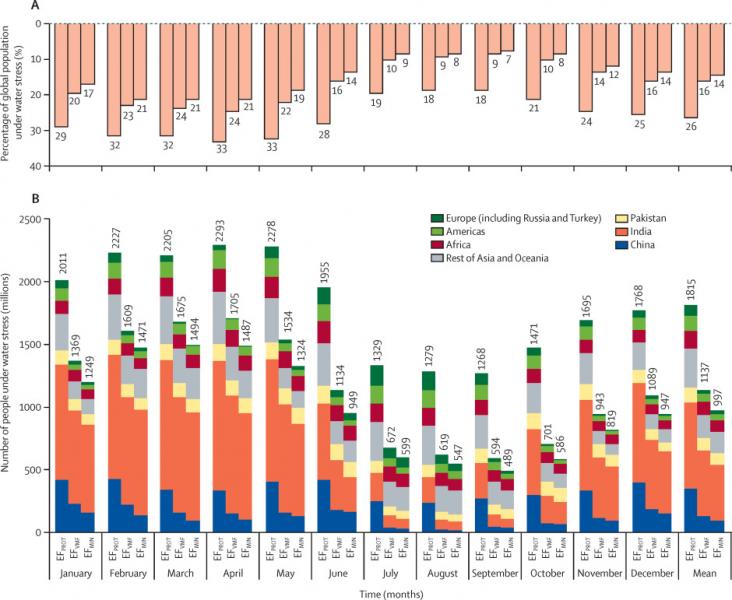
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 6 by assessing global human water stress for low to high environmental flow protection. The findings suggest that ensuring high ecological protection would put nearly half the world's population under water stress for at least 1 month per year, meaning important trade-offs are made when allocating limited water resources between direct human needs and the environment.
Underneath the façade of supposedly bubbly girls, living daily lives in many parts of Nigeria lies the problem of lack of access to proper menstrual hygiene management tools or kits.
Background: The impact of COVID-19 on physical and mental health and employment after hospitalisation with acute disease is not well understood.
Objectives: We determined the representation of women in sport sciences research leadership by assessing the proportion of women in (i) leading authorship positions of randomized controlled trials (RC
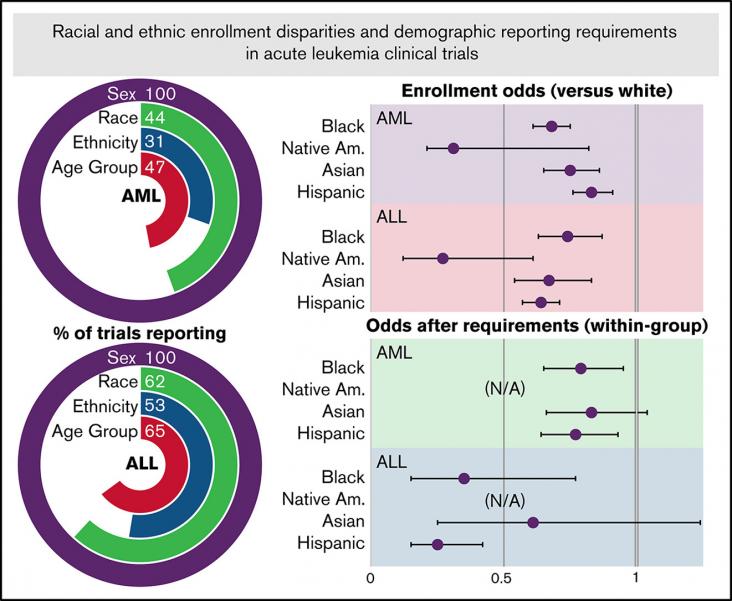
Data regarding racial and ethnic enrollment diversity for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) clinical trials in the United States are limited, and little is known about the
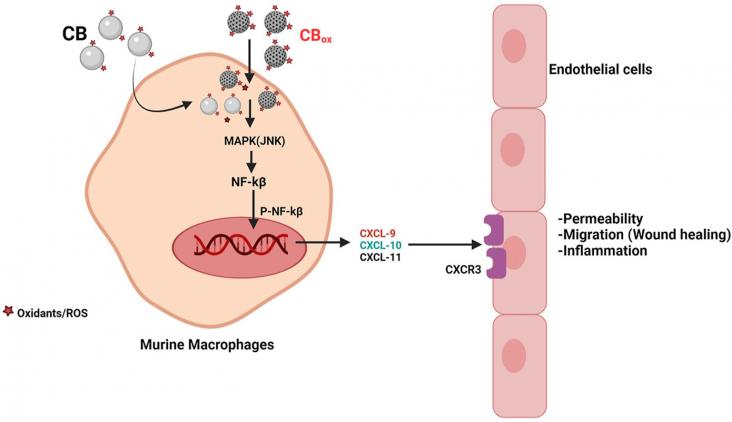
Oxidation of engineered nanomaterials during application in various industrial sectors can alter their toxicity. Oxidized nanomaterials also have widespread industrial and biomedical applications.
Amahewu is a fermented maize-based gruel or beverage consumed mainly in Southern Africa.