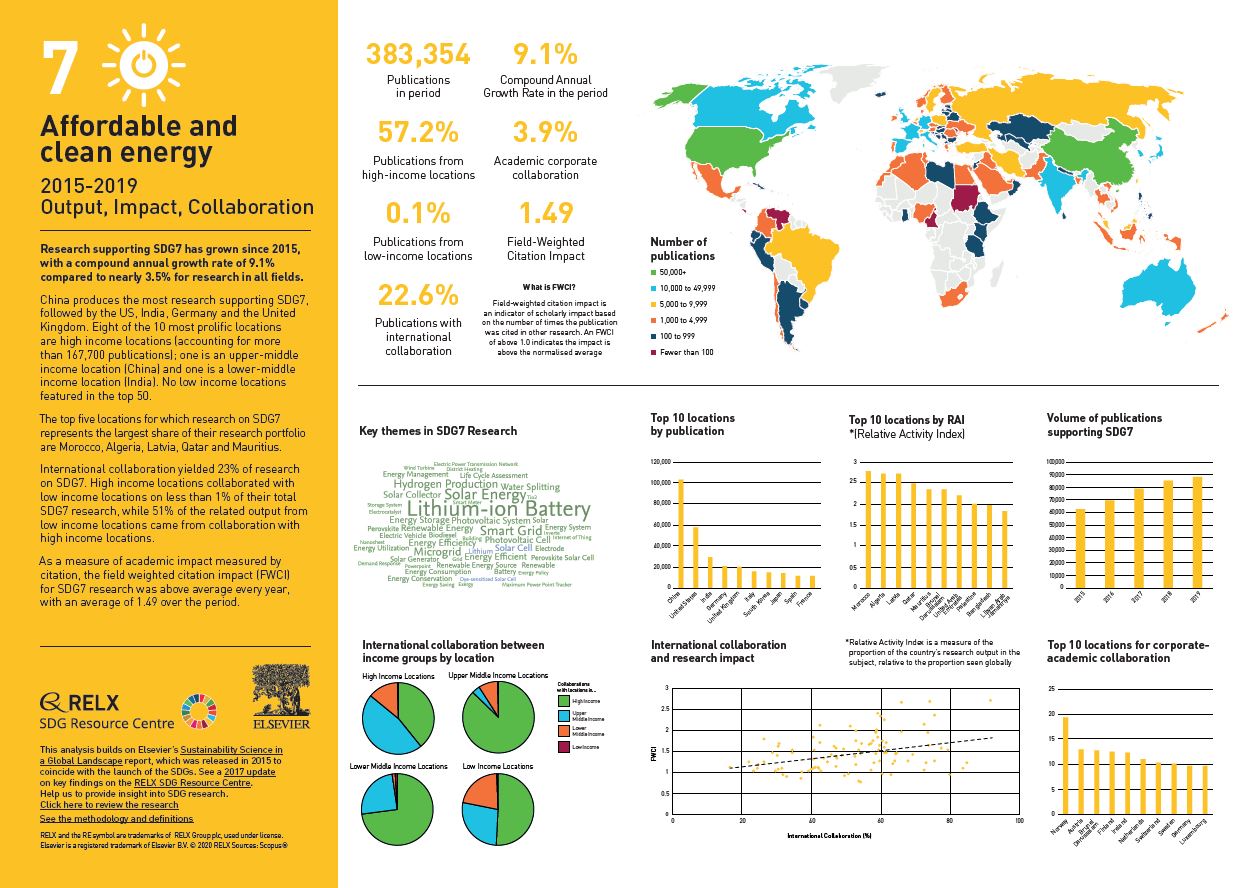
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 7.
