This Article supports SDG 3 and 7 by showing that air pollution exposure increases the risk of almost all phases of cardiometabolic multimorbidity progression.
This Article supports SDG 3 by assessing the safety and efficacy profile of abacavir used in first, second, or subsequent lines of treatment for infants, children, and adolescents living with HIV to inform 2021 WHO paediatric ART recommendations.
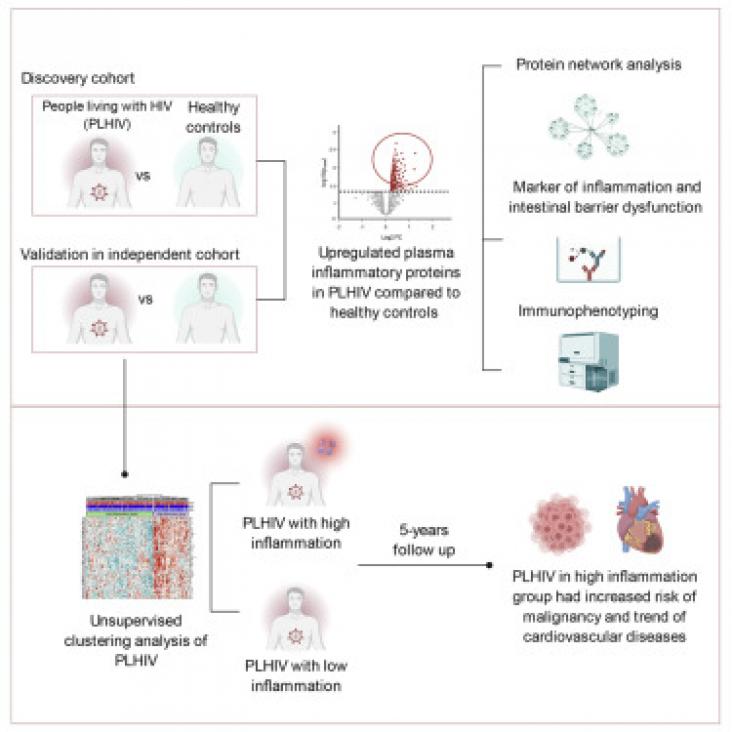
This study uses targeted plasma proteomics to show the upregulation of inflammation in people living with HIV.
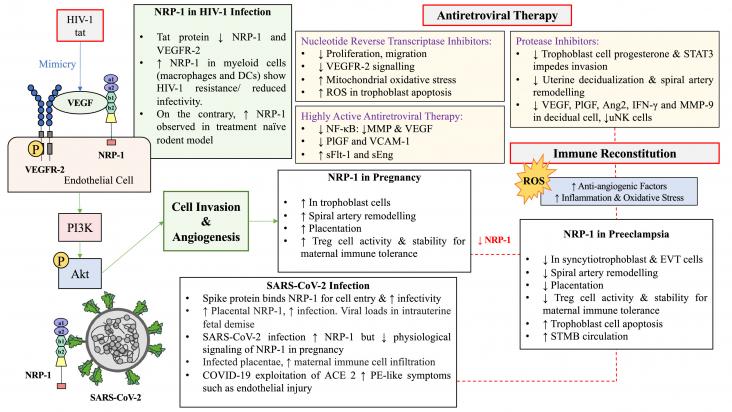
This review explores the role of transmembrane neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) in pregnancy, preeclampsia (PE), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. Since these conditions are assessed independently, this review attempts to predict their comorbid clinical manifestations.
This review article is about free radical generation during viral infection, including HIV, with a special emphasis on detection methods.

Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by progressive muscle weakness. Adenine nucleotide translocator 1 (ANT1), the only 4q35 gene involved in mitochondrial function, is strongly expressed in FSHD skeletal muscle biopsies. However, its role in FSHD is unclear. In this study, we evaluated ANT1 overexpression effects in primary myoblasts from healthy controls and during Xenopus laevis organogenesis. We also compared ANT1 overexpression effects with the phenotype of FSHD muscle cells and biopsies.
This Article supports SDG 3 and 5 by highlighting a need for greater involvement of in-country authors on research examining a wider range of gendered COVID-19 impacts, as well as increased representation of diverse topics and publications related to COVID-19 and women's well-being focused on lower income countries.
Background: Identifying how greenspace impacts the temperature-mortality relationship in urban environments is crucial, especially given climate change and rapid urbanization.
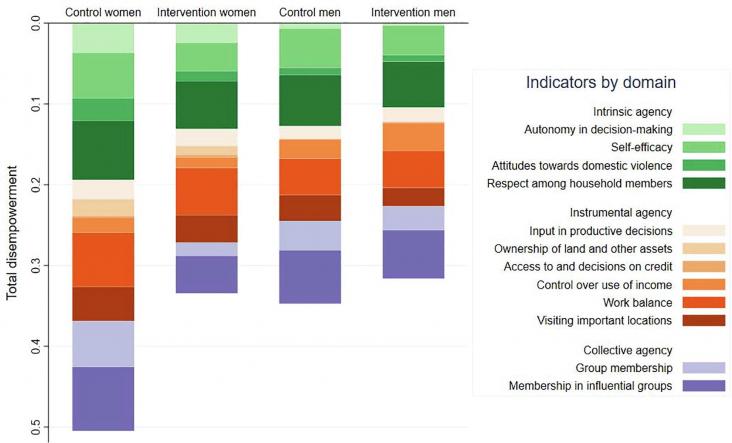
This Study supports SDG 5 and 3 by examining the role of improved women's agency on the pathway from the intervention to nutritional impacts.
This Article supports SDG 3 and 7 by estimating the prevalence of solid-fuel use with high spatial resolution to explore subnational inequalities, assess local progress, and assess the effects on health in LMICs without universal access to clean fuels.
