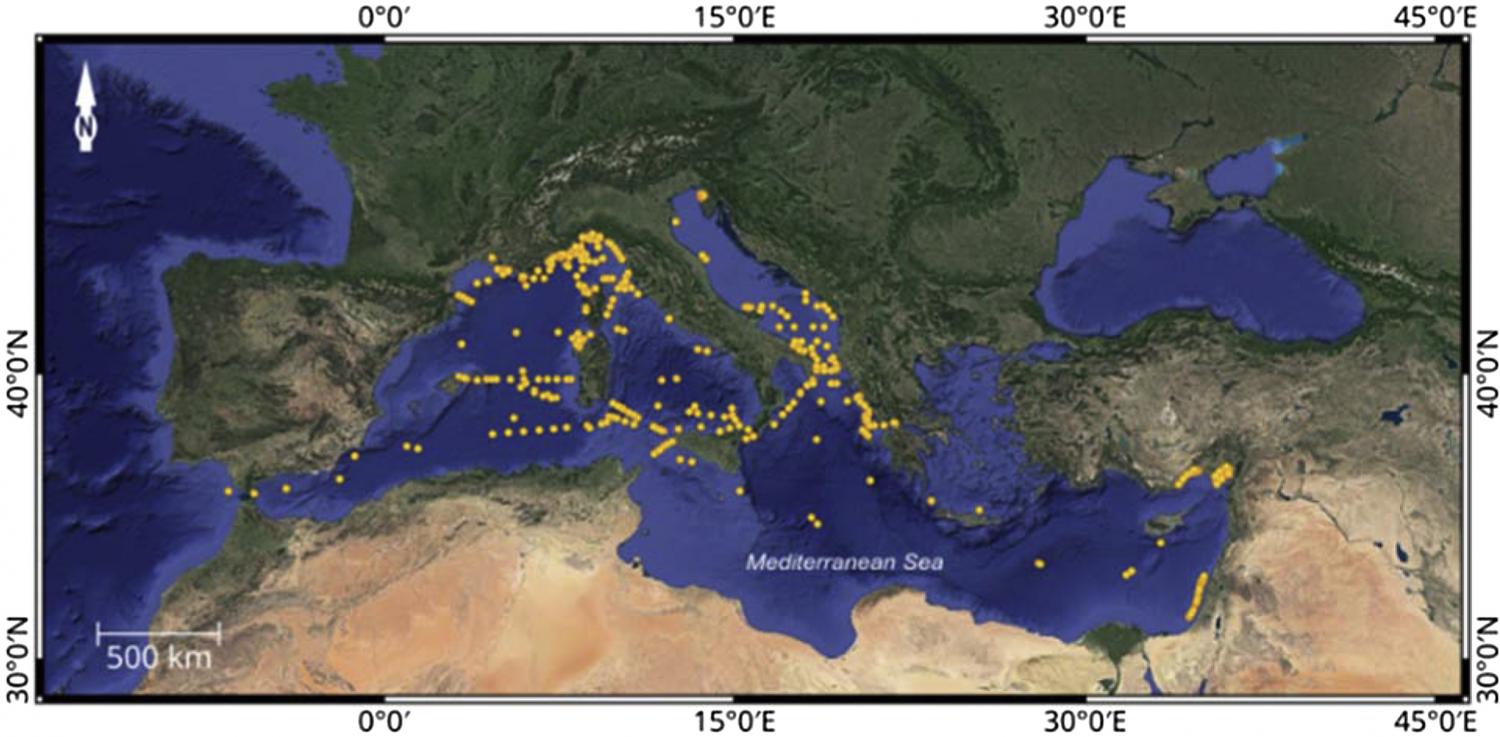
This review provides insight into the abundance, origin, distribution and composition of MPs in the sea surface and water column of the Mediterranean Sea. Literature data on MP particles on the sea surface showed an evident heterogeneous distribution and composition, with marked geographical differences between Mediterranean sub-basins. A standardized protocol for water sampling, extraction and detection of plastic debris is strongly recommended. The heterogenicity of MPs distribution and its concentration levels could be related to several factors, such as the different methodological approaches. In addition, the influence of hydrodynamic features such as currents, up and down-welling, gyres and fronts could also be responsible for this heterogeneity in concentrations. Marine litter modelling studies have been applied to understand litter sources, fate, transport and accumulation in oceans. Recent studies focused on the “plastisphere” in order to better understand the potential risk of pathogen dispersion with plastic transport in the Mediterranean Sea.
