Divorce remains illegal in the Philippines, and this Comment considers the legal situation around divorce and the risk of abuse and other mental health implications of this situation for women. It calls for legal changes to advance gender equity.
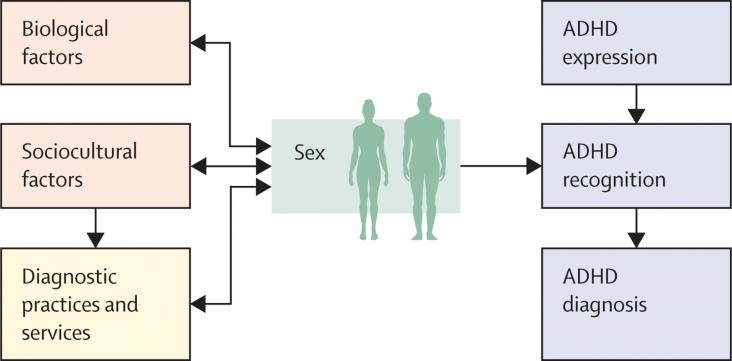
This Viewpoint looks at the reasons that females tend to be less likely to be diagnosed with ADHD, are diagnosed later in life, and are less likely to be prescribed medication. It considers potential biological factors including genetic factors, the influence of diagnostic factors such as diagnostic overshadowing, and sociocultural explanations including sex differences in presentation and compensatory behaviour.
The latest global prison trends from Penal Reform International suggest that approximately 740 000 women are in prison and that the number is rising in most regions. Neither the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development7 nor the UN definition of vulnerability make explicit reference to human rights of people deprived of their liberty.
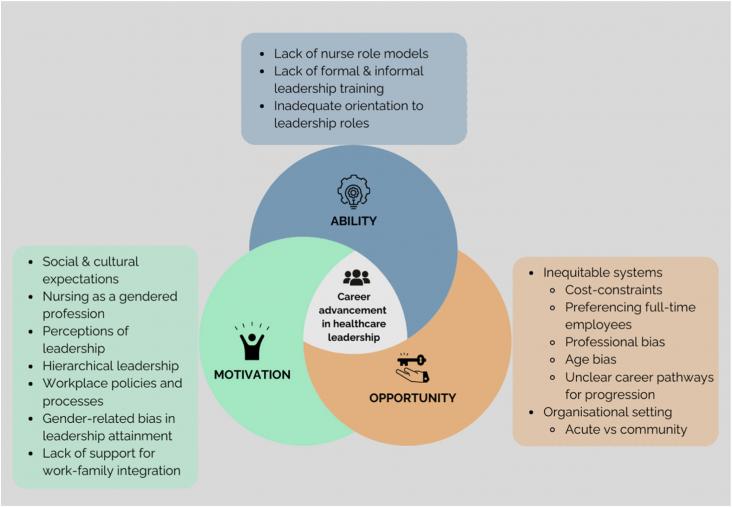
This Article supports SDG 5 by showing that women nurses aspiring to become healthcare leaders face multiple barriers, including cultural, professional, organisational, and individual barriers. The findings should help to inform workplace policies that can lessen these barriers.
Women interact with cancer in complex ways, as healthy individuals participating in cancer prevention, as patients, as health professionals, researchers, policymakers, and as unpaid caregivers. In all these domains, women often are subject to overlapping forms of discrimination, such as due to age, race, ethnicity and socio-economic status, that render them structurally marginalized. Women, power and cancer: A Lancet Commission recommends that sex and gender be included in all cancer-related policies and guidelines, making these responsive to the needs and aspirations of women in all their diversities. It identifies ten priority actions stakeholder groups can take towards lasting and impactful change.

10 December 2023 marks the 75th anniversary of one of the world's most groundbreaking global pledges: the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR).
This article highlights the impact of climate change on health, especially in the context of menopause and aging populations.
This chapter advances Goals 3 and 5 by discussing how pediatric health-care providers and systems can create healing-centered spaces to support IPV survivors and their children.
This chapter advances Goals 3 and 5 by discussing health care providers' opportunity for ARA prevention using a universal education approach that provides information on healthy and unhealthy relationship behaviors and ARA resources.

Stella Chan's interest in psychology began when she went through a tough time as a teenager. The experience gave her a sense of direction: “I wanted to learn more about psychology and how feelings work...I hoped I could do something constructive about mental health.”