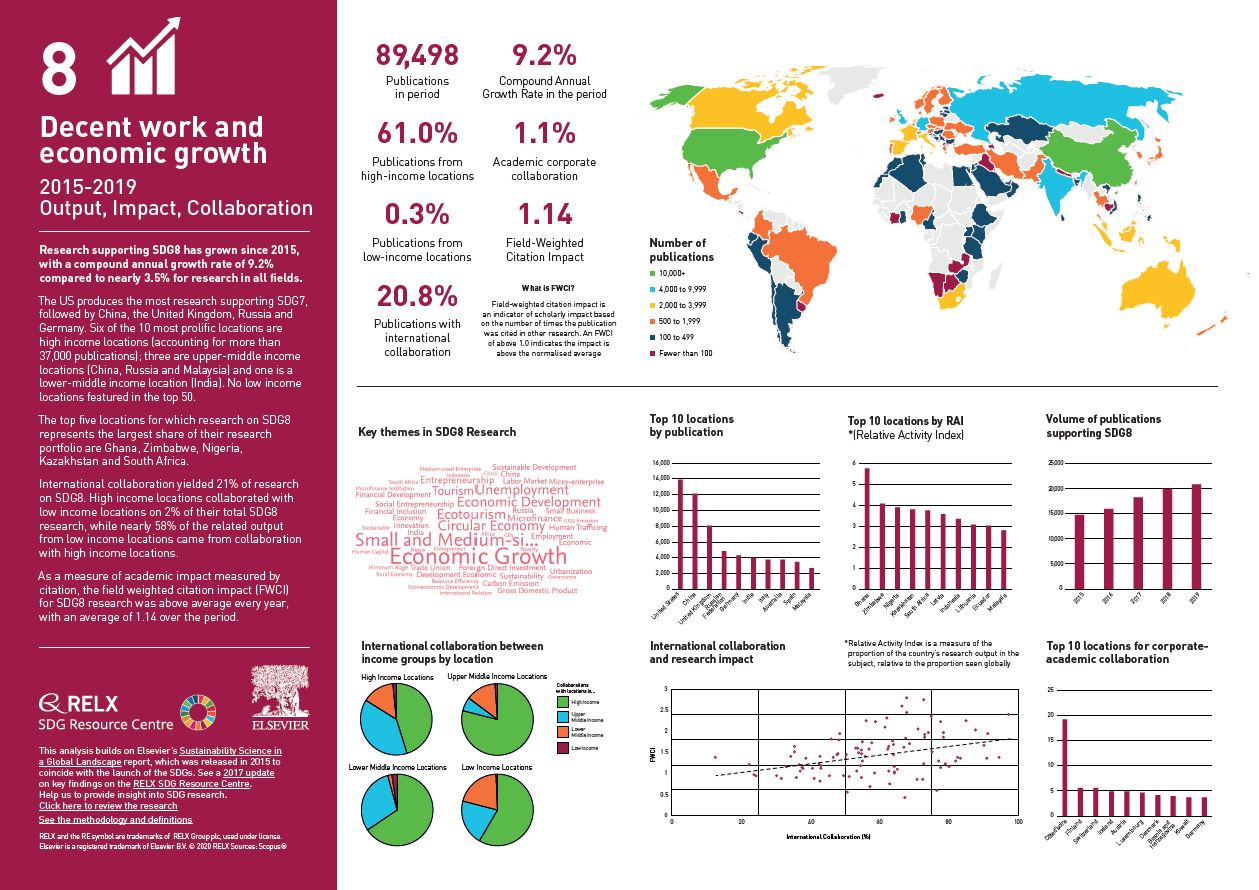
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 8.
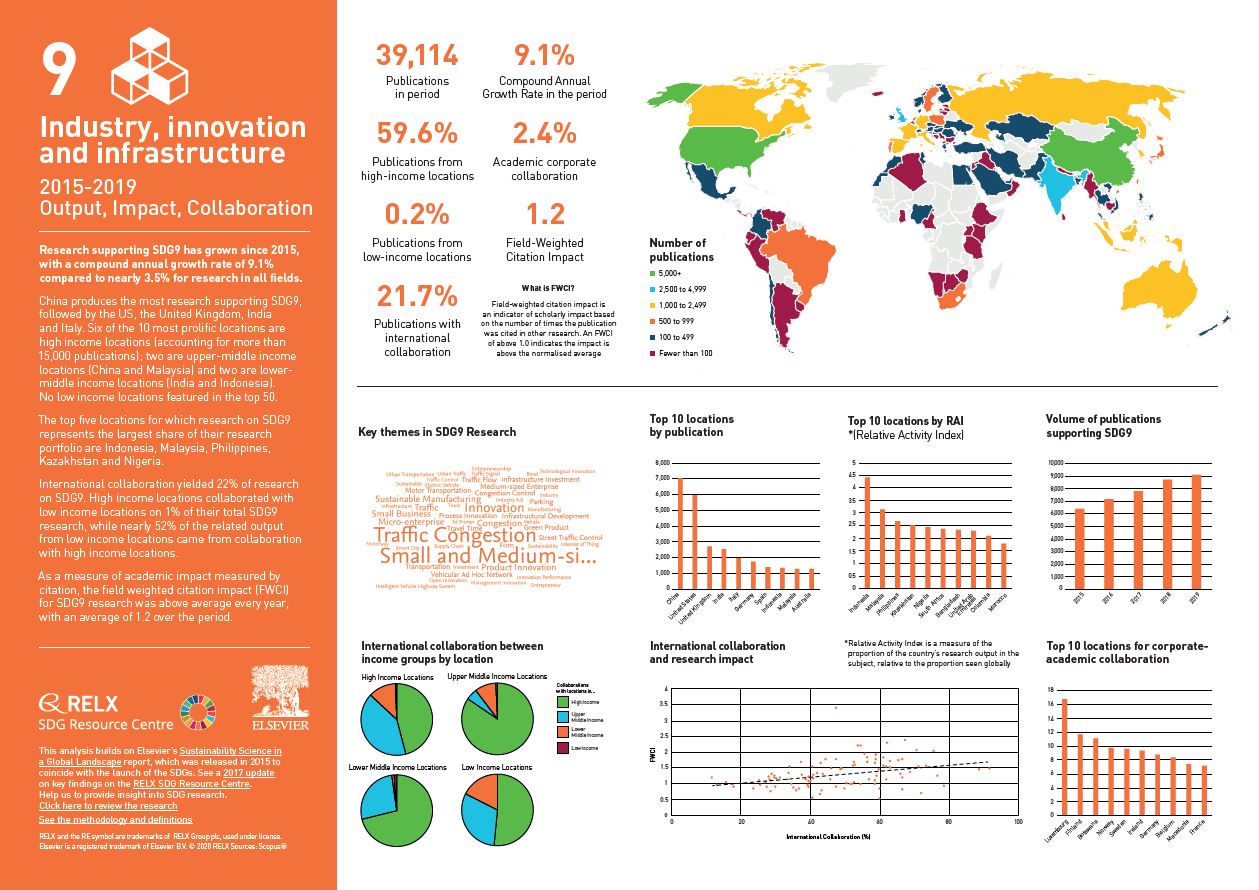
