This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by developing a deep learning algorithm for the detection of Alzheimer's using retinal photographs, with the potential for use in community screening.
This chapter advances Goals 16 and 3 by discussing how the EAAF and other international organizations, such as the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and International Commission on Missing Persons (ICMP) work globally to address large-scale human rights abuses and humanitarian crises through support/substitution of forensic services and development of local medicolegal capacities.
This article ties to SDG 3. In this article, a system innovation perspective was used to examine the factors influencing the potential for scaling up a task-sharing psychological intervention for refugees called ‘Problem Management Plus’ (PM+) in the Netherlands.
This article ties to SDG 3. This article investigated whether wartime stress exposures occurring during adolescence and early adulthood affect weathering in late adulthood via linear regression with data from the Vietnamese Health and Aging Study (VHAS).
This article ties to SDG 3. This article addresses gaps in available measurement methodologies in child protection interventions, and pilots a methodology to assess a package of key child protection interventions in a single, holistic and integrated approach.

The study shows that, despite most of the professional groups’ high level of knowledge about the study object and their high awareness of the importance of the vaccine as a preventive tool, the role of the healthcare workers as transmitters of infection is less recognised as a reason for vaccination.
Background: Inequalities undermine efforts to end AIDS by 2030.
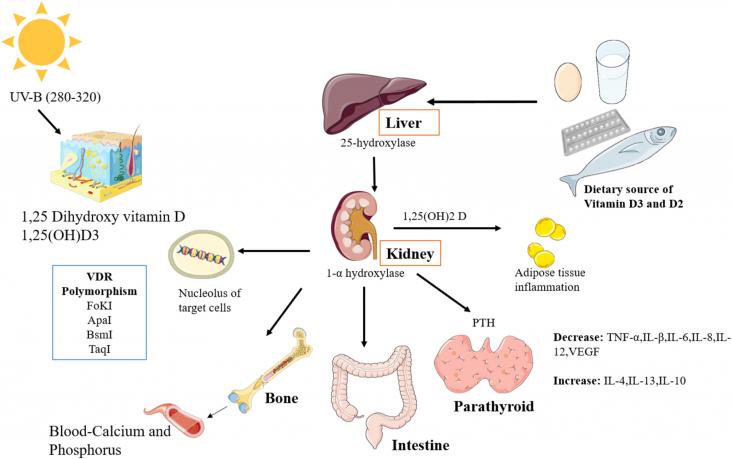
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, viral hepatitis has been a problem in human society. Vitamins play a significant role in preventing the hepatocarcinoma and liver cirrhosis.
Elsevier,
Research Ethics in Behavior Analysis: From Laboratory to Clinic and Classroom, 2023, Pages 63-86
This chapter advances the UN SDG Goal 3: Good Health and Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by discussing the importance of equity, diversity, inclusion, and accessibility (EDIA) as related to research in applied behavior analysis.
This article ties to SDG 3 & 4. The present study adapted and assessed the efficacy of a brief psychological group intervention, the STAR program: Strengths, Transitions, Adjustments and Resilience for university students who are Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs).The present study adapted and assessed the efficacy of a brief psychological group intervention, the STAR program: Strengths, Transitions, Adjustments and Resilience for university students who are Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs).
