Sustainable consumption and production (SCP) is at the core of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), specifically addressed by SDG 12. This goal aims to "ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns," acting as a cross-cutting theme that feeds into other SDGs such as those related to climate change, poverty, health, and sustainable cities.
SCP involves using services and products in a way that minimizes environmental damage, preserves natural resources, and promotes social equity. The purpose is to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, which means pursuing economic development in a way that can be sustained by the planet over the long term. SCP requires changes at all levels of society, from individuals to businesses to governments.
At the individual level, SCP implies making lifestyle choices that reduce environmental impact. This might include reducing, reusing, and recycling waste, choosing products with less packaging, and opting for more sustainable forms of transport like cycling or public transport.
For businesses, SCP entails adopting sustainable business models and practices. This could include improving resource efficiency, investing in renewable energy, designing products that are durable and recyclable, and ensuring fair labor practices.
At the government level, SCP involves implementing policies that support sustainable business practices and incentivize sustainable consumer behavior. This might involve regulations to reduce pollution, subsidies for renewable energy, and campaigns to raise awareness about sustainable consumption.
SCP also plays a role in several other SDGs. For example, sustainable production practices can help mitigate climate change (SDG 13) by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, by reducing the pressure on natural resources, SCP supports the goals related to life below water (SDG 14) and life on land (SDG 15).
While progress has been made in certain areas, challenges remain in achieving the shift towards SCP. These include existing patterns of overconsumption, limited awareness about the impacts of consumption, and the need for technological innovation to enable more sustainable production.
Substitution of beef with alternative proteins is one practical trend taken by industry and consumers to reduce the negative impact of convenience products on the environment. Numerous products based on plant, insect and fungi proteins compete to replace beef burgers in an environmentally friendly and healthy way. At the same time, there is a lack of studies which assess different options from environmental impact perspective but also with consideration of production scales, recipes, nutritional values, and sensory properties.
With the rapid development of China's economy, it has become crucial to achieve the right balance between economic development and environmental protection. Green growth is a significant approach to addressing the relationship between economic development and the environment. Low-carbon development and ecological protection are two essential aspects of green development, and they tremendously impact enterprises' resource-based supply chain. Hence, this paper seeks to explore the revenue distribution mechanism of the resource-based supply chain in the context of green development.
Using data from Eurobarometer 83.4, this study combines the two branches of research that address climate-related and biodiversity-related opinions and actions of individuals in the EU. The literature shows that the differences between climate-related and biodiversity-related policies correspond, at an individual level, to a person's basic attitudes towards environmental protection and towards nature protection, respectively.
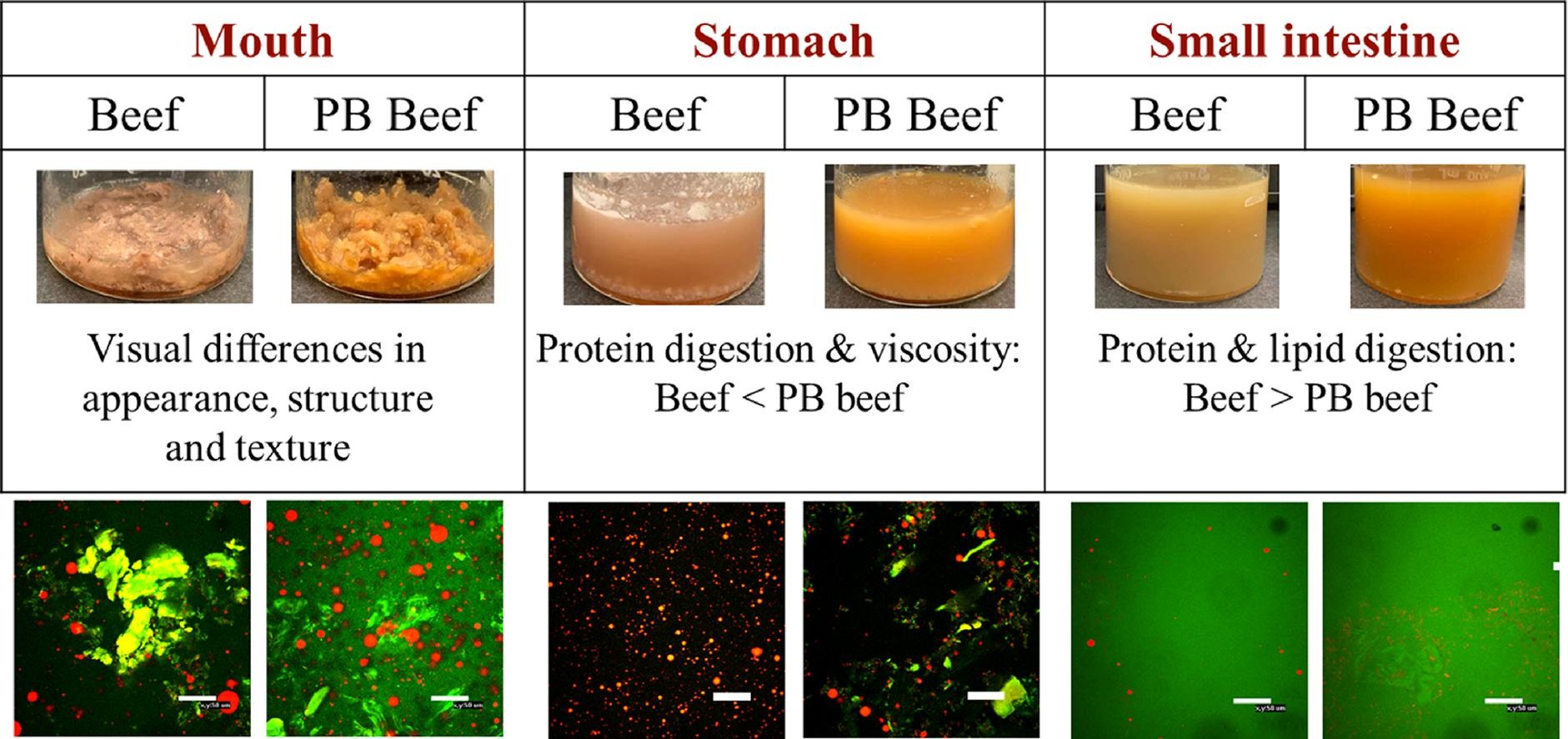
Plant-based meat analogs are likely to have different gastrointestinal fates than real meat products due to differences in their compositions and structures. Here, we compared the gastrointestinal fate of ground beef and ground beef analogs using the INFOGEST in vitro digestion model, focusing on differences in microstructure, physicochemical properties, lipid digestion, and protein digestion in different regions of the model gut.
The global market for plant-based foods intended as alternatives to cheese products is increasing and will reach almost $4 billion by 2024. In this study, an evaluation of the composition, structure and physicochemical properties of four commercial plant-based block-style products was conducted, with results compared with those for Cheddar and processed cheeses. The plant-based products had considerably lower protein contents (0.11–3.00%) compared to the Cheddar and processed cheeses (25.04 and 18.50%, respectively).
The mounting research on consumer behavior and climate change is gradually improving our understanding of effective ways to mobilize consumers to mitigate climate change. The relationship between consumer behavior and climate change is complex and most consumers are not capable of determining which behavior changes are worth doing. Research has come a long way identifying the most impactful behavior changes, but more research is needed to refine and situate these insights.
Emerging Issues in Climate Smart Livestock Production, Biological Tools and Techniques, 2022, Pages 71-90