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 9.
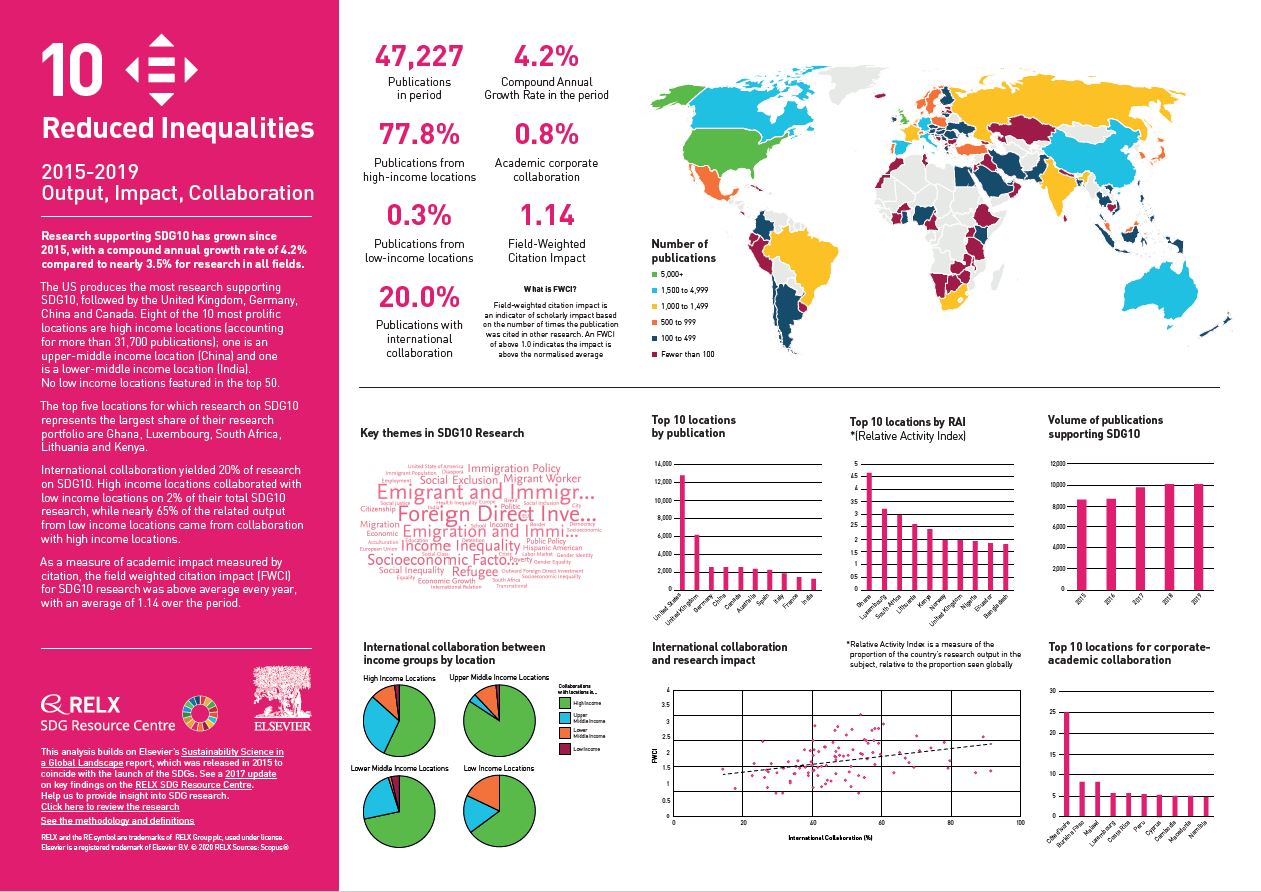
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 10.
