Elsevier,
Treatment of Skin Disease (Fifth Edition)
Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies
2018, Pages 764-768
This content links with Goal 3: Good health and well-being and Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by providing information on scleroderma, a rare multisystem disease characterized by skin fibrosis, autoantibody production, and vascular abnormalities often leading to visceral disease.
An article on global spending of dementia care, in the context of SDG 3, focusing specifically on modelling global and regional estimates from 2000 to 2019 and expected future scenarios from 2020 to 2050.
An article on air pollution and cognitive decline, in the context of SDGs 3 and 11, focusing specifically on the association between exposure to outdoor air pollutants and cognitive performance.
An article on comorbid dementia and depression, in the context of SDG 3, focusing specifically on the effectiveness of music interventions on depressive symptoms for people with dementia.
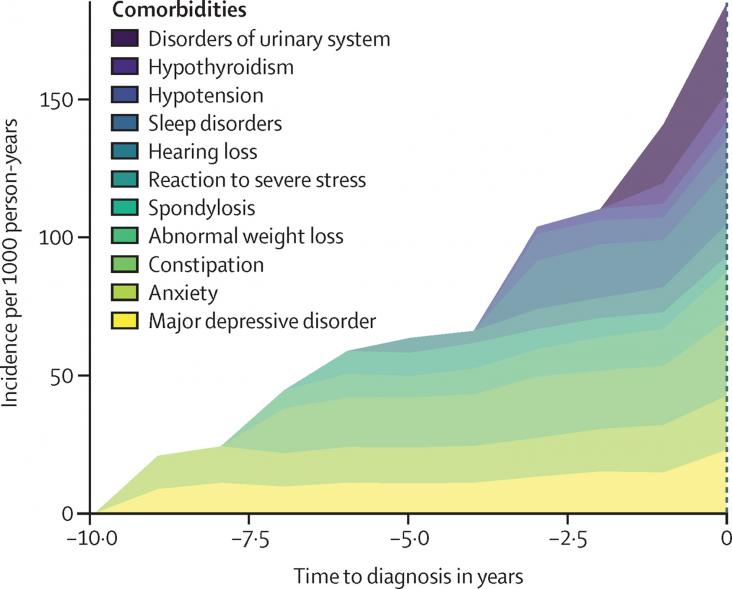
An article on Alzheimer's disease risk, in the context of SDG 3, focusing specifically on the association between health conditions diagnosed in primary care and incident Alzheimer's disease.
This article addresses ways to share the burden of care for those with dementia.
Mental health condition diagnoses were associated with other underlying chronic health conditions and a modestly increased risk of a range of adverse outcomes. The findings suggested that mental health conditions are an important risk factor in adverse maternal outcomes.
This Article supports SDGs 3, 5, and 10 by providing global, regional, and country estimates of physical and sexual violence against women by male intimate partners, calling for investments in multisectoral interventions and a strengthening of the public health response, especially in the face of post-COVID-19 reconstruction efforts, to meet SDG targets.
This papers demonstrates how simple substitutions can be made in individuals’ diets to substantially reduce their carbon and water scarcity footprints without sacrificing dietary quality. Such substitutions may be easier to promote than complex dietary patterns.