
Remington and Klein's Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant (Ninth Edition), 2025, Pages 728-744.e4
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health. Public health programs at the governmental level are in need for prevention of the maternal-fetal transmission of these viruses and access to available antiviral therapies.
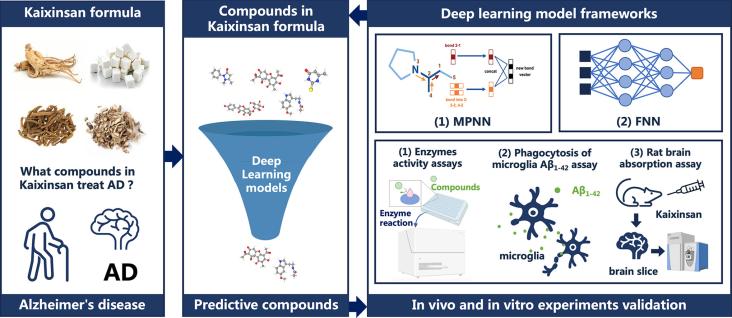
This study developed four deep learning models to identify potential Alzheimer's disease treatments from traditional Chinese medicine, specifically the Kaixinsan formula. The models successfully predicted compounds that showed significant anti-Alzheimer's activities in various experimental validations.
