emergency and disaster risk management incorporating measures for prevention, mitigation, preparedness, response and recovery. In this letter, we unpack the case of Zimbabwe's preparedness and response to cyclones and tropical storms.
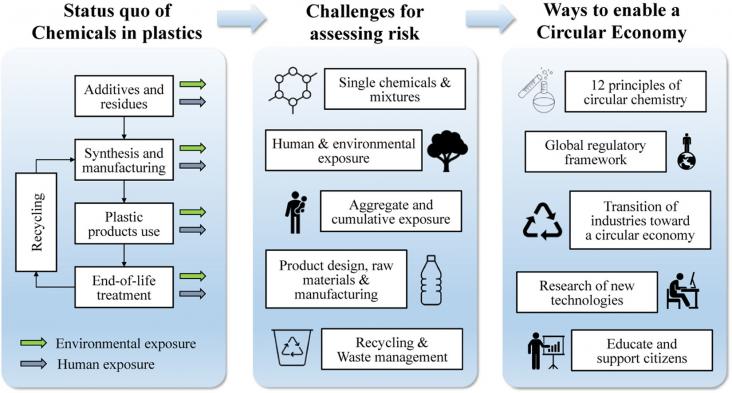
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 31, October 2021
Enabling a circular economy for plastics in Europe and beyond is an ambitious goal. To reach a fully closed loop, numerous challenges and knowledge gaps need to be overcome. This review provides a list of more than 6000 chemicals reported to be found in plastics and an overview of the challenges and gaps in assessing their impacts on the environment and human health along the life cycle of plastic products. We further identified 1518 plastic-related chemicals of concern, which should be prioritized for substitution by safer alternatives.
Global Environmental Change, Volume 70, September 2021
The purpose of the present paper is to disentangle the mechanisms that connect climate change-induced disasters, inequality and vulnerability by accounting for both directions of causality. We do so by means of a simultaneous equations approach on a panel of 149 countries from 1992 to 2018. The empirical analysis reveals that countries with higher levels of income inequality suffer greater damages when hit by a natural disaster. At the same time, inequality is found to increase the number of people affected by disasters.
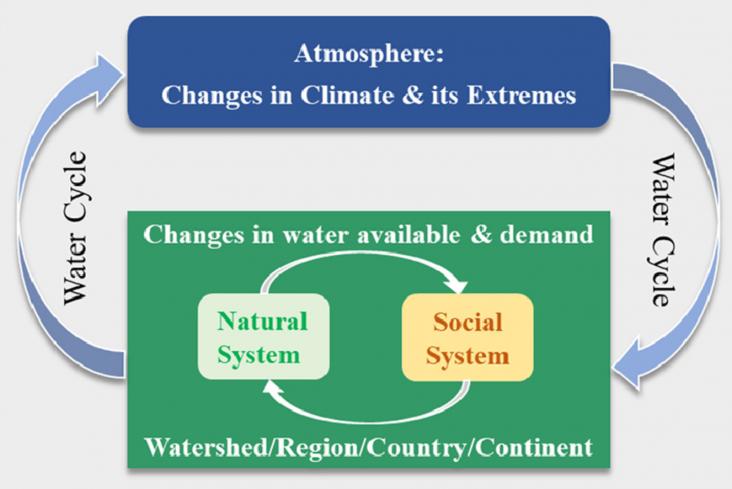
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 2, June 2021
Water is the fundamental natural resource that supports life, ecosystems and human society. Thus studying the water cycle is important for sustainable development. In the context of global climate change, a better understanding of the water cycle is needed. This study summarises current research and highlights future directions of water science from four perspectives: (i) the water cycle; (ii) hydrologic processes; (iii) coupled natural-social water systems; and (iv) integrated watershed management.