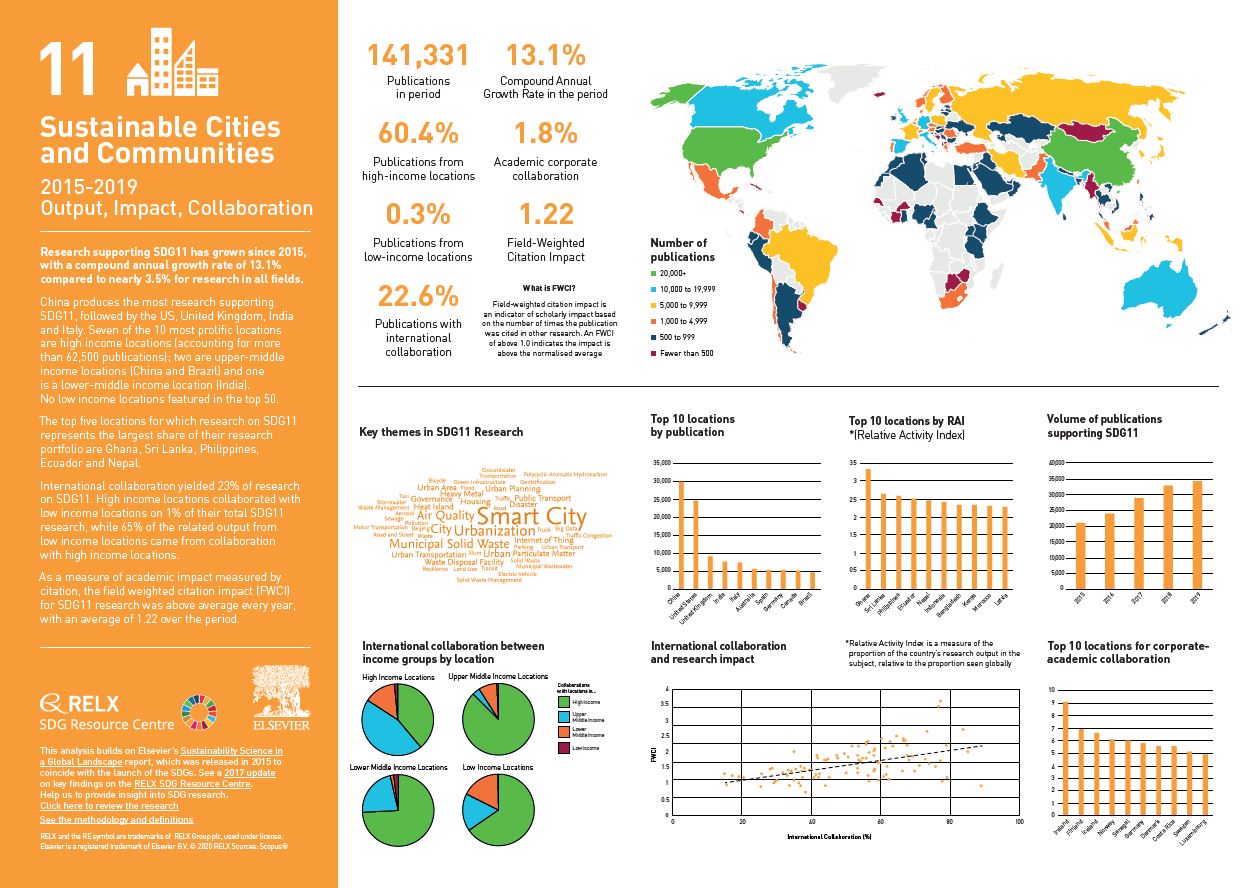
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 11.
