Despite its significant adverse impacts on the environment, society, and economy, food waste is unavoidable around the world. The increase in population and income will worsen the situation and put more pressure on food security.
Wheat is a major staple food in many diets worldwide. Authors identify a rapid and robust method for identifying fungi-infected damage to wheat crops, with the aim of reducing economic losses and hunger.
Plant-based meat substitutes are products used to replace meat in the human diet.
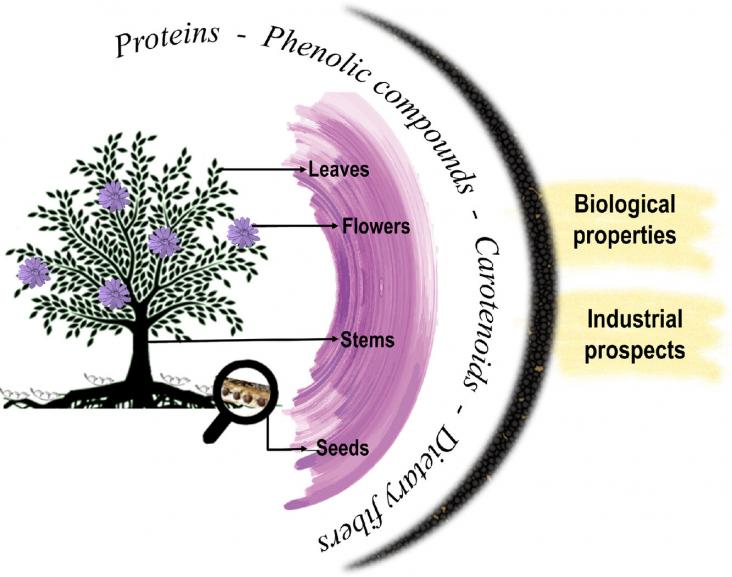
Innovative food products containing new ingredients have been designed to meet nutritional needs and new consumption trends.
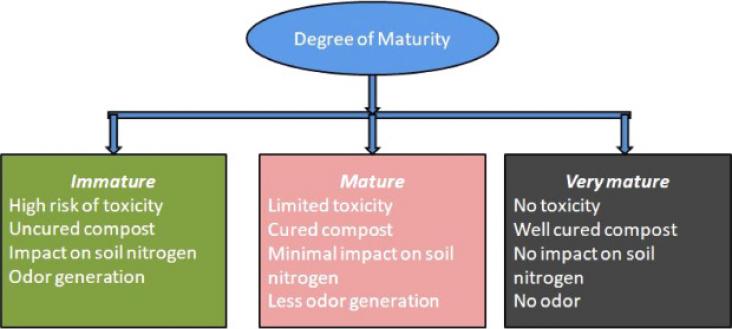
The knowledge about various indices related to the composting process has become an important and wider area of research in the current time. The review therefore focuses on the various stability and maturity indices of composting process and lays emphasis on the advantages and uses of the matured compost.
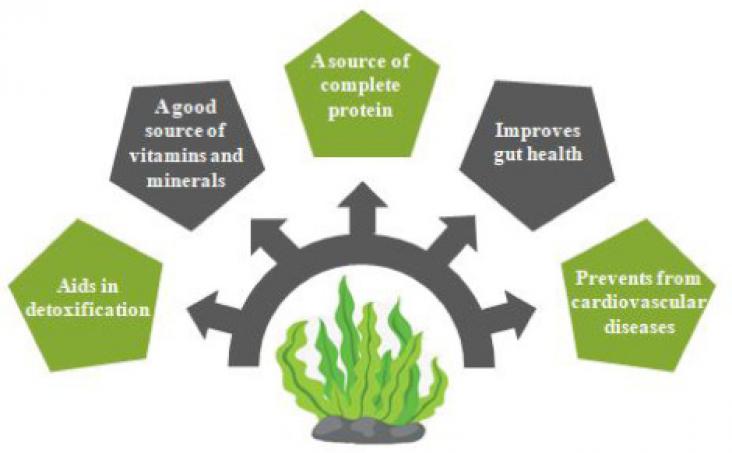
The eminent protein sources among the vegetarian population include cereals and pulses that do not satisfy the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) level.
An Article in support of SDGs 2, 13, and 15, assessing the environmental consequences and nutritional contributions of national food-based dietary guidelines while considering circular food system principles
An Editorial on the cost of living crisis, in the context of SDGs 1, 2, and 3, calling for governments to act urgently to address poverty and food insecurity to avoid further compromising the health of populations, especially children.
An Article on the increase in hunger brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic, in the context of SDG 3, focusing specifically on the Supplemental NutrAticition Assistance Program on mitigating this indirect effect of the pandemic on a national level across the USA.
Edible film, with unique biodegradable and renewable characteristics, is considered a potential alternative for petroleum-derived polymer packaging. The review provides an overview on the various aspects of edible film, such as the film formulation, source of materials, film characteristic as well as safety and regulations of edible film applications.
