This content aligns with Goal 14: Life under Water by emphasizing the significance of freshwater habitats as repositories of aquatic biodiversity.
Ocean Acidification and Marine Wildlife, 2021, pp 247-263
This chapter aligns with Goal 14: Life Below Water and Goal 13: Climate Action by discussing the impacts of ocean acidification on marine biological processes and highlighting future research directions to understand and preserve marine biodiversity.
Global warming is adversely affecting the earth's climate system due to rapid emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs).
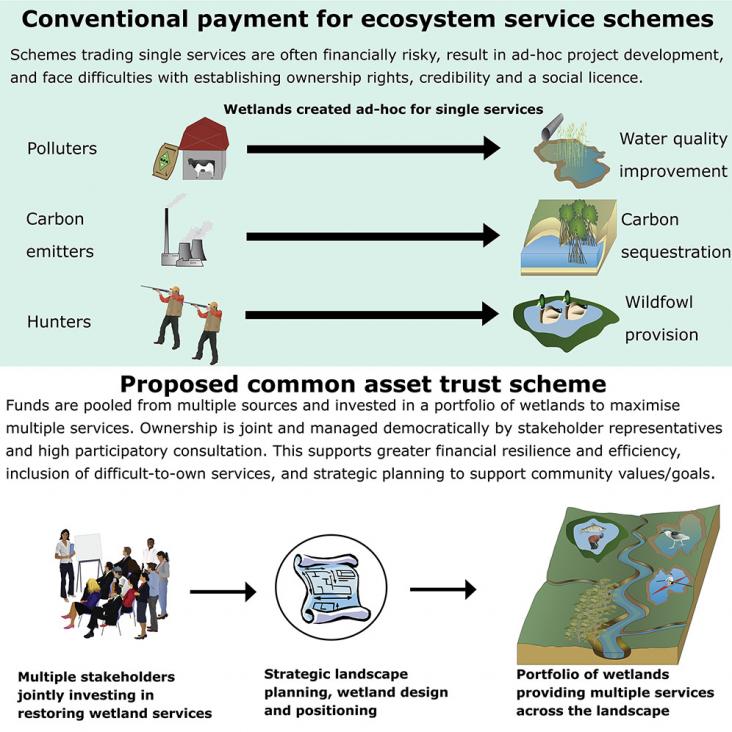
Wetlands provide ∼$47.4 trillion/year worth of ecosystem services globally and support immense biodiversity, yet face widespread drainage and pollution, and large-scale wetlands restoration is urgentl
Held in partnership with the University of Johannesburg, this Elsevier webinar discusses the SDGs and how researchers can incorporate them into their work.
Held in partnership with the University of São Paulo, this Elsevier webinar discusses the SDGs and how researchers can incorporate them into their work.
This chapter aligns with Goal 14: Life Below Water and Goal 13: Climate Action by highlighting how past marine ecosystem changes can improve our understanding of future climactic and chemical conditions of global oceans.
This book chapter advances SDG 14 by explaining how ocean currents further influence climate via freshwater transports that influence dense water formation at high latitudes. Under a warming climate and an intensifying hydrological cycle, ocean currents convey salinity anomalies that could destabilize the circulation.

This review is dedicated to ecocatalysis, a concept developed by the Grison group aiming at combining ecology and green chemistry, which could be the vector of sustainable development based on the pri
Quantification and extent mapping of seawater intrusive zones are extremely critical for coastal aquifers, especially for those impacted with anthropogenic stress.