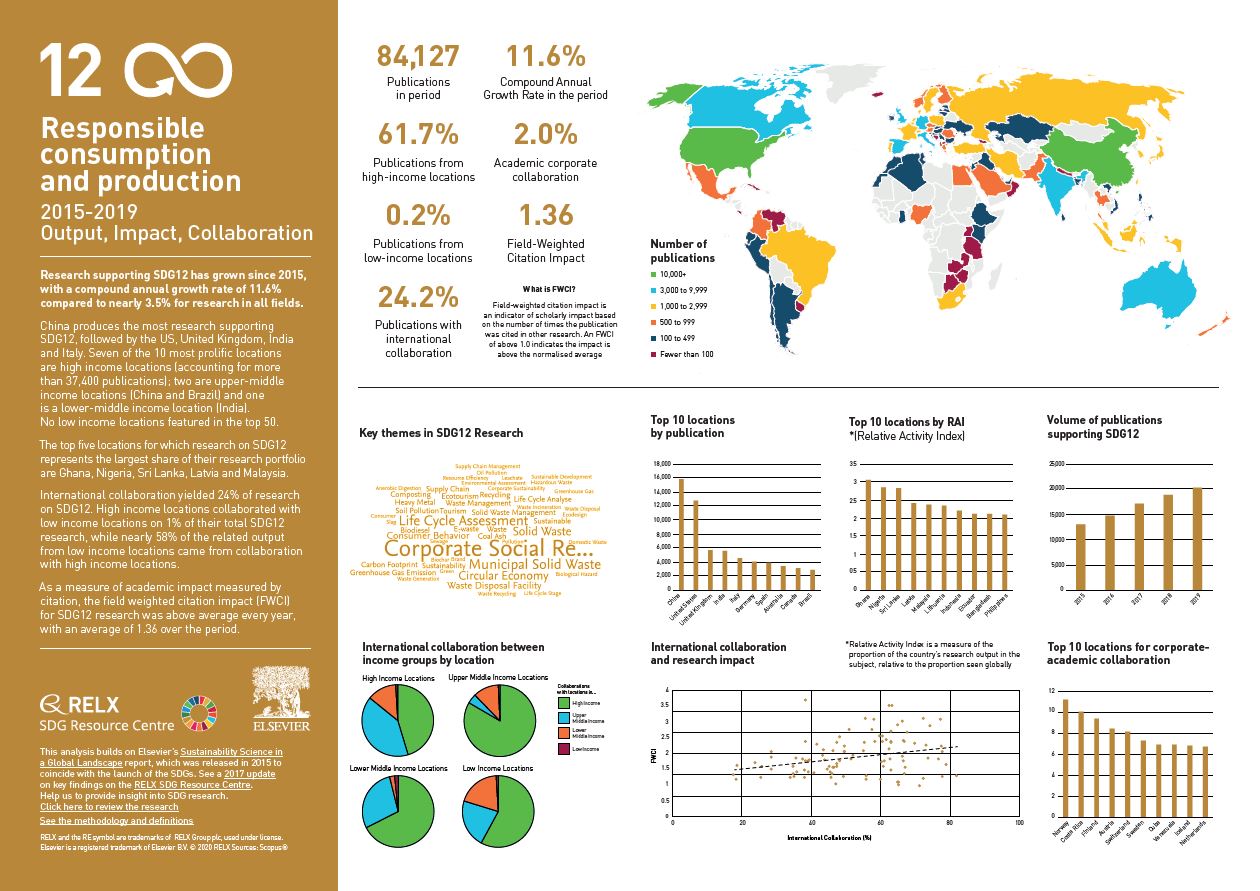
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 12.
