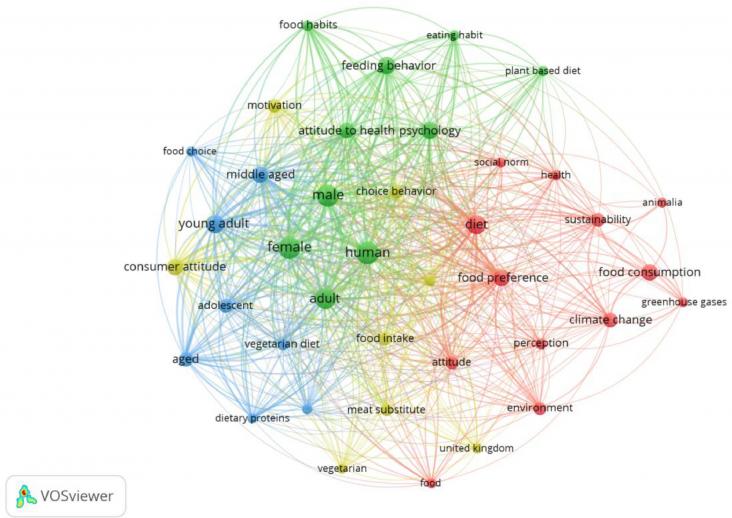
Several studies have indicated that a global reduction in meat consumption is inevitable for sustainability and public health, despite the challenges inherent to changing eating habits.
The availability of food is the basic entity for the survival of human. The resources that make a nation food secured is guided by multiple factors and can be evaluated using a set of indicators.

Cow's milk is considered a staple in many diets due to its high nutritional value. It contains almost every nutrient that the human body needs.
Meat induces large environmental impact while supplying important nutrients, and meat substitutes are increasingly adopted as direct replacers of meat products.
The Learning Circle approach is described as an inclusive and respectful way of engaging community and promoting local and traditional foods, knowledge, and practices among Indigenous youth in rural and remote locations. The flexibility of the model means that communities can prioritize activities of interest to them, identify what success of the initiatives would look like, and tailor evaluation processes accordingly. Indigenous leadership and ownership are essential to the success of such initiatives.
Despite its significant adverse impacts on the environment, society, and economy, food waste is unavoidable around the world. The increase in population and income will worsen the situation and put more pressure on food security.
Wheat is a major staple food in many diets worldwide. Authors identify a rapid and robust method for identifying fungi-infected damage to wheat crops, with the aim of reducing economic losses and hunger.
Plant-based meat substitutes are products used to replace meat in the human diet.


