Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is a peptide hormone of the incretin family. It has growth factor properties and can re-activate energy utilization.
Smart home technologies refer to devices that provide some degree of digitally connected, automated, or enhanced services to building occupants.
Increased demand for food to feed the ever-growing population led to development and adoption of synthetic chemicals as a quick and effective strategy of managing crop pests and diseases.
Focusses on the impact of the Te Tiriti o Waitangi in New Zealand and its effects on healthcare within indigenous Maori populations in the country
This study supports SDG 3 and 10 by analysing data from 415 ethnic groups in 36 low-income and middle-income countries, and showing substantial ethnic disparities in under-5 mortality across the countries studied. These findings are crucial for monitoring trends and examining the impact of health interventions on child survival across different ethnic groups.
Background: The WHO elimination strategy for hepatitis C virus advocates scaling up screening and treatment to reduce global hepatitis C incidence by 80% by 2030, but little is known about how this re
This chapter addresses Goal 3 by examining clinical virtual reality interventions which can help individuals suffering from mental health disorders.
This book chapter advances SDG3 Good Health and Wellbeing and SDG10 Reducing Inequalities by exploring a fall-detection monitoring solution that implements both accelerometer and sound-based detection algorithm.
How physical activity improves mental health.
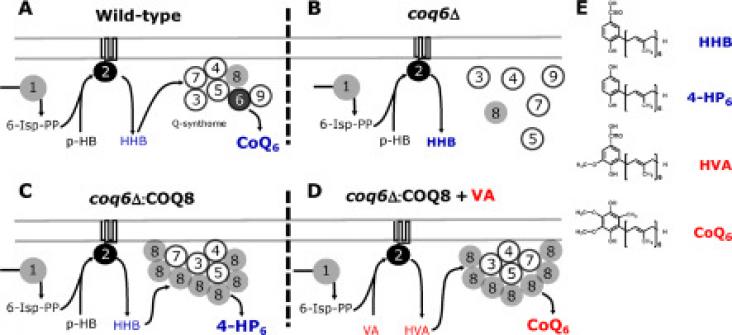
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) deficiency syndrome is a rare disease included in the family of mitochondrial diseases, which is a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by defective energy production. CoQ10 biosynthesis in humans requires at least 11 gene products acting in a multiprotein complex within mitochondria. The high-throughput screening (HTS) method based on the stabilization of the CoQ biosynthesis complex (Q-synthome) produced by the COQ8 gene overexpression is proven here to be a successful method for identifying new molecules from natural extracts that are able to bypass the CoQ6 deficiency in yeast mutant cells. The main features of the new approach are the combination of two yeast targets defective in genes with different functions on CoQ6 biosynthesis to secure the versatility of the molecule identified, the use of glycerol as a nonfermentable carbon source providing a wide growth window, and the stringent conditions required to mark an extract as positive. The application of this pilot approach to a representative subset of 1200 samples of the Library of Natural Products of Fundación MEDINA resulted in the finding of nine positive extracts. The fractionation of three of the nine extracts allowed the identification of five molecules; two of them are present in molecule databases of natural extracts and three are nondescribed molecules. The use of this screening method opens the possibility of discovering molecules with CoQ10-bypassing action useful as therapeutic agents to fight against mitochondrial diseases in human patients.