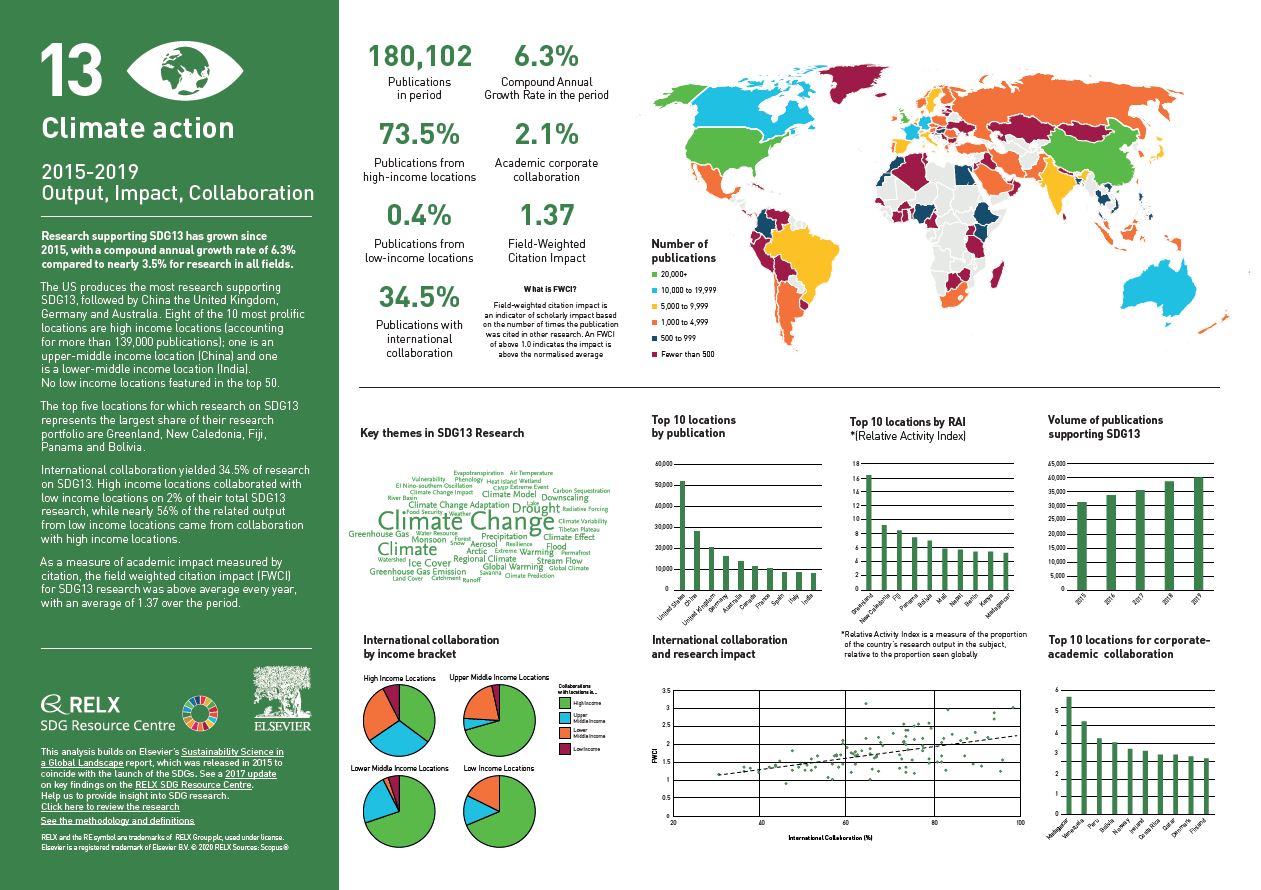
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 13.
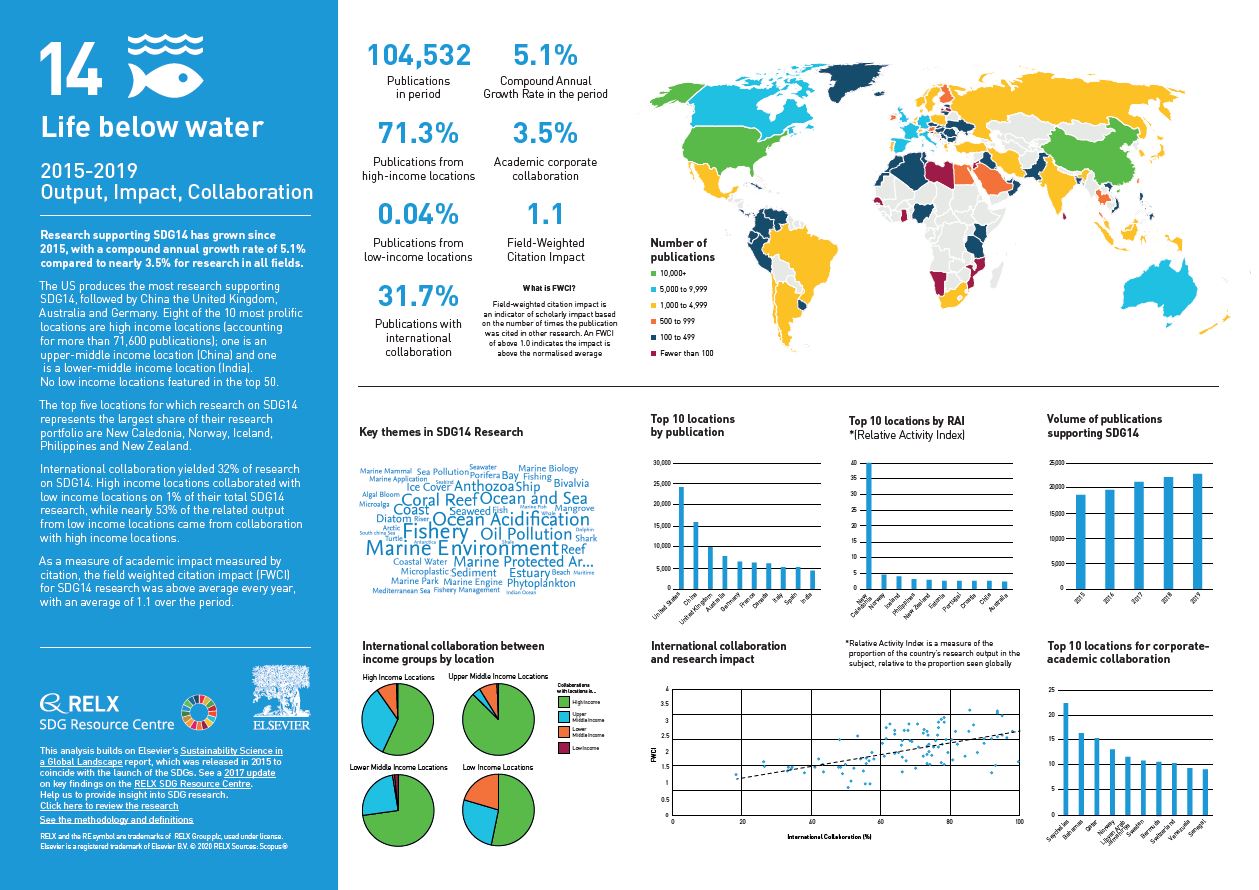
