Elsevier, Future Foods, Volume 5, June 2022
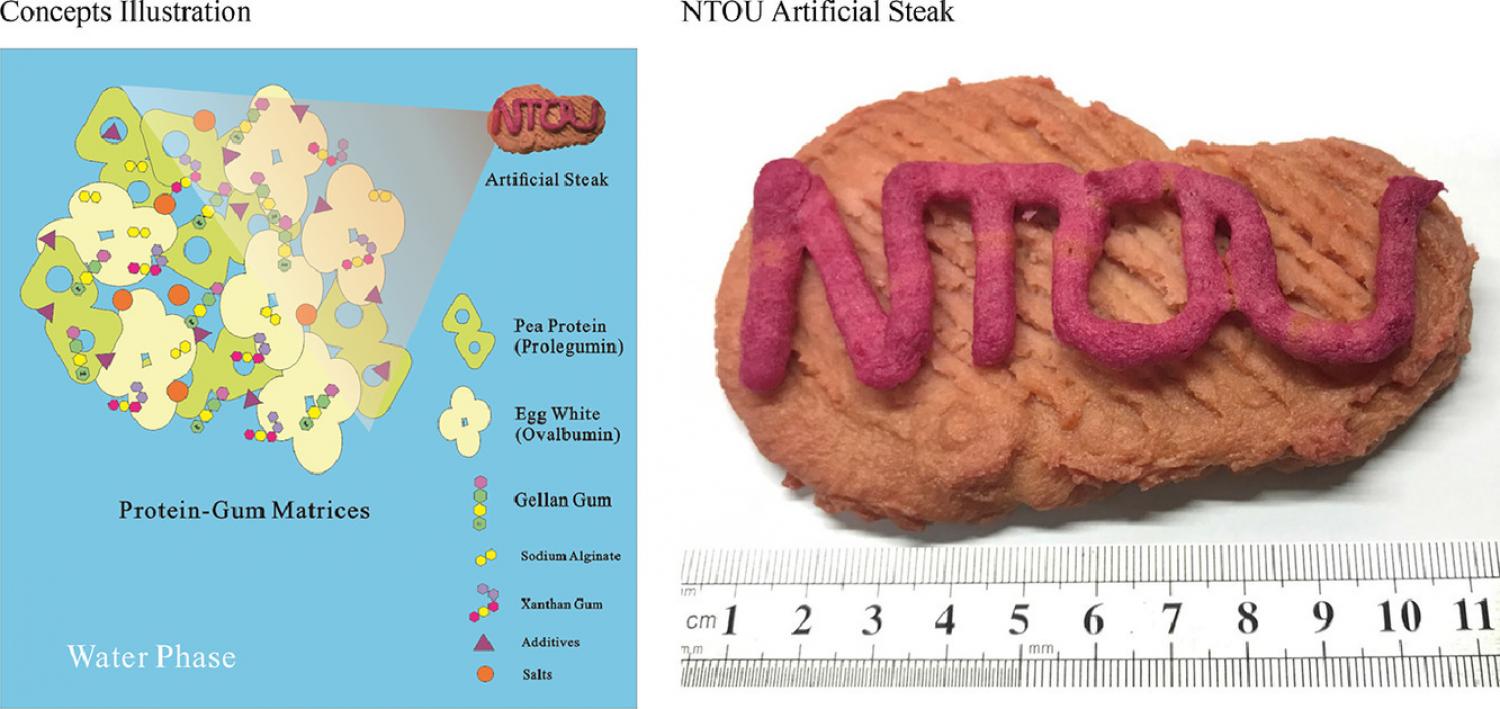
Food security and sustainability are the most urgent problems in worldwide. In the present study, the combinations of egg albumen, pea protein, and gellan gum were optimized to fabricate an artificial steak for specific populations. The relationships among the different components on the texture profile analysis, sensory evaluation, viscoelastic properties, and thermal behavior were conducted. 3D printing food was an emerging issue, this study also investigated how to fabricated an artificial steak and mitigate the impacts of meat production. Gellan gum was found to compensate for the proportion of proteins and regulate the instrumental hardness ranged from 453.82 ± 39.75 g to 2515.62 ± 144.55 g, the instrumental chewiness ranged from 156.29 ± 22.77 to 1054.66 ± 85.70 being feasible to regulated by different formulations, and extend to the customized platform and the applications of elderly’ foods. In sustainability orientation, 8.0% egg albumen /9.5% pea protein /0.7% gellan gel was computed as the optimal formulation, and 9.5% egg albumen /5.5% pea protein /0.7% gellan gel was conducted as the optimal solution in marketing orientation. The “Artificial steak” has the potential to improve food security and human well-being, reduce animal suffering, and mitigate most of the environmental impacts associated with meat production.
