Elsevier,
Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 22, June 2023
This Article supports SDG 3 by showing that an HCV testing (point-of-care) and treatment programme implemented in users of a supervised drug cosumption service in Canada was beneficial, with a large degree of positive testing, testing acceptance, and treatment engagement. The study suggests that on-site point of care testing and treatment for HCV in supervised consumption services is effective in reaching this population
Elsevier,
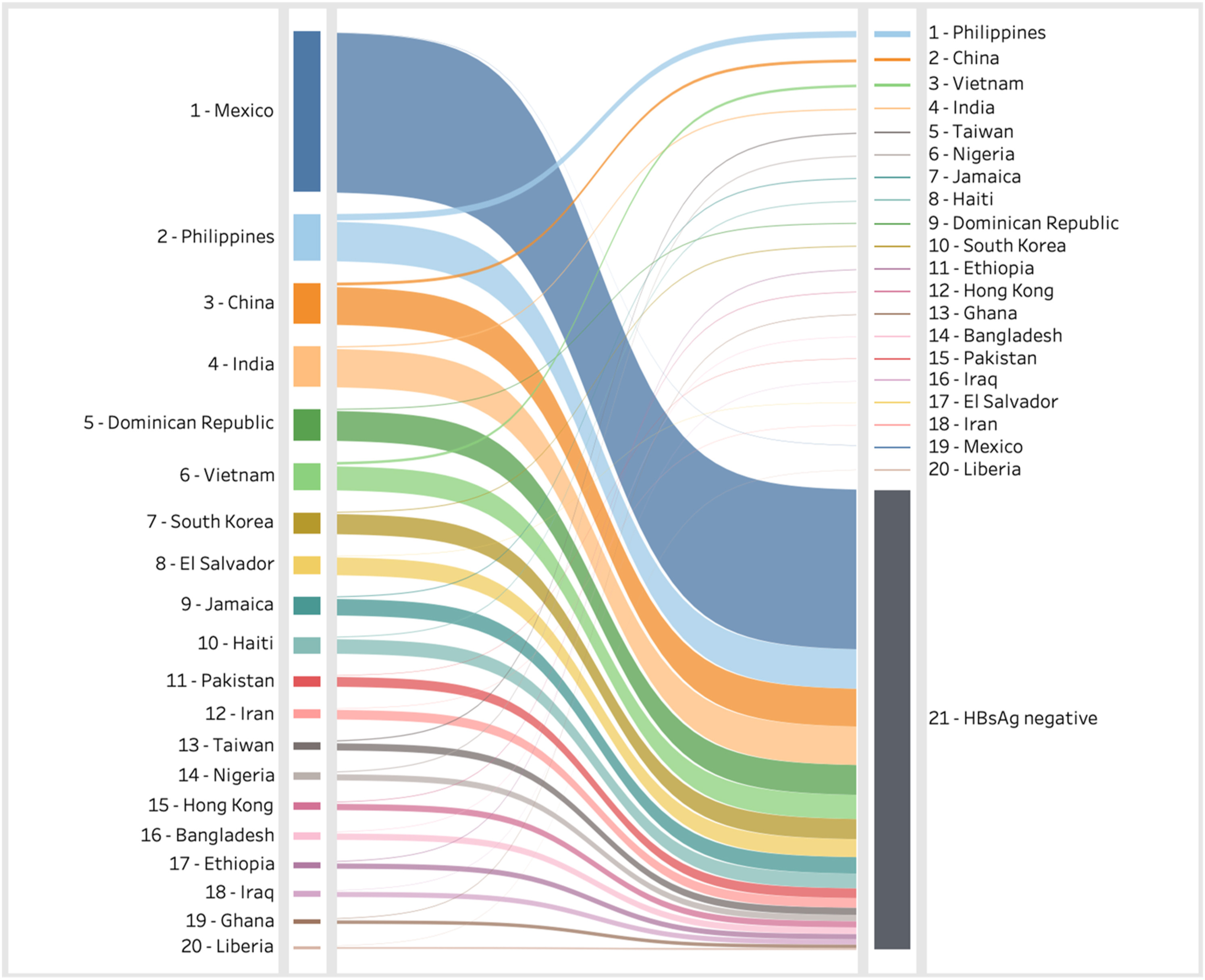
Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 22, June 2023
This Article supports SDG 3 by using modelling to estimate the impact of immigration on hepatitis B prevalence in the USA, in order to more accurately assess the hepatitis B burden, which might not be accurately measured by national serosurveys. The study found a significantly higher burden of hepatitis B (1.8 million cases), significantly higher than that found in national serosurveys.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 8, June 2023
This Article supports SDG 3 by assessing the incidence of HIV and HCV infection among people who inject drugs, a population at higher risk of these infections. In this systematic review, HCV estimates came from studies in 24 countries. Pooled HCV incidence was 12.1 per 100 person-years; data for both infections were scarce, suggesting increased efforts are needed to keep track of these infections in this population.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 11, June 2023
This Comment supports SDGs 4 and 10 by reviewing the global pledges and resolutions that have been made regarding disabled children (dating back to 1946), and highlighting how the September 2023 global summit on SDGs provides an opportunity to reaffirm global commitments on early childhood development.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Rheumatology, Volume 5, June 2023
This Article supports SDG 3 by estimating the burden of low back pain, which continues to be the leading cause of disability worldwide. The study predicts that low back pain prevalence will continue to increase, from 619 million people in 2020 to 843 million in 2050. Two-fifths of the burden are due to modifiable risk factors, and a quarter of years lived with disability are attributable to occupational ergonomic factors.
Elsevier,
eClinicalMedicine, Volume 60, June 2023
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by estimating the proportion of dementia attributable to hypertension, finding an overall global population attributable fraction of 15.8%. Results were also broken down by region and age. The authors note that the estimates from this study could help to inform public health policy at global and national levels.
Elsevier,
eBioMedicine, Volume 92, June 2023
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by describing a cohort characterization model for Alzheimer’s Disease built on medications and diagnoses data that are widely available in a structured format in electronic health records (EHRs), showing that standard machine learning applied to sequences of EHR data can produce scalable computational characterization of Alzheimer’s disease cohorts.
Elsevier,
eBioMedicine, Volume 92, June 2023
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by highlighting differential effects of sleep disturbances on resting-state neural activity in patients on the Alzheimer's disease spectrum relative to healthy adults, suggesting a key role of sleep disturbances in the neurophysiological changes seen in Alzheimer's disease, with implications for basic research and clinical intervention.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, Volume 29, June 2023
This Viewpoint supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by estimating the potential financial cost of lecanemab, a drug for early Alzheimer's disease, if it were to be approved in Europe at the same price as in the USA. The authors suggest that pricing would be unsustainable and that new payment models will be needed to address affordability and inequalities in access.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 11, June 2023
This Comment article supports SDG 3 and 16 by highlighting how complex humanitarian settings have become fertile environments for spreading misinformation, disinformation, and malinformation, and how the 2021 release of the Oxford Statement on International Law Protection in Cyberspace, which touches on sovereignty, incitement, human rights, criminal law, general rules of international humanitarian law, and international criminal law, is an important first step to address this type of disinformation.