This Article supports SDG 3 by examining the potential impact of WHO's triple-intervention elimination strategy on cervical cancer incidence among women with HIV in South Africa. The authors note that cervical cancer elimination among women with HIV would necessitate more frequent screening (every 3 years).
This Article supports SDG 3 by examining the potential impact of WHO's triple-intervention elimination strategy on cervical cancer incidence among women with HIV in South Africa. The authors note that cervical cancer elimination among women with HIV would necessitate more frequent screening (every 3 years).
This Article supports SDG 3 by highlighting findings from a population-level study of STI burden in Uganda, showing the need for global investment in innovative approaches that simultaneously test and treat HIV and STIs within existing health infrastructure, such as integrated HIV and STI service programmes within the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief programme.
This chapter advances Goals 3 and 13 by explaining why CE philosophy should be considered in national policies to guide waste and environmental management efforts.
Experts in the field, along with patient representatives from the Sarcoma Patient Advocacy Global Network (SPAGN), met at an international consensus meeting in 2022 to define best clinical practice of tenosynovial giant cell tumour (TGCT). Although usually not life-threatening, TGCT may cause chronic pain and adversely impact function and quality of life. A global effort is needed to make active systemic treatments available to TGCT patients worldwide and avoid discrimination.
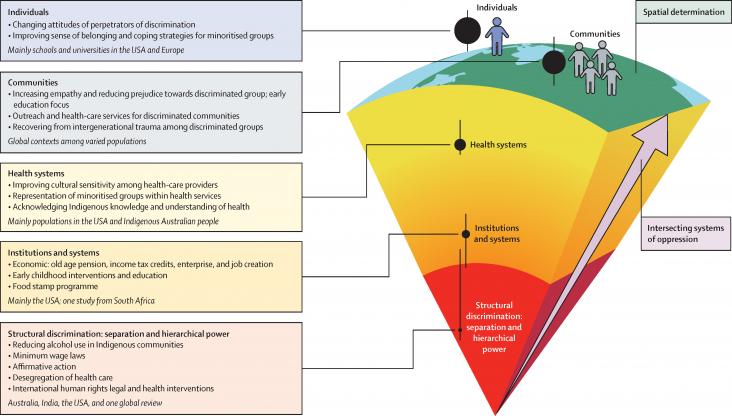
This Series paper supports SDGs 3 and 10 by focusing on wider societal action to confront the health effects of racism, highlighting that broader, deeper, transformative action is needed compared with current measures to tackle the adverse effects of racism on health.
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 10 by showing that, globally, Black women are at higher risk of adverse perinatal outcomes of neonatal death, stillbirth, preterm birth, and small-for-gestational-age babies than White women, even after adjusting for maternal characteristics. Moreover, these racial disparities in perinatal outcomes were consistently observed across all geographical regions.
An ongoing challenge in HIV-1 vaccine research is finding a novel HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env)-based immunogen that elicits broadly cross-neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) without requiring complex sequential immunization regimens to drive the required antibody affinity maturation.
Cabotegravir (CAB) is an integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) formulated as a long-acting injectable drug approved for pre-exposure prophylaxis and use with a long acting rilpivirine formulation for therapy in patients with virological suppression. However, there has been no comprehensive review of the genetic mechanisms of CAB resistance. Studies reporting the selection of drug resistance mutations (DRMs) by CAB and the results of in vitro CAB susceptibility testing were reviewed.
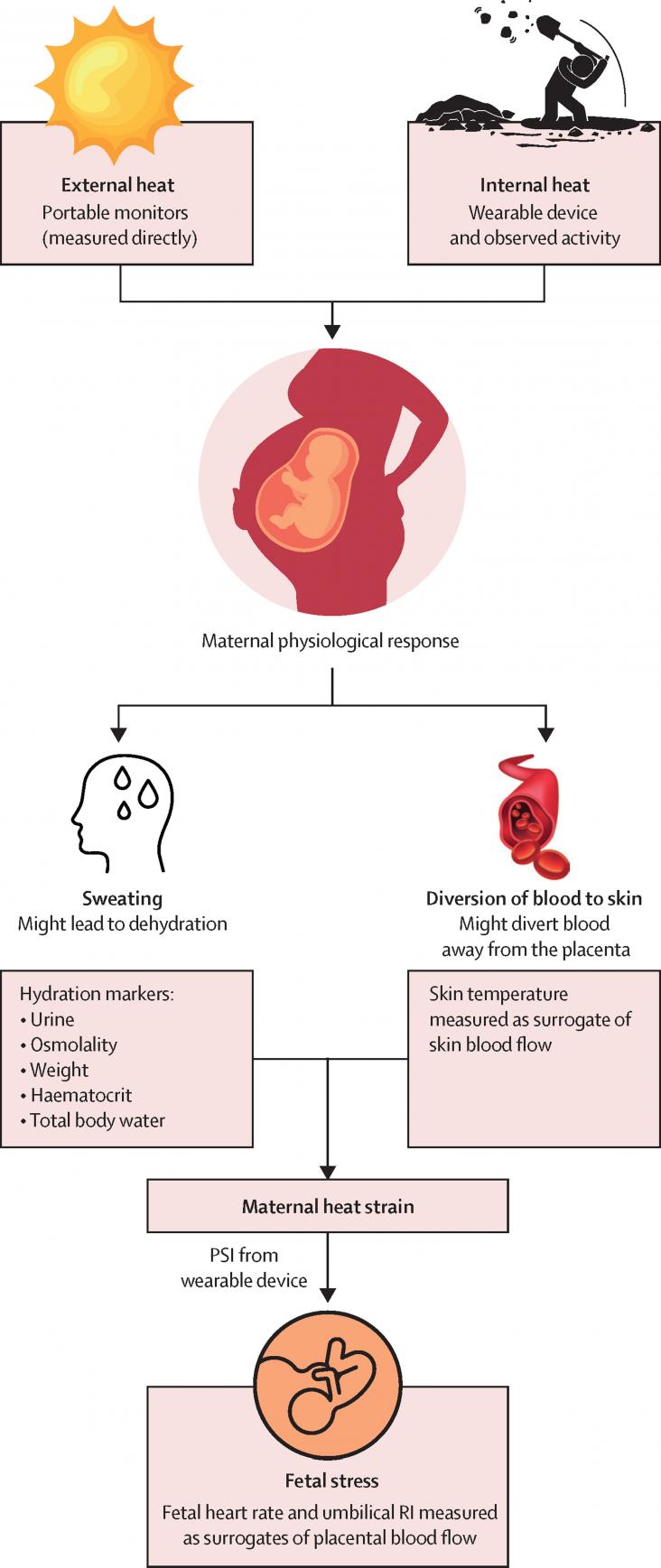
This Article supports SDGs 3, 5, and 13, focusing on the mechanisms for adverse outcomes caused by environmental heat stress in pregnant subsistence farmers.
