Māori and Pacific families’ experiences and perspectives of cardiovascular care; A qualitative study
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, Volume 48, June 2024
Māori and Pacific people want to take charge of their heart health but face challenges. Participants described important obligations to family, community and tikanga (the culturally correct way of doing things). Participants described times when health care undermined existing responsibilities, their dignity and/or their mana, and they felt excluded from treatment as a result.
This study analyses the linguistic and metalinguistic abilities of individuals with Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS).
This study supports SDG 3 by showing that adolescents’ cognitions around learning and success are associated with future mental health outcomes.
To understand how best to help patients and improve health during an epidemic it is necessary to have good modelling techniques and protocols.
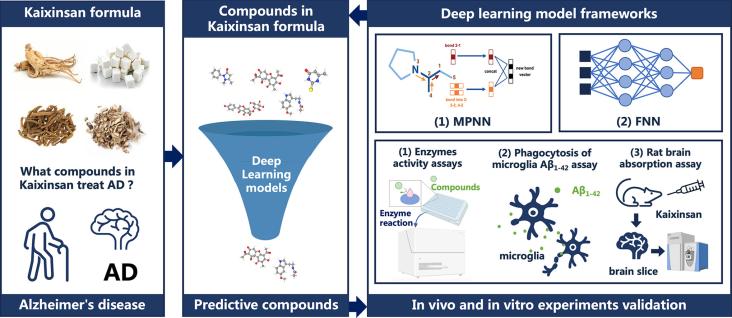
This study developed four deep learning models to identify potential Alzheimer's disease treatments from traditional Chinese medicine, specifically the Kaixinsan formula. The models successfully predicted compounds that showed significant anti-Alzheimer's activities in various experimental validations.
This article supports SDG 3 by showing that using an interactive mHealth application can reduce dementia risk factors in populations who are underserved and at increased risk.
This article looks at complications that arise from combinations of Alzheimers and osteoporosis in mouse models
This investigation aimed to understand preclinical biomarker and genetic Alzheimer’s disease research participation in underrepresented groups to facilitate greater diversity in future biomarker research and clinical trials.
This study finds that impaired cellular immune dysfunction in AD patients was significantly correlated with abnormal MRS, and neuroimmune dysfunction may contribute to the pathogenesis of AD and alter the metabolism of neurotransmitters such as aspartic acid and MI in the brains of AD patients.
This study identified key biochemical pathways and protein changes in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) human hippocampus, revealing increased expression of proteins VGF, GFAP, HSPB1, and APP, with UBC being most centrally involved, and highlighted the roles of four hub proteins (CD44, APP, ITGB2, APOE) linked to amyloid plaques and two (RPL24, RPS23) to neurofibrillary tangles, along with the impact of modified proteins on immune activation and synaptic disruption, uncovering potential therapeutic targets involving specific proteins, microRNAs, and transcription factors.
