
Human health is better now than at any time in history, but these gains have come at a high price: the degradation of nature’s ecological systems on a scale never seen in human history. A growing body of evidence shows that the health of humanity is intrinsically linked to the health of the environment, but by its actions humanity now threatens to destabilise the Earth’s key life-support systems. As a Commission, we conclude that the continuing degradation of natural systems threatens to reverse the health gains seen over the last century. The SDGs provide a great opportunity to integrate health and sustainability through the judicious selection of relevant indicators relevant to human wellbeing, the enabling infrastructure for development, and the supporting natural systems, together with the need for strong governance.
Elsevier,
Aquatic Functional Biodiversity, An Ecological and Evolutionary Perspective, 2015, Pages 127-155
This book addresses goals 13 and 14 by discussing conservation and biodiversity factors in freshwater ecosystems
A changing climate alters the living conditions for almost every species on earth.
Integration and interconnection are two key themes in this chapter, which primarily addresses goals 8 (decent work and economic development) and 13 (climate action) although has links to several others.
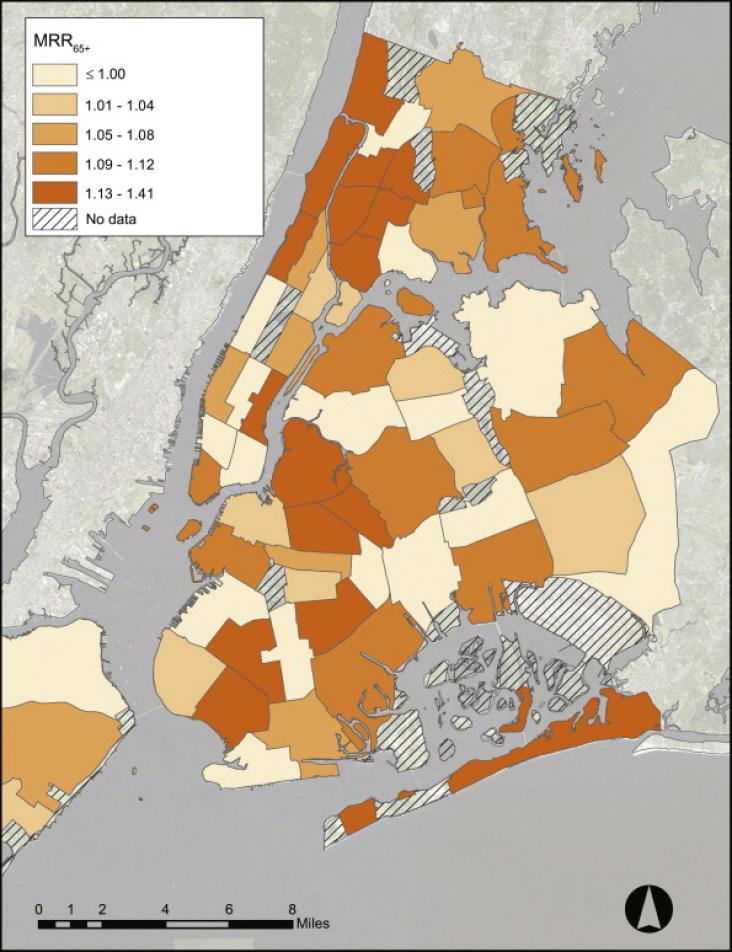
The health impacts of exposure to summertime heat are a significant problem in New York City (NYC) and for many cities and are expected to increase with a warming climate.
This paper examines the development and use of scenarios as an approach to guide action in multi-level, multi-actor adaptation contexts such as food security under climate change.
This article describes the key challenges and opportunities in modeling and optimization of biomass-to-bioenergy supply chains.
Energy is central to the survival and prosperity of human society, which explains the social sciences' interest in energy production, consumption and distribution.
Western diets are characterised by a high intake of meat, dairy products and eggs, causing an intake of saturated fat and red meat in quantities that exceed dietary recommendations.
In 1997, the global value of ecosystem services was estimated to average $33. trillion/yr in 1995 $US ($46. trillion/yr in 2007 $US).
