
The Paris Agreement goal of stabilizing temperature below 1.5C calls for a reduction of global energy consumption. Energy Efficiency policies are necessary but not sufficient to reduce energy consumption. Energy Conservation and Energy Sufficiency Policies complement Energy Efficiency policies, together they can reduce energy demand. The article presents some existing and new policies which address sufficiency. There is the need for coherent policy package with different types of policy instruments addressing efficiency and sufficiency.
Identified methane emissions and leaks from biomethane and biogas supply chains.
Reflects upon emergent challenges and opportunities of developing Positive Energy Districts (PEDs) in Europe. Combines attention to rapid implementation, context-specificity and replicability. Identifies three key themes to enable conditions for upscaling PEDs across contexts. The key themes are: framework conditions, prefiguration and emerging impact of PEDs. Combines expertise of PED-EU-NET core group, spanning PED initiatives across Europe.

This article supports SDGs 5, 7 and 10 by integrating the principles of equality, diversity, and inclusivity (EDI) into all aspects to correct historical and structural inequalities, and establishing an inclusive culture to achieve the justice urgently needed for the global transition to net zero. the progress can be made in the fields of energy and artificial intelligence.
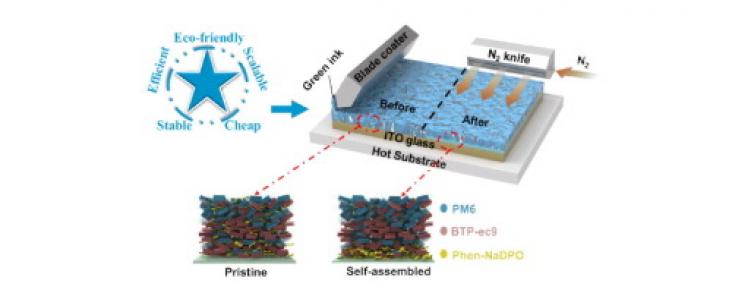
The ultimate goal of organic solar cells (OSCs) is to deliver cheap, stable, efficient, scalable, and eco-friendly solar-to-power products contributing to the global carbon neutral effort. This work demonstrates great potential to close the lab-to-fab gap of OSCs.
Climate policy targets.
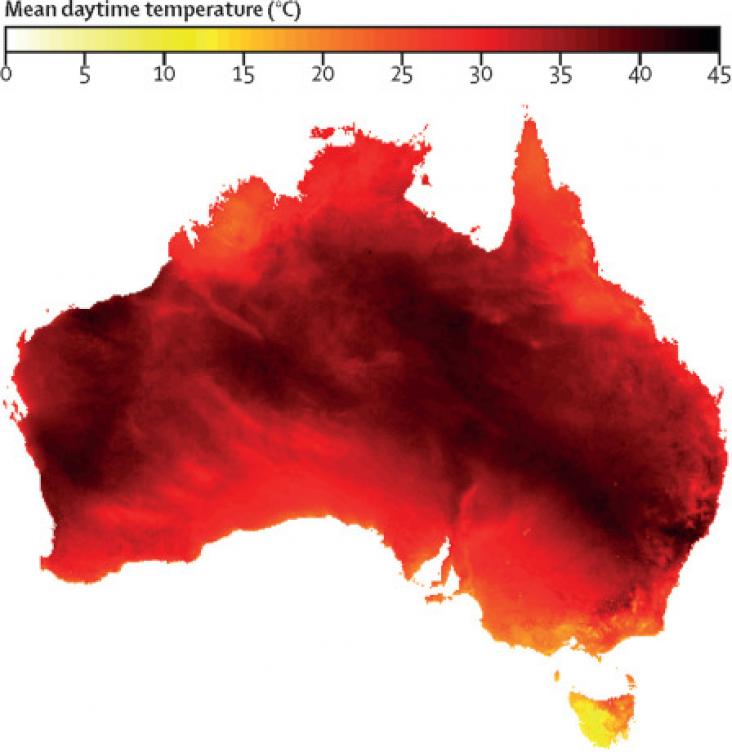
Background: Increasing air conditioner use for cooling indoor spaces has the potential to be a primary driver of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The impact of climate change and increasing demand for energy requires the development of more sustainable energy technologies. Hence, thermal energy storage (TES) methods can contribute to more appropriate thermal energy production-consumption through bridging the heat demand-supply gap. In addition, TES is capable of taking over all elements of the energy nexus including mechanical, electricity, fuel, and light modules by means of decreasing heat losses, waste recovery, and energy-saving approaches to improving the system's performance.
An all-around solution addressing the water-energy-food nexus for remote rural areas.
The optimal control of a water reservoir system represents a challenging problem, due to uncertain hydrologic inputs and the need to adapt to changing environment and varying control objectives.
