Shows how practical economic levers can make the shipping industry more environmentally sustainable.
This article advances SDG # 13, 14, and 15 by arguing that ecosystem integrity is neglected but important for climate adaptation goals, and shows how linking ecosystem integrity to climate, biodiversity and sustainable development goals is crucial for optimal outcomes.

Monitoring the ocean carbon cycle is key to improved understanding. Satellites play a major role in our global carbon monitoring system. To make full use of satellite observations for ocean carbon monitoring the remote-sensing community needs to work closely with in-situ data experts, physical and biogeochemical modellers, Earth system scientists, climate scientists and marine policy experts.
Increasing shipping traffic in the Arctic Ocean creates an emerging need to understand the consequences of maritime operations on the Arctic environment and coastal Indigenous and non-Indigenous commu
Fisheries Research, Volume 265, 2023, 106744
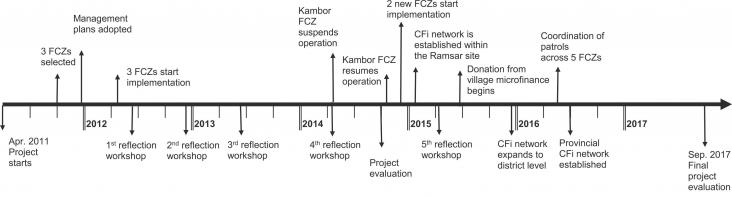
A critical reflection on fisheries conservation in the Mekong River is offered here. Adaptive co-management helped balance conservation and livelihood outcomes. No-take zones facilitated basic fish conservation measures led by local fishermen. Fishermen perceiving livelihood benefits of conservation supported no-take zones. Long-term mechanisms to support community-led conservation initiatives are needed.
This study systematically evaluates the successful human stewardship in managing marine protected areas to provide useful lessons for future marine conservation actions.
This study provides a better understanding of the burrowing behaviour of the sub-legal size clams discarded on the sediment after being disturbed and contributes important data to improve practices for minimizing mortality of dislodged clams that are discarded on the sediment surface.
The living infinite: Envisioning futures for transformed human-nature relationships on the high seas
Marine Policy, Volume 153, 2023, 105644, ISSN 0308-597X
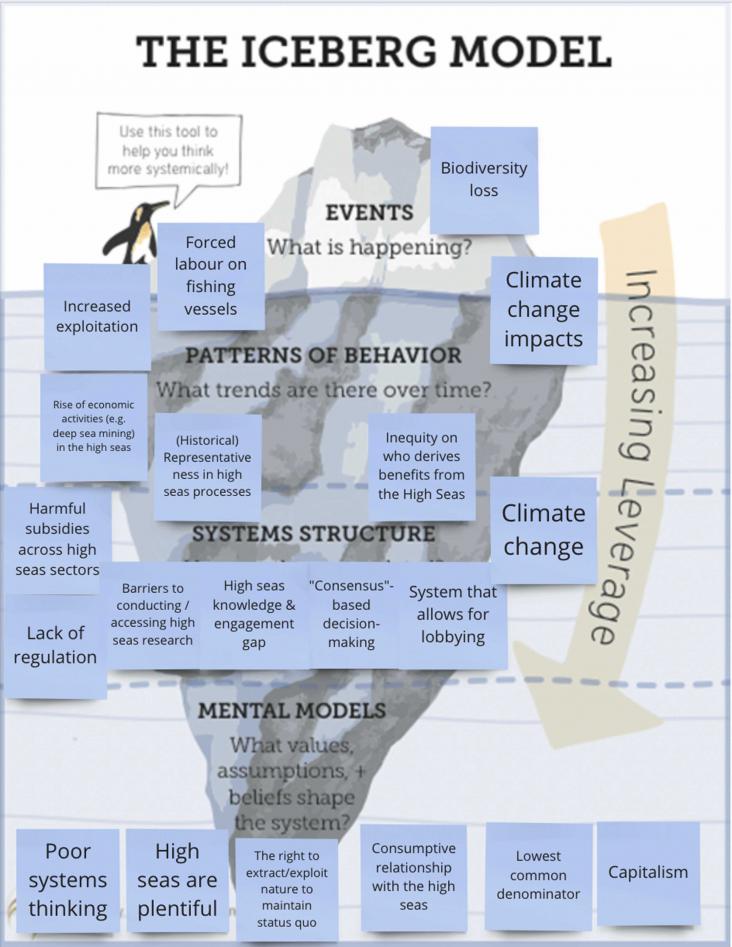
We are at a critical crossroads for the future governance of the high seas. We used the Nature Futures Framework to explore desirable futures for the high seas. Creative endeavours of co-production encourage imagination to address challenges. Participatory processes are important tools in the science-policy interface. Stories and art can be powerful ways to overcome barriers.
Selective copepod grazing and water mass origin impacted spring bloom composition. Diatom bloom enhanced zooplankton recruitment and deep carbon export. Spring bloom composition impacted summer plankton community. Mixo- and heterotrophic protists dominated the nutrient-poor summer months. Copepod grazers controlled the summer protist community.
This study proposes a deep learning model based on a convolutional neural network, which can effectively fuse atmospheric information (wind field) and station water level information and can effectively forecast the station water level and also have a good response to the anomalous water level increase brought by storm surge.