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 14.
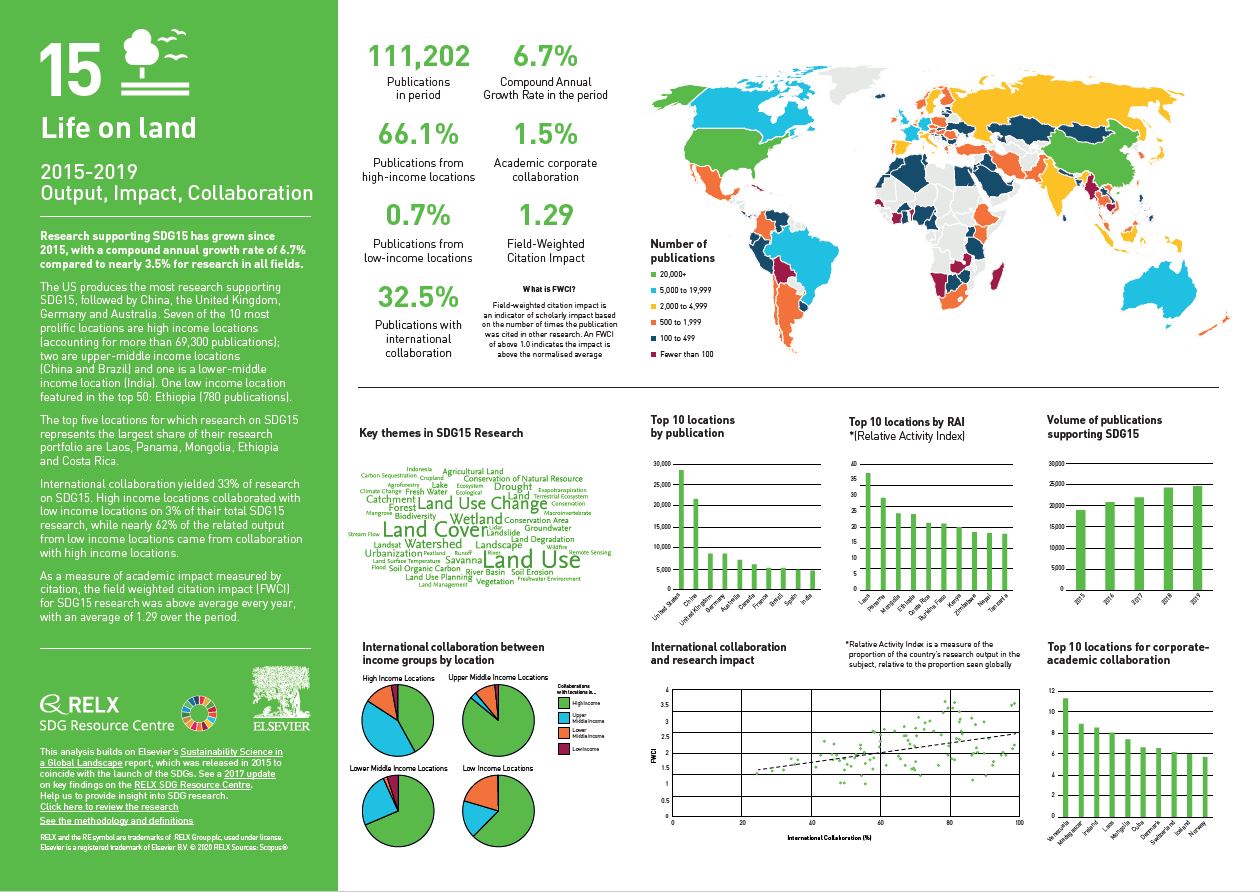
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 15.
