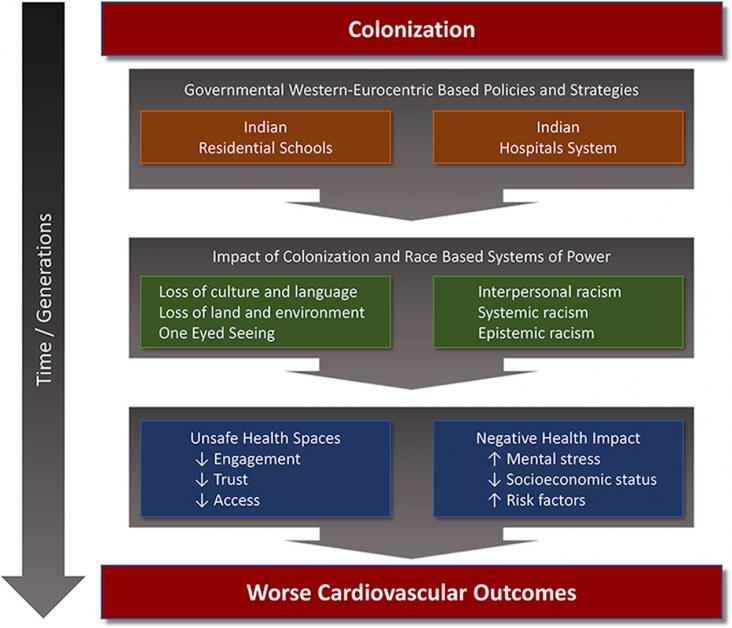
Colonization and enforced genocidal strategies have collectively fractured and changed Indigenous people by attempting to erase and dismiss their voices and knowledge.
This study investigates the capabilities, performance outcomes, and barriers of drones applied to humanitarian logistics (HL).

Roaa Al Feel, an early-career researcher, discusses her passion for using data science for social good.
A Health Policy paper on the threats posed by climate change to population health in China, in the context of SDGs 3, 9, and 13, focusing specifically on how the country can manage these risks to lead a green recovery.
This Comment article supports SDGs 3 and 10; Muneera Rasheed presents some guidelines for decolonisation in global health research, highlighting the need to challenge current systems to fight power asymmetries in the context of academic research partnerships between high-income and low-income countries and other behaviours that undermine equitable collaboration.
Ketogenic diets consist of low carbohydrate/high fat, shifting energy reliance from glucose to ketone bodies.
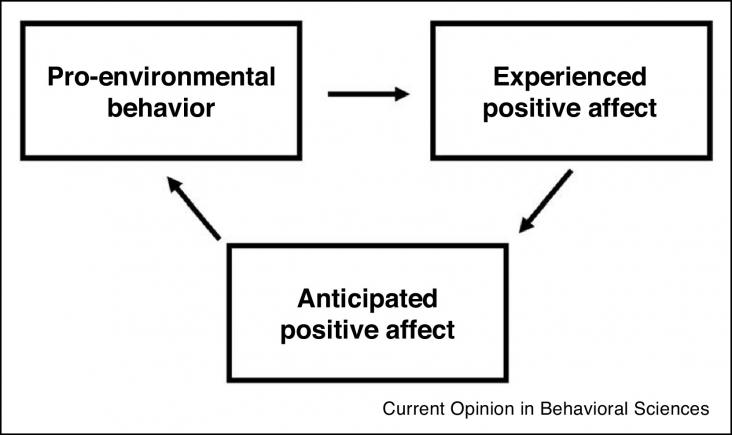
Recent findings and emerging trends concerning the role of affect and emotion in climate change perceptions and judgments as well as their potential as drivers of sustainable action are reviewed.
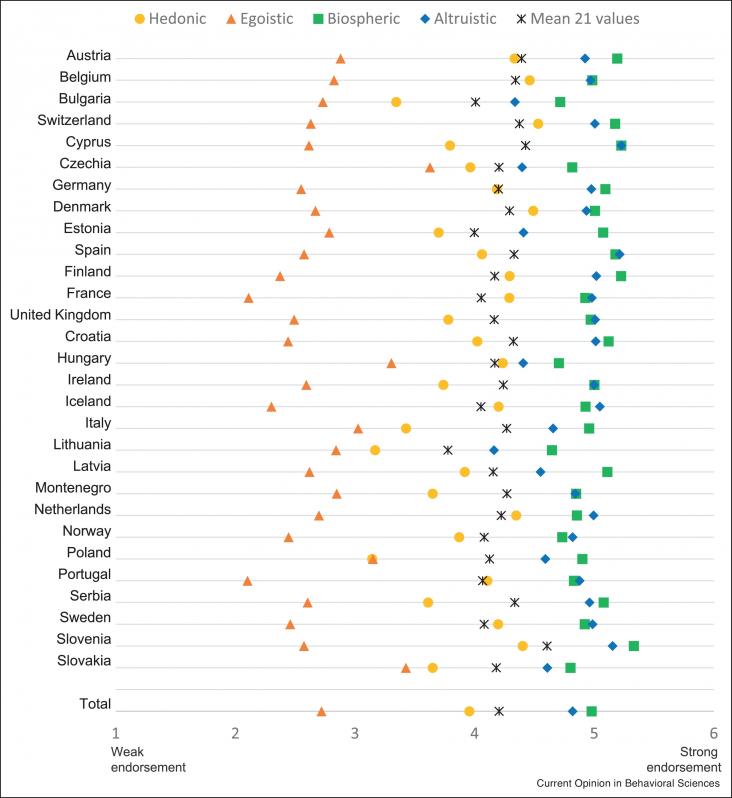
Environmental values and identities, at the personal and group level, motivate individuals’ climate actions.
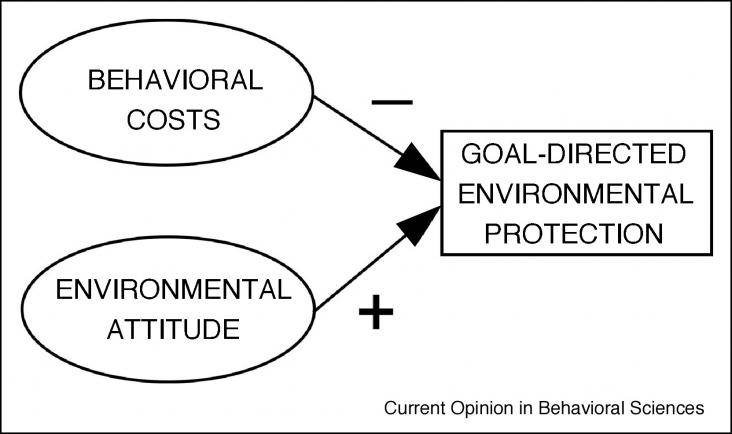
The fact that a behavior can be instrumental for multiple goals does not logically entail that people are typically propelled into action for multiple reasons.