
As the world scrambles to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, hydrogen has emerged as a potential silver bullet to help mitigate climate change. Hydrogen has been in consideration as a potential aid to decarbonization for over 50 years. However, it is only now that it has gained traction in government strategies, business plans, and the media. But what makes the attention given to hydrogen in the 2020s different from the 1970s? This article relates to SDGs 7 and 13.

RX, a RELX business, has published the RX Sustainability Playbook to support event and operations teams in making more sustainable choices when planning conferences and events. This resource is useful for anyone looking reduce the carbon footprint and waste in their events and is related to SDGs 12 and 13.
This study systematically evaluates the successful human stewardship in managing marine protected areas to provide useful lessons for future marine conservation actions.
This opinion highlights how tapping into natural biodiversity, while incorporating information about local environmental and climatic conditions, enables crop production in marginal soils.
The living infinite: Envisioning futures for transformed human-nature relationships on the high seas
Marine Policy, Volume 153, 2023, 105644, ISSN 0308-597X
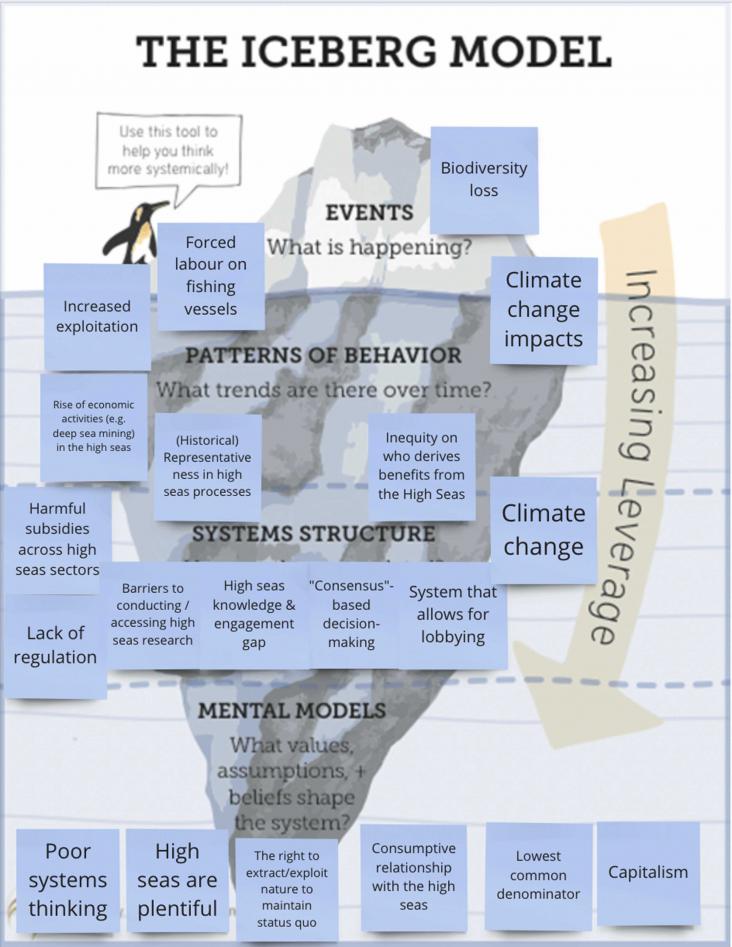
We are at a critical crossroads for the future governance of the high seas. We used the Nature Futures Framework to explore desirable futures for the high seas. Creative endeavours of co-production encourage imagination to address challenges. Participatory processes are important tools in the science-policy interface. Stories and art can be powerful ways to overcome barriers.
The main idea of this work is: To provide a brief review of India's capability for the deployment of carbon capture, utilization, and storage technology on a large scale.
Increasing plant productivity resilience to drought plays an important role in ecosystem services, and while soil organic matter (SOM) promotes plant growth, its role in mitigating aboveground biomass (AGB) loss as a result of drought in alpine grasslands is unclear. This study by Zhao et al., 2023 examined 209 alpine grassland sites on the Tibetan Plateau and revealed that AGB decreases with increasing aridity (above 0.37), and a stronger positive relationship between AGB and SOM is observed in more arid conditions, suggesting the significance of soil carbon sequestration strategies for biomass production and climate change mitigation in arid areas.
This article supports SDG # 13 by calculating the share of climate damages that fossil fuel companies owe the world.
This article advances SDG # 13 by quantifying the extent - and rigor - of existing regulation and makes recommendations for future policies for addressing the issue of Methane emissions.
Selective copepod grazing and water mass origin impacted spring bloom composition. Diatom bloom enhanced zooplankton recruitment and deep carbon export. Spring bloom composition impacted summer plankton community. Mixo- and heterotrophic protists dominated the nutrient-poor summer months. Copepod grazers controlled the summer protist community.
