Climate change mitigation requires energy transition supported by public to maximize policy acceptance. We examine if transiency of residence and life satisfaction affect climate change perceptions and opinions on energy sources. We find that transiency of residence and life satisfaction have significant effect in shaping views towards climate change. Results indicate that individuals concerned about local impact of climate change are supportive of renewable energy sources.
Fish experiencing abnormally high or prolonged elevations in temperature can exhibit impaired reproduction, even for species adapted to warm water environments.
Cyclones and tropical storms are important threats to public health faced by countries worldwide as they are associated with infectious disease outbreaks, unsafe food and water to mention a few.
This book chapter advances SDGs 2, 13, and 15 by summarizing the impact of high temperature on wheat production, physiological traits contributing to heat tolerance, and how to integrate new tools such as trascriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics with plant breeding.
This book chapter advances SDGs 9, 13, and 15 by highlighting coastal management problems related to the reclamation process that have been addressed through geoinformatics. The findings of the study carried out offer a detailed overview of the quantity and quality of research materials reported thus far on the subject of the recycling process, remote sensing, and Geographical Information System innovations.
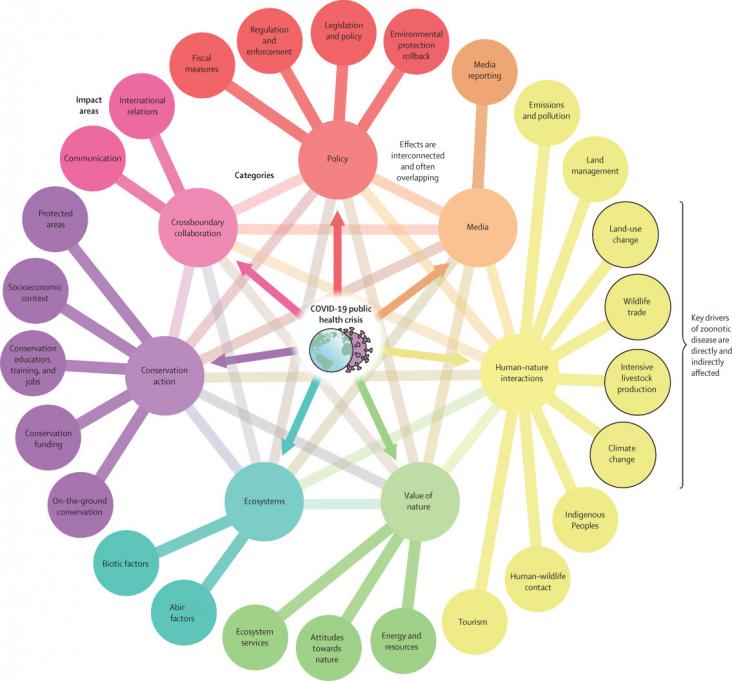
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, caused by zoonotic SARS-CoV-2, has important links to biodiversity loss and ecosystem health.
An Article in support of SDGs 12 and 13, assessing the potential benefits of moving to more sustainable diets for greenhouse gas emissions, land use, mortality, and cancer rates.
