Facultative polyandry protects females from compromised male fertility caused by heatwave conditions
Animal Behaviour, Volume 178, August 2021
Why is polyandry such a common mating behaviour when it exposes females to a range of significant fitness costs?

Since the launch of the United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, the SDGs have been widely adopted by governments and corporations in an effort to improve their sustainabil
This study, which supports SDG's 13 and 15 looks at how important drivers like water level and bioturbation affect soil characteristics in the development of novel ecosystems aiming to improve the functioning of degraded landscapes.
This study supports SDGs 13,14 and 15 by unveiling the palaeoenvironment in response to global climate changes.
Global warming is adversely affecting the earth's climate system due to rapid emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs).
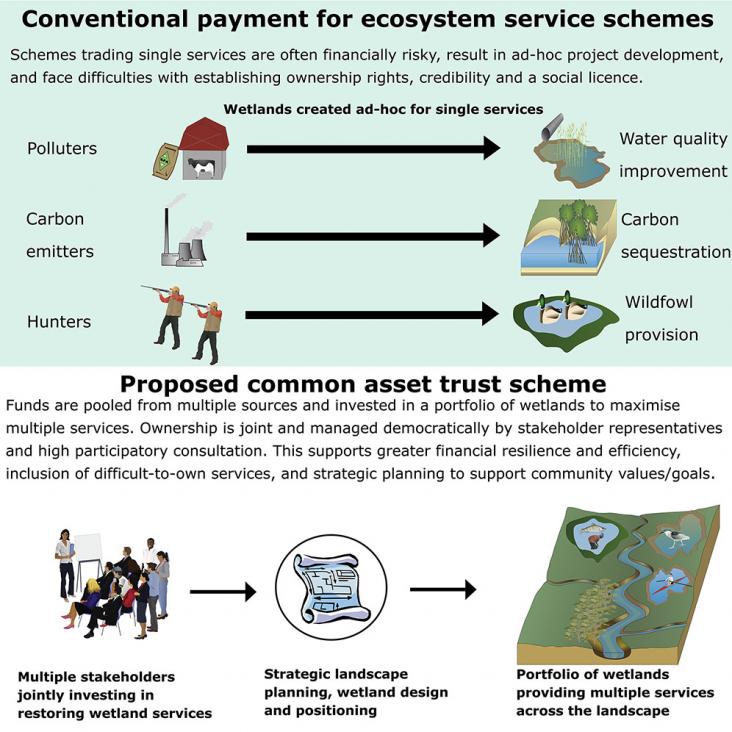
Wetlands provide ∼$47.4 trillion/year worth of ecosystem services globally and support immense biodiversity, yet face widespread drainage and pollution, and large-scale wetlands restoration is urgentl
Held in partnership with the University of Johannesburg, this Elsevier webinar discusses the SDGs and how researchers can incorporate them into their work.
Held in partnership with the University of São Paulo, this Elsevier webinar discusses the SDGs and how researchers can incorporate them into their work.
This book chapter advances SDGs 9, 13, and 15 by using several economic indicators of sustainable resource management to help answer questions such as what extent is it possible to know whether the available resources are being managed in a sustainable way? Could it be said that current generations are using the resources to meet their needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own?

This review is dedicated to ecocatalysis, a concept developed by the Grison group aiming at combining ecology and green chemistry, which could be the vector of sustainable development based on the pri