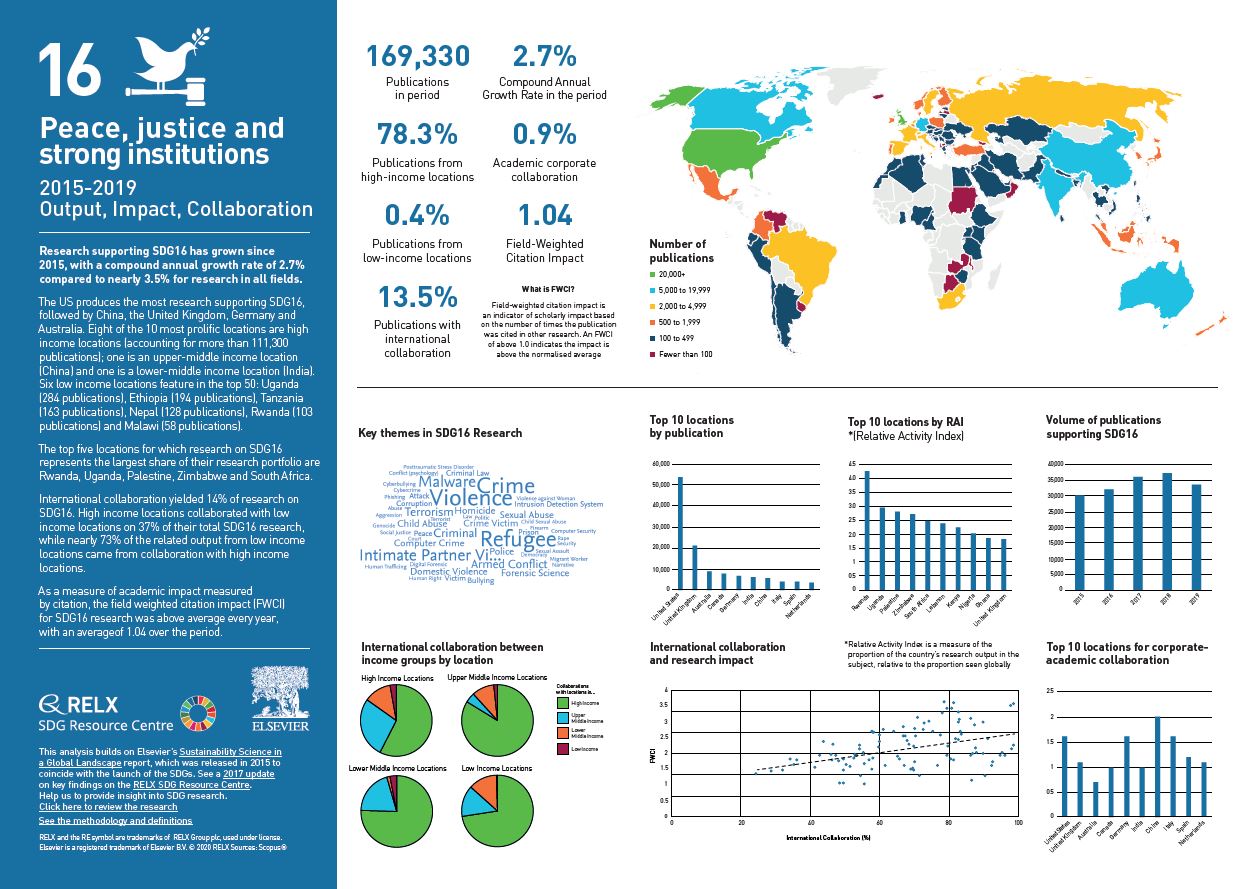
Over the past five years, we have used data and analytics to help the research and healthcare communities navigate the sea of research and to put collaboration, both interdisciplinary and international, at the heart of scientific progress on the SDGs. View findings for SDG 16.