This article highlights the impact of climate change on health, especially in the context of menopause and aging populations.

Approximately 15 per cent of the world's population live with some form of disability and 80 per cent live in developing countries. This Special collection aims to highlight this important issue and hopefully provide measures towards an inclusive and supported environment for all irrespective of disability. All book chapters and journal articles are free to download and share.
This chapter advances Goals 3 and 5 by discussing how pediatric health-care providers and systems can create healing-centered spaces to support IPV survivors and their children.
This chapter advances Goals 3 and 5 by discussing health care providers' opportunity for ARA prevention using a universal education approach that provides information on healthy and unhealthy relationship behaviors and ARA resources.
Background: Hong Kong is among the many populations that has experienced the combined impacts of social unrest and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Elsevier,
The South African Herbal Pharmacopoeia
Monographs of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants
2023, Pages 321-344
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health and Wellbeing by providing information about lessertia frutescens, an adaptogenic tonic, and commercial tablets that are popular to counteract the muscle-wasting effects associated with HIV-AIDS in patients and to stimulate appetite.
World AIDS Day, observed annually on 1st December, is an opportunity for people around the globe to unite in the fight against HIV/AIDS, support those affected, and remember those who have lost their lives to the disease. Elsevier is proud to support World AIDS Day 2023 with a special issue of freely available journal articles and book chapters highlighting research around HIV/AIDS.

Stella Chan's interest in psychology began when she went through a tough time as a teenager. The experience gave her a sense of direction: “I wanted to learn more about psychology and how feelings work...I hoped I could do something constructive about mental health.”
The study unveils a significant occurrence of sexual violence among recently arrived asylum-seeking women in France, especially notable among those who had previously experienced sexual violence. It underscores the heightened risk linked to the absence of support for accommodation.
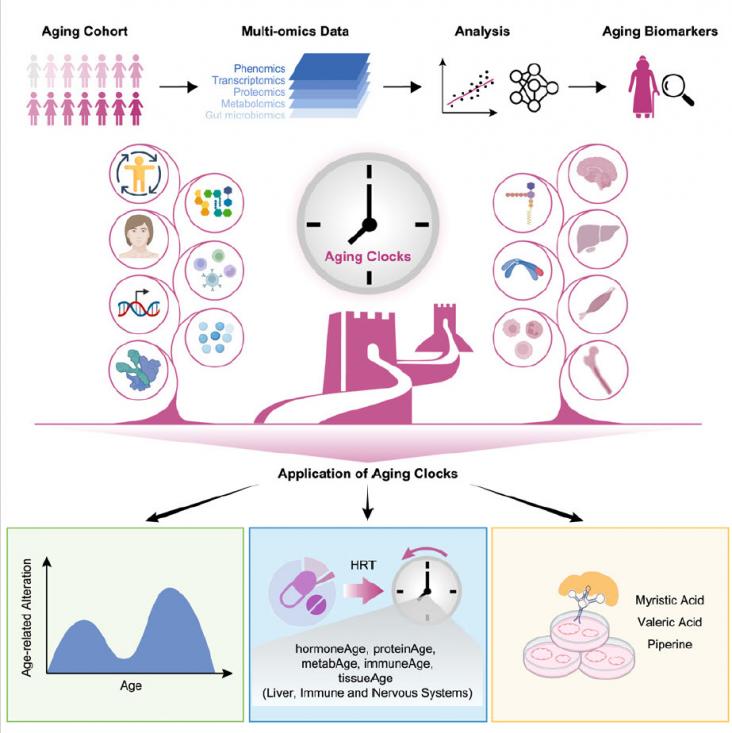
This study identifies a set of markers associated with aging in women, and uses them to create an "aging clock" that can measure a person's biological age. The clock reveals distinct aging patterns and suggests that hormone replacement therapy can slow down some aspects of aging.
