Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders that are marked by high levels of blood sugar over a prolonged period. This chronic condition arises from issues related to the production or utilization of insulin, a hormone critical for regulating blood sugar levels. The global prevalence and impact of diabetes are significant, making it a crucial focus area within several of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
One of the primary SDGs affected by diabetes is SDG 3, which emphasizes "Good Health and Well-being." This goal underscores the importance of preventive measures, early diagnosis, effective treatment, and management of chronic conditions like diabetes mellitus. The goal aims to reduce the disease's mortality rate and improve the quality of life for those living with the condition. Implementing strategies for better healthcare access, raising awareness about the disease, and investing in research for advanced treatment options are critical steps in achieving this goal.
Diabetes also has a strong connection with SDG 2, "Zero Hunger," which aims for the end of all forms of hunger and malnutrition. This goal is closely linked to diabetes management and prevention, as a balanced diet and proper nutrition are key factors in controlling blood sugar levels. Promoting sustainable agriculture and ensuring access to healthy, nutritious food can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This goal also emphasizes the importance of education on healthy eating habits, which is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes.
The condition intersects with SDG 1, "No Poverty," and SDG 10, "Reduced Inequalities." Diabetes often disproportionately impacts socioeconomically disadvantaged groups. People living in poverty are more likely to develop diabetes due to factors such as limited access to healthy food, lack of healthcare, and poor living conditions. This disparity highlights the need for equitable healthcare access and support for vulnerable populations. Addressing these inequalities is essential for reducing the prevalence of diabetes and its complications among these groups.
Furthermore, diabetes is deeply connected with SDG 4, "Quality Education." Education plays a vital role in diabetes prevention and management. Educating the public about the risks associated with diabetes, the importance of regular health check-ups, lifestyle choices, and the management of the disease can significantly reduce its incidence. Schools, community centers, and healthcare facilities are key platforms for disseminating information about diabetes and promoting healthy lifestyles.
The relationship between diabetes and the SDGs is a clear example of how health is intertwined with various aspects of sustainable development. Addressing diabetes effectively requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses healthcare, nutrition, education, and social equality. Efforts to combat diabetes contribute to the broader agenda of sustainable development, demonstrating the interconnected nature of these global goals. By focusing on preventive measures, enhancing healthcare systems, promoting healthy lifestyles, and addressing social determinants of health, significant progress can be made towards the SDGs and in the fight against diabetes.
World Diabetes Day 2025: Empowering Global Health
Diabetes remains a pivotal global health challenge, but once a year, the world unites in a singular mission raising awareness and fostering change. This unity finds its voice in World Diabetes Day 2025.
Diabetes, a non communicable disease, affects millions across the globe. Yet, not all are aware of its repercussions or preventive measures. World Diabetes Day 2025 provides a platform for everyone from medical professionals to the general public to learn, share, and act.
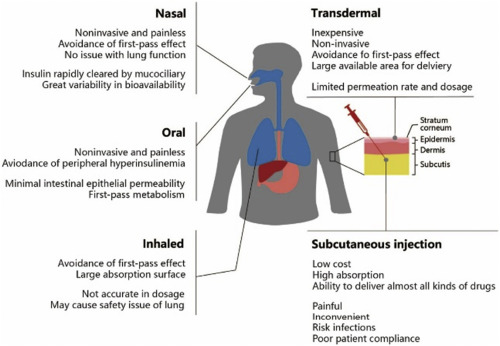
Diabetes Without Needles, Non-invasive Diagnostics and Health Management, 2022, Pages 27-92
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness in the working-age diabetic population in India and across the world. It may lead to permanent blindness if not detected in the early stages. The prevalence of DR among diabetics in India was 10% and 16.9% in 2014 and 2019, respectively. In 2019, the International Diabetes Federation estimated that Diabetic Mellitus will affect 101 million people in India in 2030; the largest number in any nation in the world.