Background: Falls in older adults, notably those with Alzheimer's dementia (AD), are prevalent. Vision and balance impairments are prominent falls risk factors in older adults.
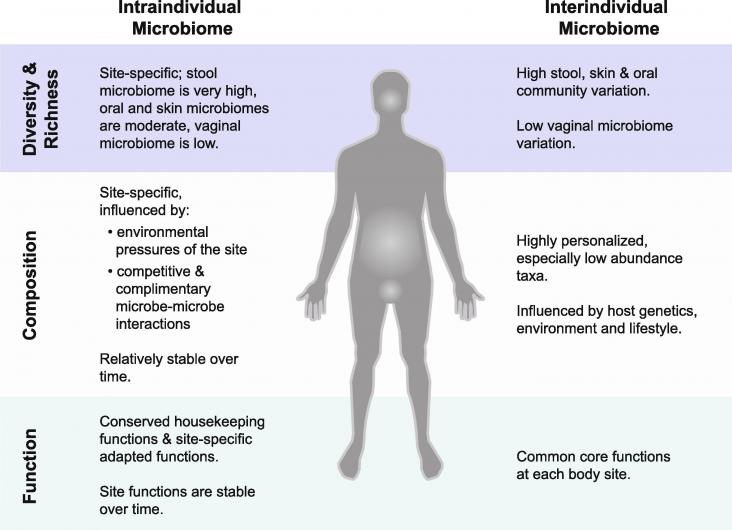
Trillions of microbes cover the surfaces of our bodies and inhabit our gastrointestinal tract.
Introduction: Dermatologic disease represents a significant burden worldwide, but the regional effect of skin disease in the Caribbean and how it relates to socioeconomic status remain unknown.
In this paper, we revisit the entrepreneurship and poverty relationship under a eudaimonic perspective that brings together conversion factors, and future prosperity expectations.
Cities with many pedestrian barriers can inhibit community mobility, access to services, and social participation for people with disabilities.
Exaggerations of the detrimental impact of recreational drug use on the brain is killing Black People.
Enhancing the Diversity of Neuroscience Researchers.
This paper investigates mutations in the S protein that can potentially decrease the effect of hepatitis B vaccination in vaccine recipients.
Background: Hepatitis B causes more than 800 000 deaths globally each year. Perinatal infections are a major driver of this burden but can be prevented by vaccination within 24 h of birth.
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDD) such as Alzheimer's (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are distinct clinical entities; however, the aggregation of key neuronal proteins, presumably leading to neuronal demise appears to represent a common mechanism. It has become evident that advanced glycation end products (AGEs) trigger the accumulation of such modified proteins, which eventually contributes to the pathological aspect of NDDs. Increased levels of AGEs are found in amyloid plaques in AD brains and in both advanced and early PD (incidental Lewy body disease). The molecular mechanisms by which AGE dependent modifications may modulate the susceptibility towards NDDs, however, remain enigmatic and it is unclear whether AGEs may serve as biomarker of NDD. This study detected differential associations between NDD, sex and oxidative stress markers.
