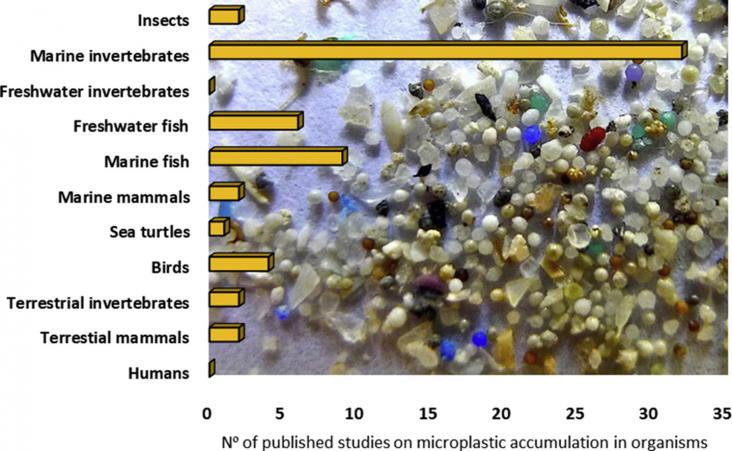
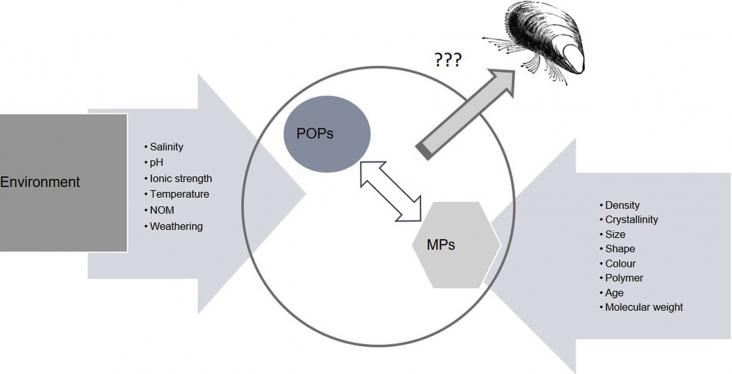
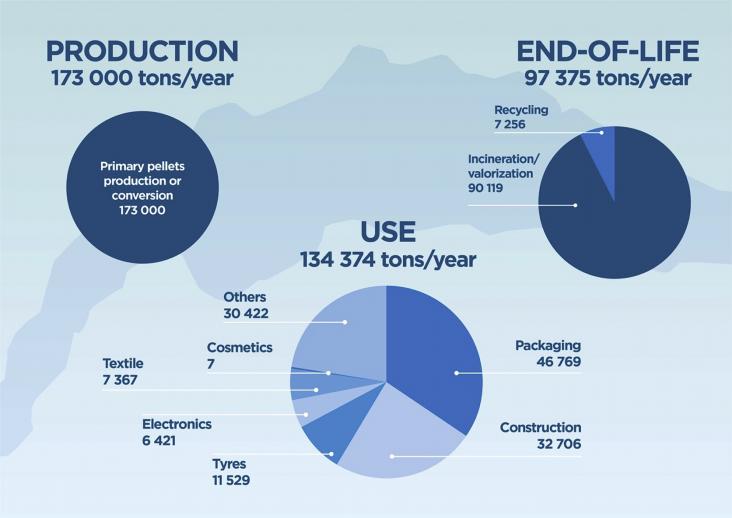
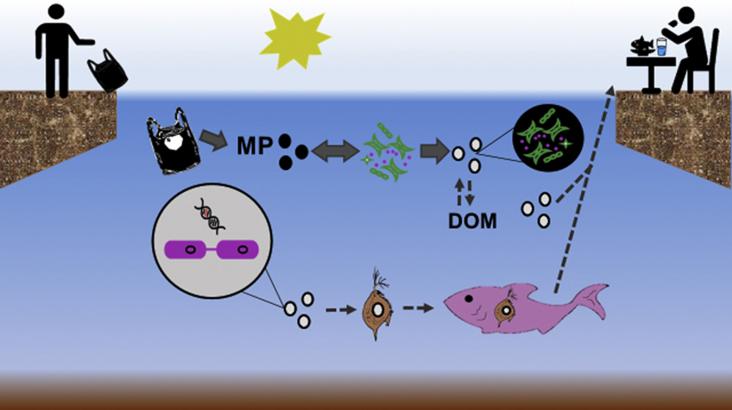
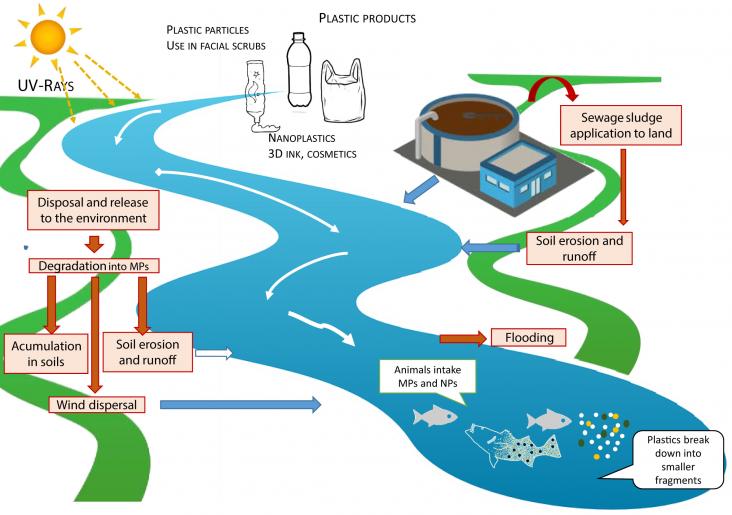
This special issue’s focus on micro-plastics in the environment supports multiple SDGs. As a result of global plastic production and consumption practices, micro- and nanoplastics are emerging pollutants in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. Research continues to identify microplastic’s detrimental impacts on biota, ecosystem services and human health.
SDG 9, target 5 encourages enhanced scientific research and technological capabilities across all countries. This special issue seeks to explore current microplastic research and enhance scientific methodologies and analytical techniques surrounding micro- and nanoplastic in the environment. Strengthening of microplastic research will significantly support many of the SDGs, including SDGs 3 (good health and well-being), 12 (responsible consumption and production), 14 (life below water) and 15 (life on land).
TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, Volume 112, March 2019
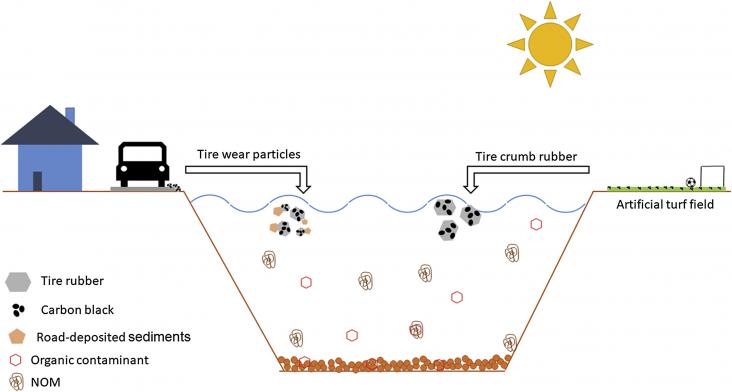
Plastics are a frequently observed component of marine debris and there is growing concern about microplastic (MP) ecotoxicity, and the impacts of additives, sorbed hazardous organic contaminants, heavy metals, and biofilm on MP surfaces. The relative importance of MP from different terrestrial and freshwater sources is poorly understood and limits our ability to develop best management practices.
TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, Volume 110, January 2019
This review provides insight into the abundance, origin, distribution and composition of MPs in the sea surface and water column of the Mediterranean Sea. Literature data on MP particles on the sea surface showed an evident heterogeneous distribution and composition, with marked geographical differences between Mediterranean sub-basins. A standardized protocol for water sampling, extraction and detection of plastic debris is strongly recommended.