Background: Exposure to cold or hot temperatures is associated with premature deaths.
Background: Because of the limited epidemiological evidence on the association between acute air pollutants and allergy, there is a need to investigate this association, especially between the short-t
The results suggest that the ongoing pandemic has led to the rise of common mental health problems among indigenous people during the pandemic. The results can contribute to the formation of mental health policy for indigenous people and the development of suitable mental health intervention strategies especially during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Disruptions to cancer screening services have been experienced in most settings as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic.
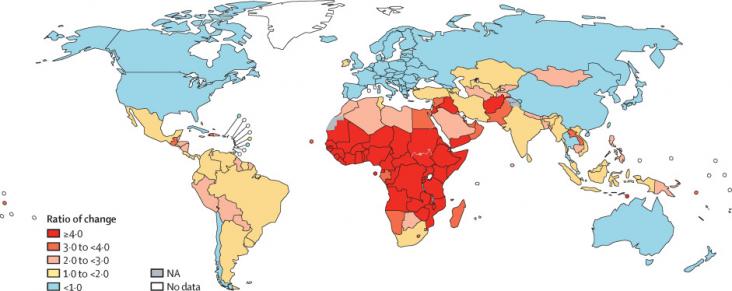
Background: WHO has launched an initiative aiming to eliminate cervical cancer as a public health problem. Elimination is a long-term target that needs long-lasting commitment.
Disruptions to cancer screening services have been experienced in most settings as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Background: Rohingya girls living in the refugee camps in Bangladesh are disproportionately vulnerable to child marriages and teenage pregnancies.
Background: Criteria for low-dose CT scan lung cancer screening vary across guidelines.
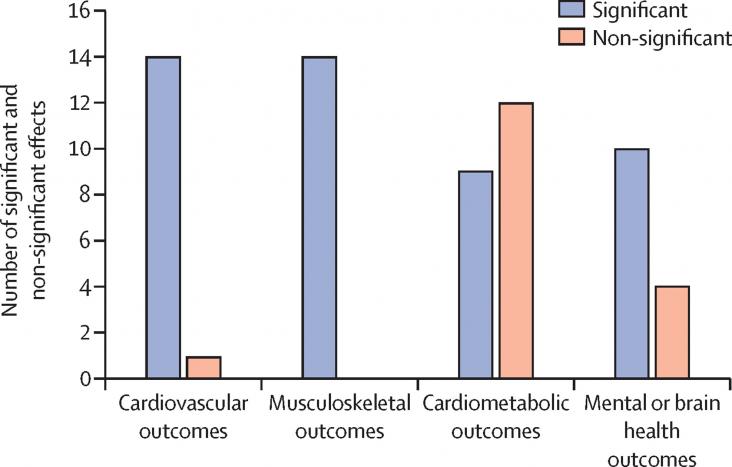
Approximately 1·5 billion people worldwide live with a physical, mental, sensory, or intellectual disability, about 80% of which are in low-income and middle-income countries.
This Comment article advances SDG 3 and 10 by making a case for bridging language barriers in global health research and overcoming the colonial legacy of language in global health (from the naming of infectious diseases to the use of global health terms with problematic historical connotations), with the aim of facilitating knowledge co-production and more equal research partnerships.
