Porous liquids form a new class of materials, which are liquid at room temperature and possess permanent porosity. The latter is a characteristic generally associated with solid-state only.
Background: The association of air pollution with multiple adverse health outcomes is becoming well established, but its negative economic impact is less well appreciated.
Buildings consume vast amounts of energy and pollute the environment in various ways.
Among the major pollutants in the atmosphere, carbon oxides are the result of multiple factors, mainly due to human activities.
In this paper, we use standard scenarios focussing on renewable energy, energy efficiency and grid investments.
Herein, we present a multigram scale-up route for the preparation of novel polymer composite nanoparticles as potential multifunctional rechargeable material for future, sustainable batteries.
The demand-supply balance of electricity systems is fundamentally linked to climate conditions.
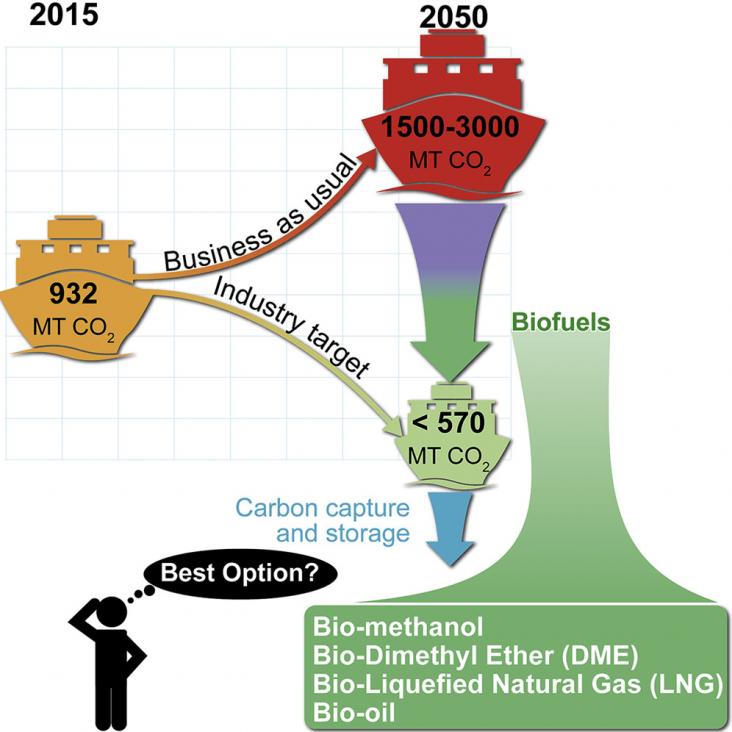
The greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the marine sector were around 2.6% of world GHG emissions in 2015 and are expected to increase 50%–250% to 2050 under a “business as usual” scenario, making the d
Background: 3 billion people worldwide rely on polluting fuels and technologies for domestic cooking and heating.

This article highlights the winning proposals of the fifth edition of the Elsevier Foundation Green & Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. The winning proposals were chosen for their innovative green chemistry aspects and their large positive impact on the environment, contributing to SDGs 7, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14 and 15.
