Energy conservation is a critical element in the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly linked to SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy, SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production, and SDG 13: Climate Action. However, its impact spans across multiple other goals too, illustrating the interconnected nature of the SDGs.
SDG 7 aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. Energy conservation plays an indispensable role in this goal. By encouraging the efficient use of energy and reducing overall demand, we can stretch our existing energy resources further. This is particularly relevant in underprivileged areas where energy infrastructure is limited or non-existent. Energy conservation measures, such as the use of energy-efficient appliances and lighting, can make the existing energy supplies more accessible and affordable to all.
SDG 12 calls for ensuring sustainable consumption and production patterns. Energy conservation is a key part of this goal. A large portion of the world's energy is consumed by industries. Adopting energy-efficient technologies and practices can significantly reduce the energy demand of these industries, leading to more sustainable production patterns.
SDG 13 focuses on taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. Energy conservation contributes to this goal by reducing the demand for energy production, especially from fossil fuels, which are the primary source of greenhouse gases. Lower energy demand translates to lesser greenhouse gas emissions, thereby mitigating climate change.
Beyond these specific goals, energy conservation has ripple effects on several other SDGs. For instance, conserving energy can reduce air pollution (contributing to SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being) and limit the environmental impacts of energy production, such as water pollution and habitat destruction (contributing to SDG 14: Life Below Water and SDG 15: Life on Land).
Pierre Boissery, Philippe Lenfant, Gilles Lecaillon, Anaïs Gudefin, Sebastien Fonbonne, Mohamed Selfati, Najib El Ouamari, Robert Brunet, Free Espinosa, Hocein Bazairi, Chapter 7 - The ecological restoration: A way forward the conservation of marine biodiversity, Editor(s): Free Espinosa,
Coastal Habitat Conservation, Academic Press, 2023, Pages 171-191, ISBN 9780323856133
Water Conservation and Wastewater Treatment in BRICS Nations, Technologies, Challenges, Strategies and Policies, 2020, Pages 321-328
Insect pollinators are becoming visible to societies. Many peer-reviewed papers evidence biophysical and ecological aspects of managed and non-managed insect pollinators. Evidence on stressors of declines yield peer-reviewed calls for action. Yet, insect pollinator declines are inherently a human issue, driven by a history of land-use trends, changes in technologies, and socio-cultural perceptions that unwittingly cause and perpetuate declines. Conservation requires integrating social and ecological understandings to reconfigure human behaviors across societies’ sectors.
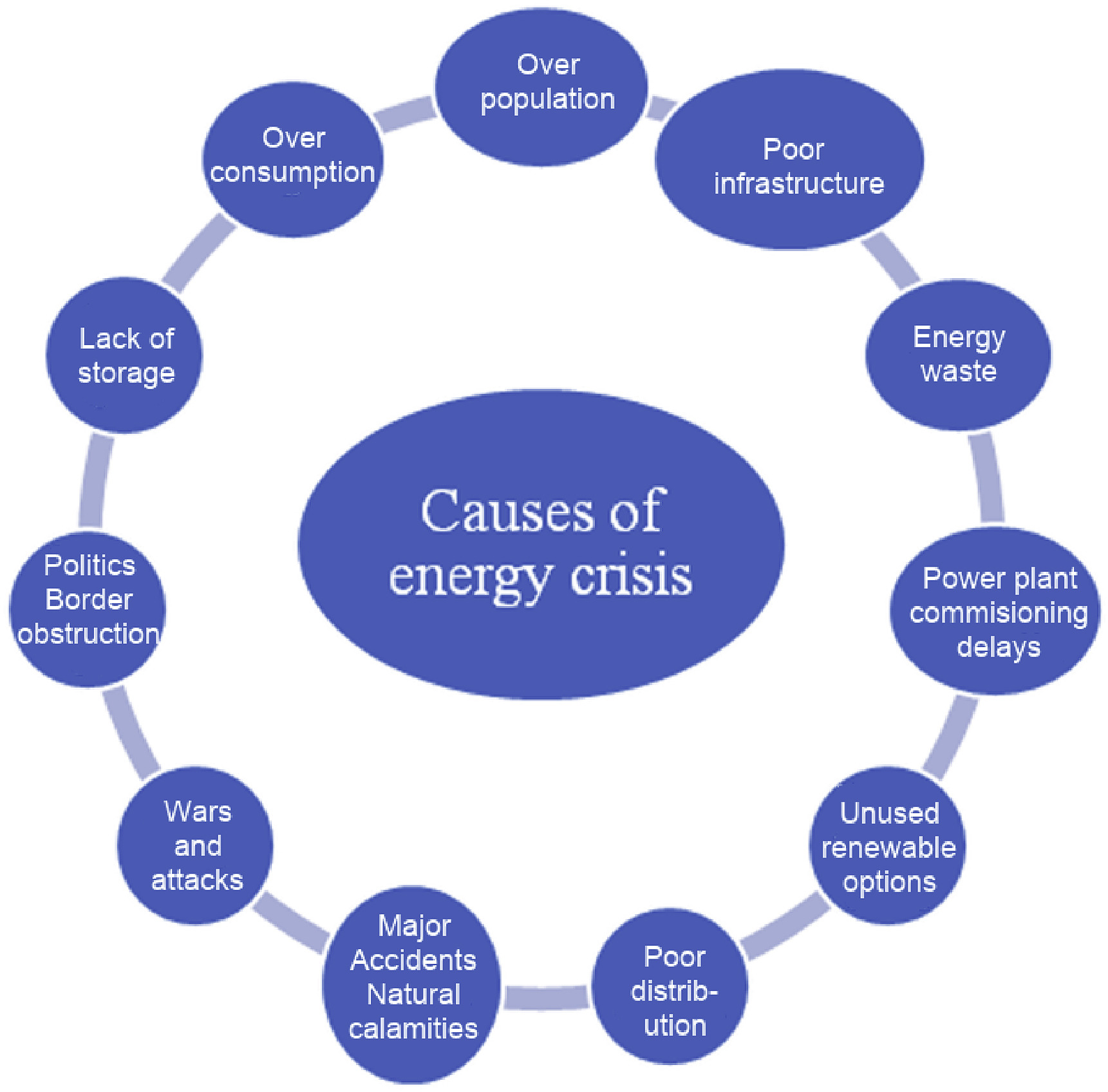
Nepal has been suffering from a serious energy crisis for decades. It has severely affected its economic, social and political developments. Owing to the continuously evolving energy situation in Nepal, and the recent progress in renewable energy technologies, this study aims to provide an up to date perspective on the current energy crisis in Nepal. In particular, the current energy production and consumption profiles are reviewed, and the main factors contributing to a widening gap between the energy supply and demand are identified.