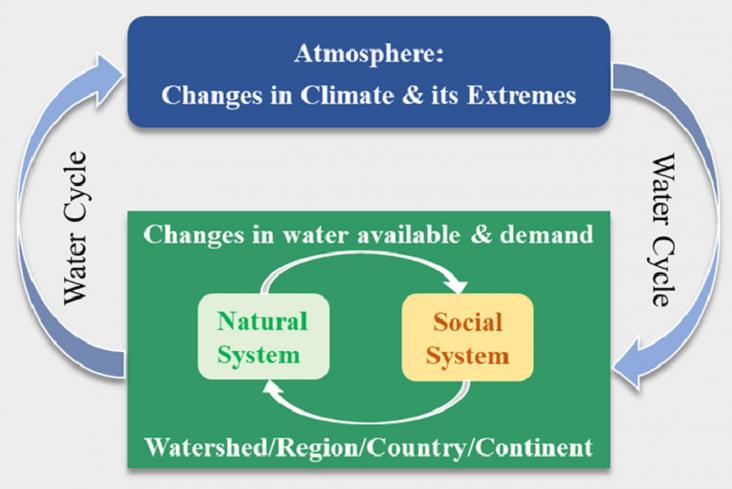
Water is the fundamental natural resource that supports life, ecosystems and human society. Thus studying the water cycle is important for sustainable development.
As sea level rise drives saltwater farther inland, drinking water supplies of some coastal cities will be contaminated.
Climate change has affected diverse spheres and its impact is being witnessed worldwide. Soil, the basis of human sustenance, is both directly and indirectly affected by climate change.



After a massive disaster, many residents in affected areas are forced to temporarily stay in evacuation shelters.

