Elsevier, Free Radical Biology and Medicine, Volume 151, 1 May 2020
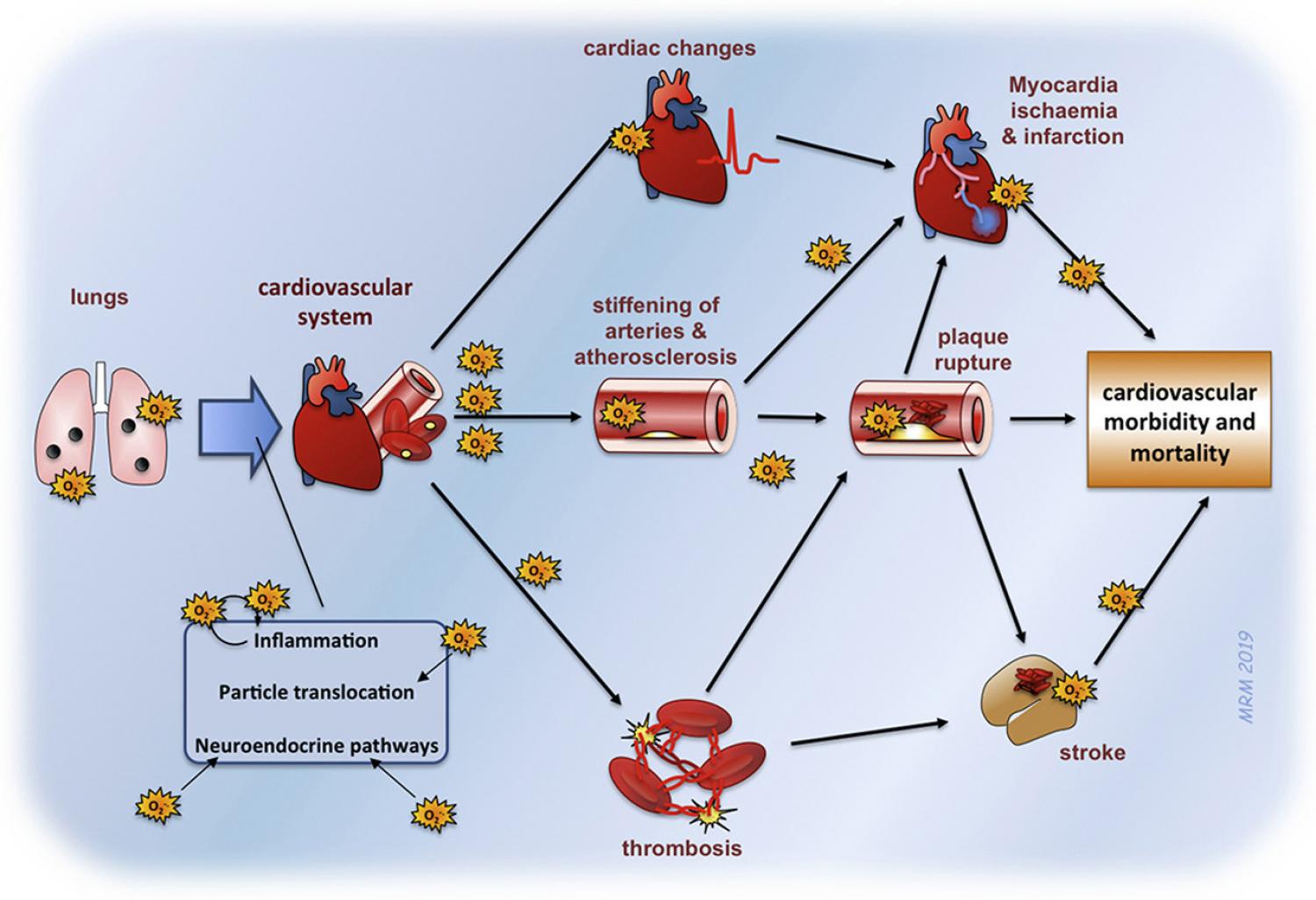
Cardiovascular causes have been estimated to be responsible for more than two thirds of the considerable mortality attributed to air pollution. There is now a substantial body of research demonstrating that exposure to air pollution has many detrimental effects throughout the cardiovascular system. Multiple biological mechanisms are responsible, however, oxidative stress is a prominent observation at many levels of the cardiovascular impairment induced by pollutant exposure. This review provides an overview of the evidence that oxidative stress is a key pathway for the different cardiovascular actions of air pollution.