Journal for Nurse Practitioners, Volume , 2021
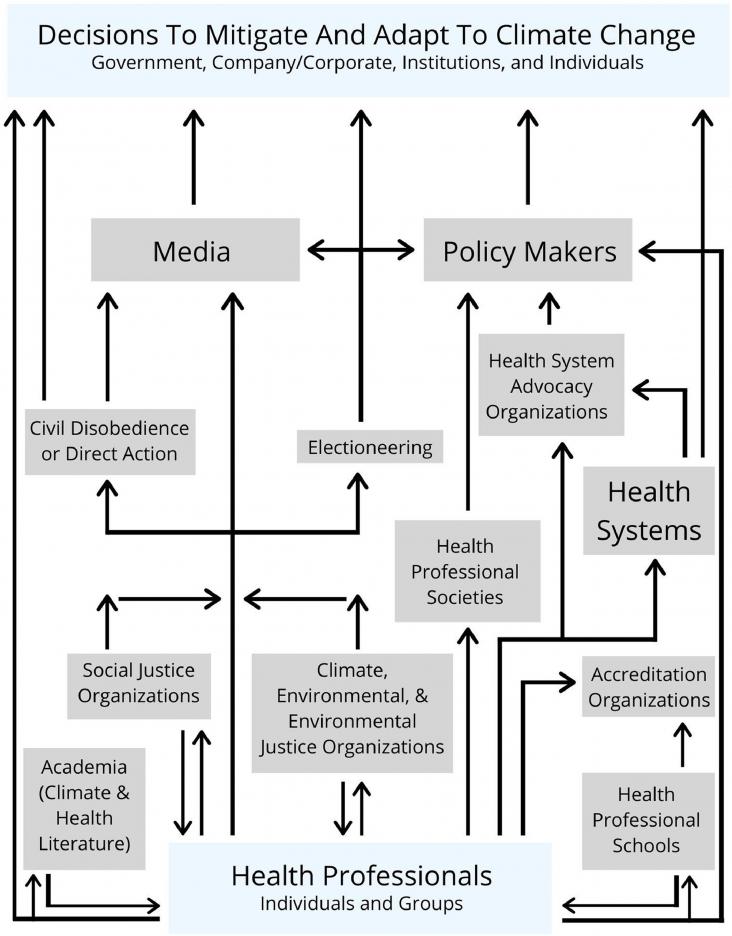
Climate change is the most critical public health crisis of the 21st century. Physical and medical sequelae of climate and weather-related events are well documented and may be addressed in clinical practice. Mental health impacts of climate change are increasingly addressed in the literature but remain underrecognized by clinicians. This report focuses on mental health impacts of climate change through the theoretical framework of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, September 2020
Tillage is the most common agricultural practice dating back to the origin of agriculture. In recent decades, no-tillage (NT) has been introduced to improve soil and water quality. However, changes in soil properties resulting from long-term NT can increase losses of dissolved phosphorus, nitrate and some classes of pesticides, and NT effect on nitrous oxide (N2O) emission remains controversial. Complementary management that enhances the overall environmental benefits of NT is therefore crucial.
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, September 2020
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, September 2020
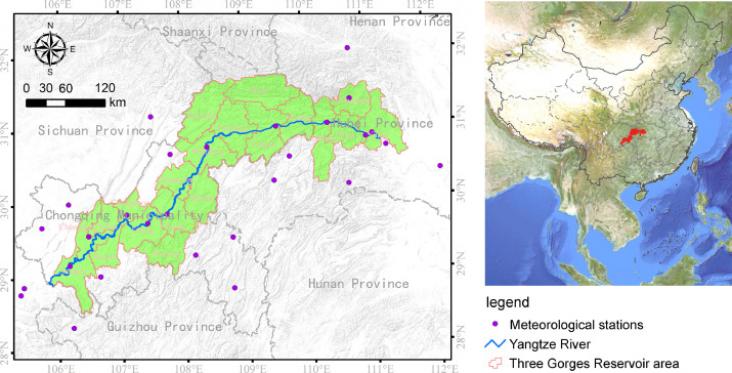
Climate, land use and land cover (LULC) changes are among the primary driving forces of soil loss. Decoupling their effects can help in understanding the magnitude and trend of soil loss in response to human activities and ecosystem management. Here, the RUSLE model was applied to estimate the spatial-temporal variations of soil loss rate in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area during 2001–2015, followed by a scenario design to decouple the effects of climate and LULC changes. The results showed that increasing rainfall generated as much as 2.90 × 107 t soil loss in the TGR area.
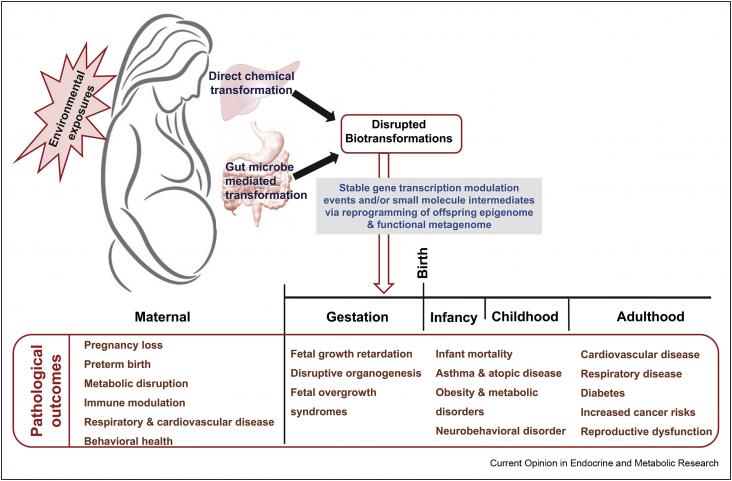
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research, Volume 11, April 2020
Climate change will expose mammals to an array of stressors, some new, and some with increased frequency and severity. Those stressors influence endocrine and metabolic function, with potential consequences for the survival and persistence of mammalian species. Here, we review the similar consequences of climate change on the physiological function of terrestrial mammals, including direct effects of increasing air temperatures and reduced water availability, as well as the indirect effect of reduced or unpredictable food supply.
