Climate change, a global phenomenon characterized by alterations in weather patterns, rising global temperatures, and an increase in extreme weather events, poses a significant challenge to sustainable development and directly impacts the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs, a collection of 17 interlinked global goals designed as a "blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all" by 2030, are intrinsically connected to climate action.
Central to this relationship is SDG 13: Climate Action, which calls for urgent measures to combat climate change and its impacts. This goal acknowledges that without immediate and sustained action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the achievement of other SDGs is at risk. Climate change exacerbates existing challenges such as poverty (SDG 1), hunger (SDG 2), and health issues (SDG 3) by disrupting livelihoods, food security, and health conditions. For instance, increased temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affect crop yields, leading to food insecurity. Similarly, the spread of diseases is influenced by climatic conditions, directly impacting public health.
Furthermore, climate change has a disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including those living in poverty, exacerbating inequalities (SDG 10). It affects access to clean water (SDG 6) and sanitation, with changing weather patterns disrupting water supply. The degradation of natural habitats and ecosystems under climate stress threatens life below water (SDG 14) and life on land (SDG 15), leading to biodiversity loss and affecting the livelihoods of those dependent on these ecosystems.
The economic impacts of climate change are also profound, affecting sustainable industrialization (SDG 9) and undermining economic growth (SDG 8). Severe weather events cause extensive damage to infrastructure and lead to economic losses, while changes in climatic conditions can impact industries such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism.
Moreover, climate change poses challenges to achieving sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11) as urban areas face increased risks of flooding, heatwaves, and air pollution. This necessitates the development of resilient infrastructure and adaptive urban planning. Additionally, the energy sector, integral to most economic activities, must transition towards clean and renewable sources (SDG 7) to mitigate climate change, highlighting the interdependence of the SDGs.
Global partnerships (SDG 17) are crucial in addressing climate change, as it is a global issue requiring international cooperation and funding. Developed countries are urged to support developing nations in climate mitigation and adaptation efforts, recognizing the shared responsibility and differing capacities among nations.
Global climate change and land degradation are two grand changes facing humanity. In this perspective, we examine how degraded and abandoned farmland can be harnessed to fight climate change. Building upon and extending natural climate solutions, we suggest that the carbon capture and storage of abandoned farmland can be accelerated and maximized through restoring the diversity of plant species, applying biochar to soil, and co-developing renewable energy such as solar power. The benefits of these approaches extend far beyond climate-change mitigation and land restoration.
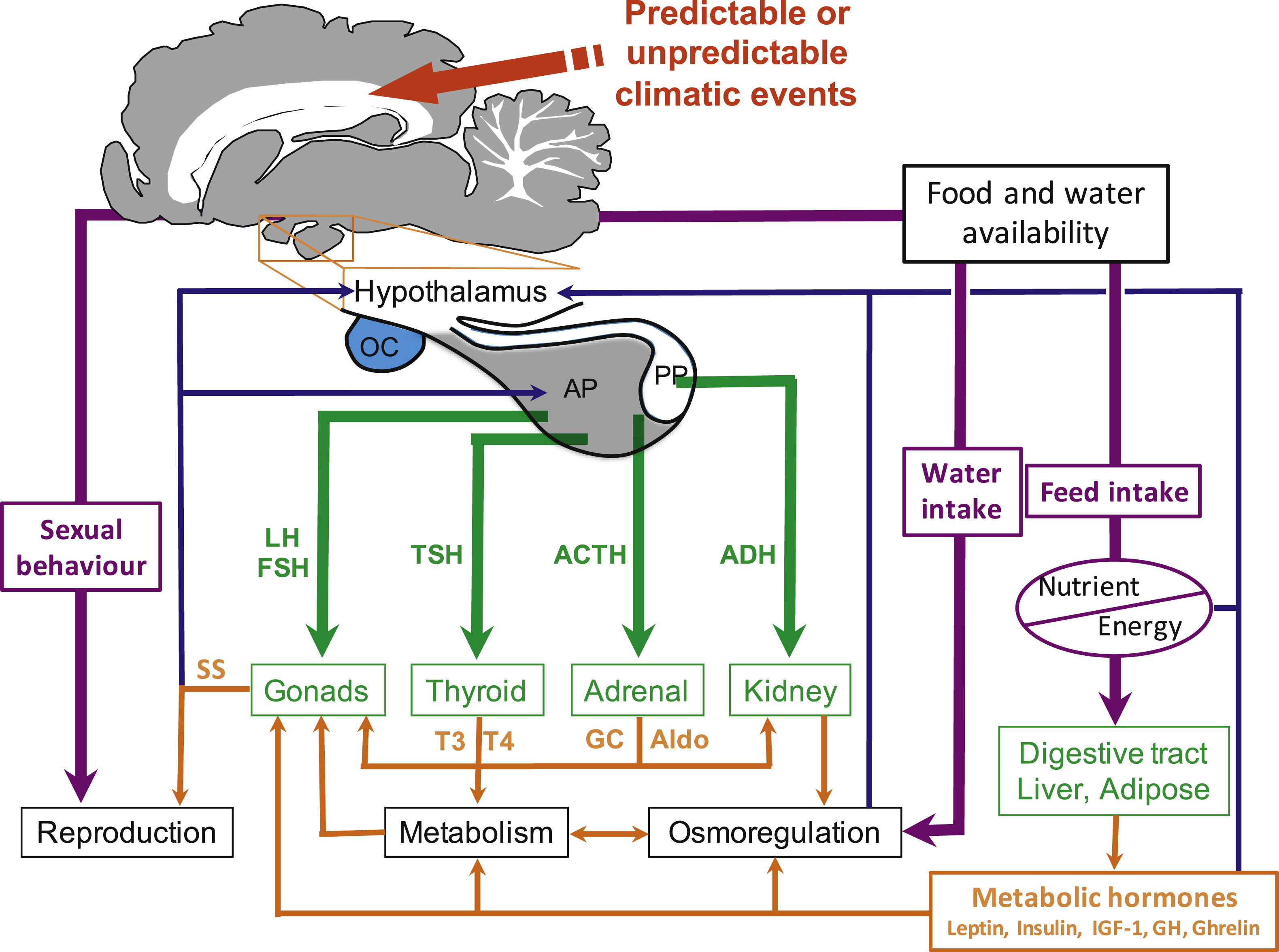
Climate change will expose mammals to an array of stressors, some new, and some with increased frequency and severity. Those stressors influence endocrine and metabolic function, with potential consequences for the survival and persistence of mammalian species. Here, we review the similar consequences of climate change on the physiological function of terrestrial mammals, including direct effects of increasing air temperatures and reduced water availability, as well as the indirect effect of reduced or unpredictable food supply.
Although several empirical studies and systematic reviews have documented the mental health impacts of global climate change, the range of impacts has not been well understood. This review examines mental health impacts of three types of climate-related events: (1) acute events such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires; (2) subacute or long-term changes such as drought and heat stress; and (3) the existential threat of long-lasting changes, including higher temperatures, rising sea levels and a permanently altered and potentially uninhabitable physical environment.
Approximately 1 billion people currently live in informal settlements, primarily in urban areas in low- and middle-income countries. Informal settlements are defined by poor-quality houses or shacks built outside formal laws and regulations. Most informal settlements lack piped water or adequate provision for sanitation, drainage, and public services. Many are on dangerous sites because their inhabitants have a higher chance of avoiding eviction. This paper considers how to build resilience to the impacts of climate change in informal settlements.