Elsevier,
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, Volume 42, June 2022, 100991
The diseased state in dolphins had metabolic consequences with a shift towards protein degradation. This may constrain the way cetaceans could cope with extra stressors (e.g., human disturbances). Provides insight to how we deal with conservation policies and the impact of stressors on population dynamics.

This article proposes a feasible framework to operate a global market of blue carbon, which helps to mitigate climate change.
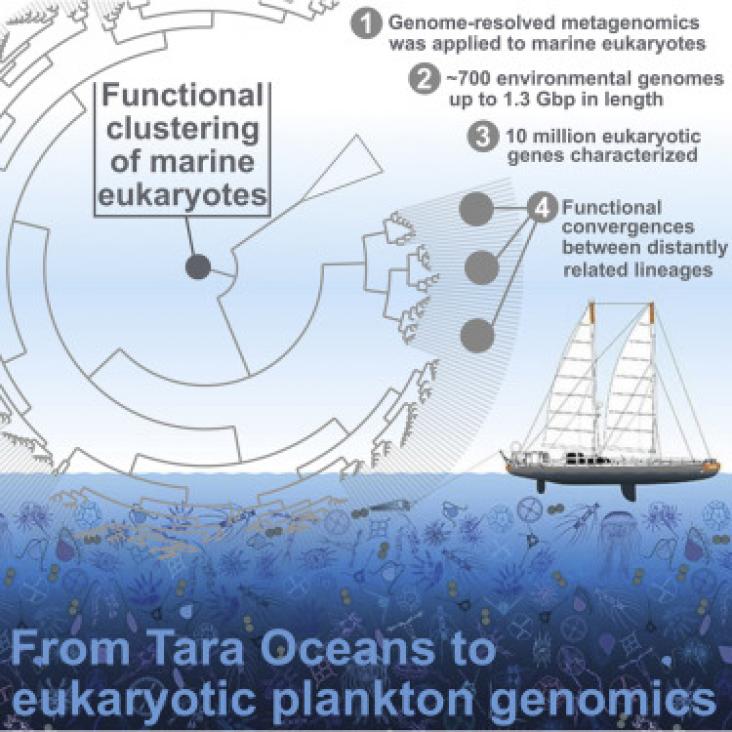
Marine plankton occur throughout the ocean and are major functional organisms involved in nutrient production and transfer. This paper surveys the global, sunlit ocean and recovers new genomes of species that are still uncultured and uncharacterized. This highlights the magnitude of yet unexplored ecology and diversity that remains to be discovered within the world’s oceans.
With the continuous development of human society, people's over-exploitation of nature leads to frequent environmental problems.

Aquaculture has been viewed as a potential pathway to healthy and sustainable diets by increasing global nutrient-rich food production while minimizing environmental impacts.
The predicted future climate change can be expected to have an impact on the biogeochemical conditions in pit lakes that must be considered when modelling pit lake water quality. Climate change might e.g., affect temperature and precipitation patterns, which can influence other factors such as water balance, hydrology, limnology, and biogeochemical prediction

This article demonstrates that, by actively engaging in the interdependent phases of recognizing hybridity, enabling conditions for reflexivity and partnership building, 'inclusivity' tensions can not only be acknowledged but softened and, in some cases, reframed when managing for biodiversity, equity, and justice goals.
Temperature and sea level rise threats to aquaculture were the main focus in science and the news. At least 10 countries linked current impacts on aquaculture to climate change. Global papers cited technology for adaption, while regional papers cited governance.
An article focused on (i) understanding how climate change is decreasing ocean biodiversity and (ii) identifying the planetary health impacts accelerated by ocean biodiversity erosion.
Authors measure nutrient content in coral reef fishes in Seychelles and show that reef fish are important sources of selenium and zinc and contain levels of calcium, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids comparable with other animal-source foods.
