This content supports the SDG Goal 3: Good health and well-being by discussing the clinical aspects, epidemiology, and molecular virology of the major hepatitis viruses.
This Article supports SDG 3 by analysing two vaccination strategies for hepatitis A outbreaks in men who have sex with men: pre-emptive (before an outbreak occurs) and reactive (once an outbreak has started). The study shows that both strategies can be cost-saving, but pre-emptive vaccination can save more money, suggesting that a pre-emptive strategy should be the first choice, and reactive used if the pre-emptive vaccination fails to prevent the outbreak.
The Philippine government included the health impacts of climate change as a priority area for research funding. An analysis of stakeholders was done to assist the government in engaging research and government stakeholders in producing climate change and health research.
This review focuses on the potential exposure routes, human health impacts, and toxicity response of MPs/NPs on human health, through reviewing the literature on studies conducted in different in vitro and in vivo experiments on organisms, human cells, and the human experimental exposure models.
This paper discussed the development and testing of a gamma radiation dose rate calculation model for the marine environment, and evaluates the potential use for such a model in both short term nuclear emergency response management and emergency response planning.
Background: Empirical, updated country-level estimates on the proportion of cirrhosis attributable to viral hepatitis are required.
An Article in support of SDGs 2, and 3, assessing the impact of incorporating dietary assessment in 10 year absolute risk charts for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Elsevier,
Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health (Second Edition), Mechanisms, Consequences, and Opportunities, 2022, Pages 3-25
This chapter reviews the state of global infant and young child nutrition, its long-term health consequences, the mechanisms involved, and potential approaches to addressing these challenges.
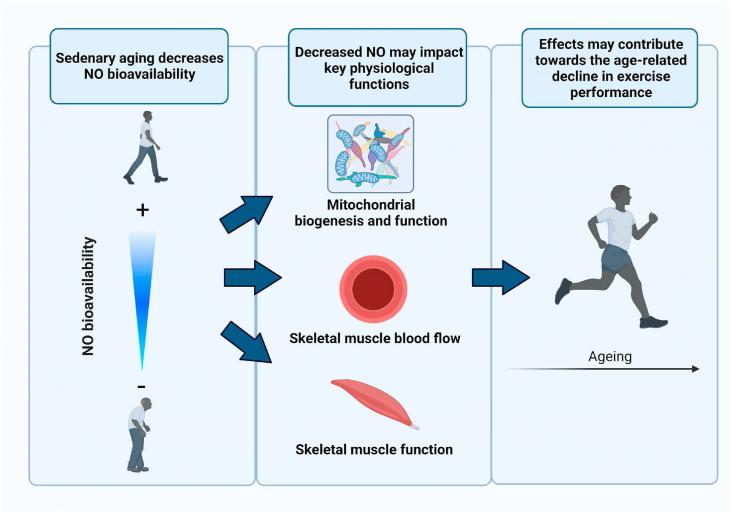
Worldwide, individuals are living longer. This population aging is associated with an anticipated increase in the burden of the leading causes of death in modern societies — chronic, degenerative diseases such as cardiovascular, kidney and Alzheimer's disease — which is largely driven by age-related declines in physiological function. Engaging in healthy lifestyle practices that preserve physiological function with age has important implications for reducing the risk of morbidity and mortality and preserving healthspan — the period of an individual's life when one is generally healthy and devoid of serious chronic disorders. In this regard, regular exercise and physical activity are considered key “first line” strategies for healthy aging.
