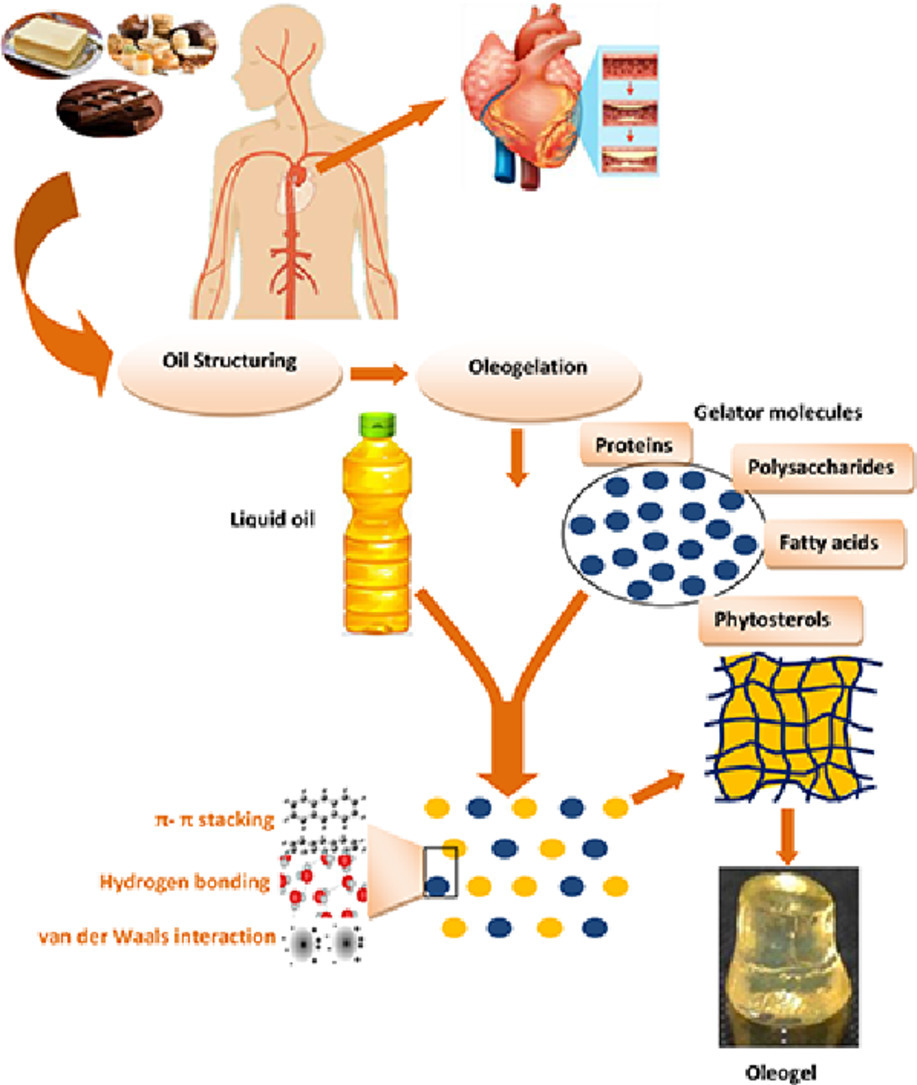
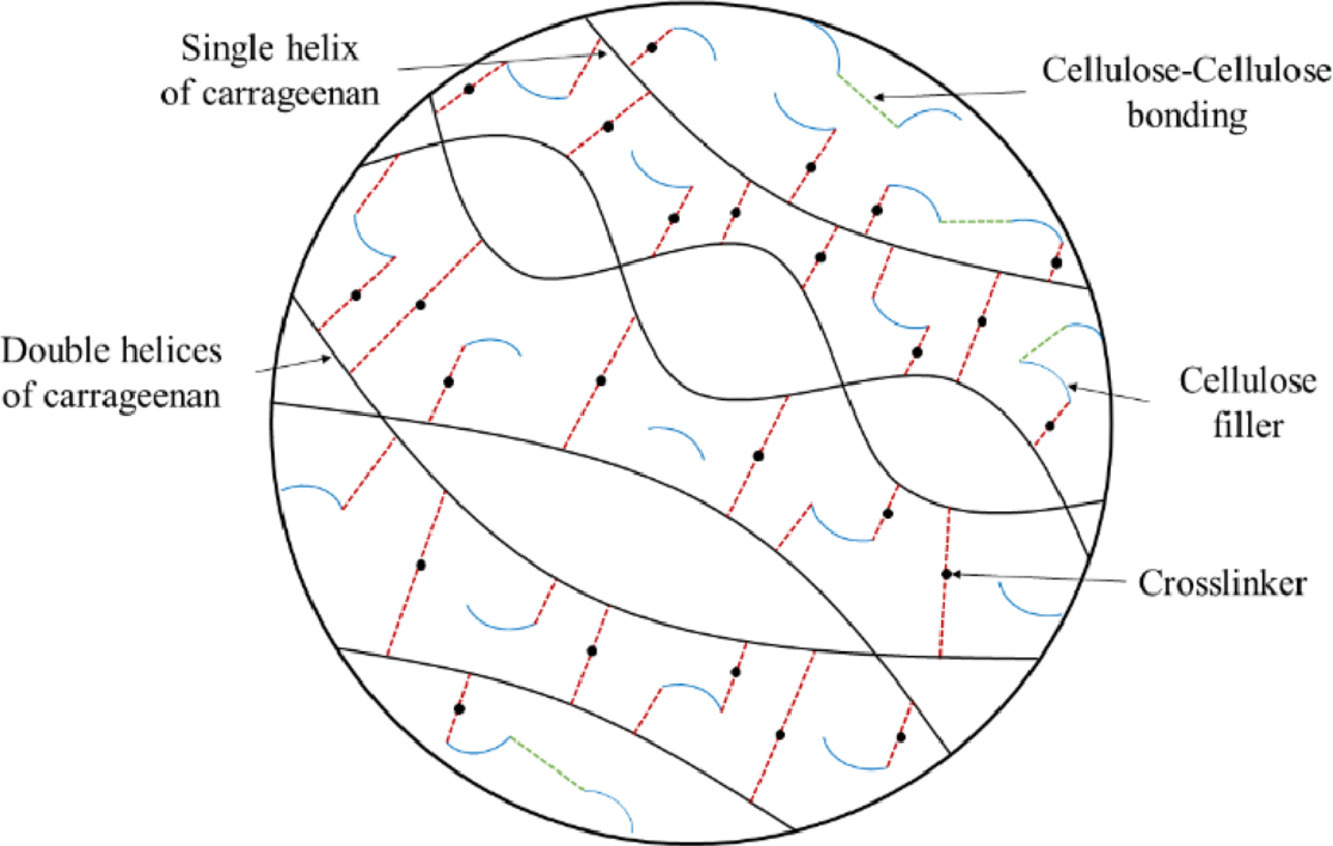
Health and well-being have a central role in the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) endorsed by the United Nations, emphasizing the integral part they play in building a sustainable future. The third SDG explicitly calls for ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages. This goal encompasses a wide range of health objectives, from reducing maternal and child mortality rates, combatting disease epidemics, to improving mental health and well-being. But beyond SDG 3, health is intrinsically linked with almost all the other goals.
When addressing SDG 1, which aims to end poverty, one cannot neglect the social determinants of health. Economic hardship often translates into poor nutrition, inadequate housing, and limited access to health care, leading to a vicious cycle of poverty and poor health. Similarly, achieving SDG 2, ending hunger, also contributes to better health through adequate nutrition, essential for physical and mental development and the prevention of various diseases.
Conversely, the repercussions of climate change, encapsulated in SDG 13, profoundly impact health. Rising global temperatures can lead to increased spread of infectious diseases, compromised food and water supplies, and increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, all posing severe health risks. Conversely, the promotion of good health can also mitigate climate change through the reduction of carbon-intensive lifestyles and adoption of healthier, more sustainable behaviors.
SDG 5, advocating for gender equality, also has substantial health implications. Ensuring women's access to sexual and reproductive health services not only improves their health outcomes, but also contributes to societal and economic development. Furthermore, achieving SDG 4, quality education, is also critical for health promotion. Education fosters health literacy, empowering individuals to make informed health decisions, hence improving overall community health.
Lastly, SDG 17 underlines the importance of partnerships for achieving these goals. Multi-sector collaboration is vital to integrate health considerations into all policies and practices. Stakeholders from various sectors, including health, education, agriculture, finance, and urban planning, need to align their efforts in creating sustainable environments that foster health and well-being.
Hence, the relationship between health, well-being, and the SDGs is reciprocal. Improving health and well-being helps in achieving sustainable development, and vice versa. In this context, health and well-being are not just outcomes but are also powerful enablers of sustainable development. For the world to truly thrive, it must recognize and act upon these interconnections.
Background: Numerous studies have quantified the associations between ambient temperature and enteric infections, particularly all-cause enteric infections. However, the temperature sensitivity of enteric infections might be pathogen dependent. Here, we sought to identify pathogen-specific associations between ambient temperature and enteric infections.
Advances in Life Course Research, in press 2022, 100466