Elsevier, Sustainable Materials and Technologies, Volume 21, September 2019
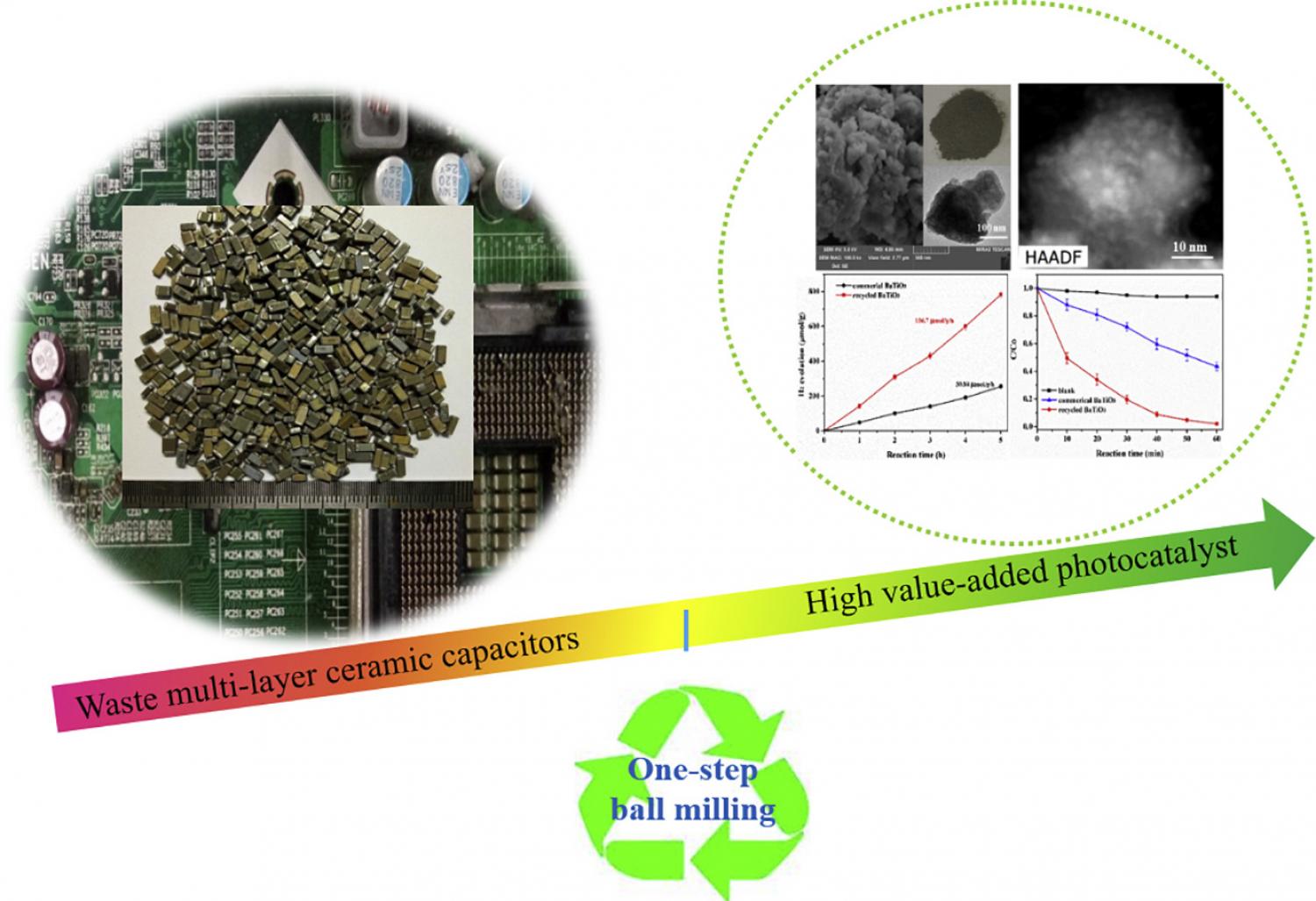
Waste multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), containing BaTiO 3 , Ag, Pd, Ni and Sn etc., are valuable secondary resource. The existing recycling process has great challenges when considering environmentally friendly and efficient separation and recovery of resources. From a new perspective of resource recycling, we directly utilized the complex components of waste MLCCs as a Nb–Pb codoped and Ag-Pd-Sn-Ni loaded BaTiO 3 nano-photocatalyst through one-step ball milling process. The as-prepared photocatalyst exhibited superior photocatalytic performance. The simulated sunlight H 2 evolution rate and RhB degradation rate of the recycled sample could reach 156.7 μmolg −1 h −1 and 0.06207 min −1 , which were 3.08 and 4.5 times higher than those of commercial BaTiO 3 . The recycled sample exhibited excellent photostability and reusability. The superior photocatalytic performance was attributed to the Nb–Pb codoping and Ag-Pd-Sn-Ni loading, which enhanced the visible light absorption and efficient charge separation. Moreover, DFT calculations were applied to explore the enhanced mechanism. Compared with the previous studies only focused on the resource recovery, our study demonstrates a simple and sustainable process to convert e-waste into high value-added and high-efficient photocatalyst, which is more significant for waste utilization and environmental protection.