Biomass and Bioenergy, Volume 123, April 2019
Pyrolysis converts biomass into liquid, gaseous and solid fuels. This work reviews the existing models for biomass pyrolysis, including kinetic, network and mechanistic models. The kinetic models are based on the global reaction mechanisms and have been extensively used for a wide range of biomass under various operating conditions. Major emphases have been on the network models as these models predict the structural changes during biomass pyrolysis. Key aspects of various network models include reaction schemes, structural characteristics and applications to CFD simulations.
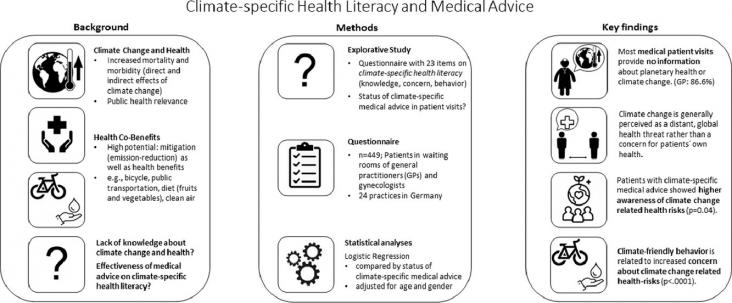
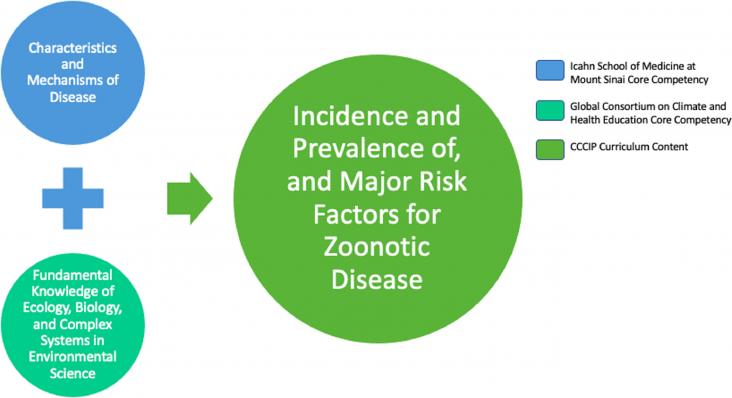
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, Volume 4, 2021,100038,
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Transition, Volume 1, 2021,100001,
Public Health in Practice, Volume 2, 2021,100095,
Heliyon, Volume 7, Issue 9, 2021, e07838,
Current Research in Ecological and Social Psychology, Volume 2,2021,100008,
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, Volume 4, 2021, 100058
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, 2021, 100065
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, Volume 4, 2021, 100070
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, Volume 4, 2021, 100050
Sustainability of Life Cycle Management for Nuclear Cementation-Based Technologies, Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, 2021, Pages 181-232
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Sea-level rise poses a significant threat to Small Island Developing States (SIDS) due to the concentration of people, assets, and infrastructure in coastal zones. This review assesses literature on key emerging topics in sea level rise including: the lasting impact of near-term mitigation on long-term sea-level rise; new global coastal vertical elevation data and their impact on existing sea-level rise projections; and the interaction of sea-level rise with other hazards, including salinization, tropical cyclones and extreme precipitation.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Sea level rise and land subsidence — induced flooding are projected to have severe impacts on highly populated Asian deltaic cities. These cities are already suffering from frequent floods, though few comparative analyses have been conducted on the similarities and differences of their adaptation approaches. Thus, this study aims to investigate the current adaptation pathways of Asian deltaic cities to flooding induced by slow onset events such as urbanization-induced land subsidence and sea level rise, by looking at Tokyo, Jakarta, Manila, and Ho Chi Minh City as case studies.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
As sea level rise drives saltwater farther inland, drinking water supplies of some coastal cities will be contaminated. This paper evaluates how climate change is shifting the location of ‘salt lines,’ the zone where coastal fresh water meets the ocean, and implications for drinking water management. It focuses on changes from climate, as opposed to water overuse or water quality mismanagement, and reviews recent literature along three dimensions. Firstly, the paper reviews regulations on salinity in drinking water.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Droughts are significant drivers of land degradation, which in turn has adverse effects on resource-dependent rural populations and can potentially lead to livelihood losses and subsequent migration out of affected areas. Linkages between land degradation and migration are complex and not particularly well documented, as they occur within a larger context of multi-scale interactions of socio-economic, political, demographic, and environmental processes. Given these uncertainties, further research in this field is needed.
Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, Volume 50, June 2021
Climate change has affected diverse spheres and its impact is being witnessed worldwide. Soil, the basis of human sustenance, is both directly and indirectly affected by climate change. Soil erosion, vegetation degradation and soil salinisation are becoming prevalent, causing a threat to future food security. Saline soils are found mainly in North and Central Asia, Africa and South America. Various factors such as excess irrigation and poor drainage, groundwater salinity, sea level rise and intrusion, irregular rainfall contribute to the process of soil salinisation.