The Planetary Health Diet Index (PHDI) is a novel measure adapted to quantify alignment with the dietary evidence presented by the EAT-Lancet Commission on Food, Planet, Health. This review aimed to examine how population-level health and sustainability of diet as measured by the PHDI changed from 2003 to 2018, and to assess how PHDI correlated with inadequacy for nutrients of public health concern (iron, calcium, potassium, and fiber) in the United States. Although there have been positive changes over the past 20 years, there is substantial room for improving the health and sustainability of the United States diet. Shifting diets toward EAT-Lancet recommendations would improve nutrient adequacy for iron, fiber, and potassium. Policy action is needed to support healthier, more sustainable diets in the United States and globally.
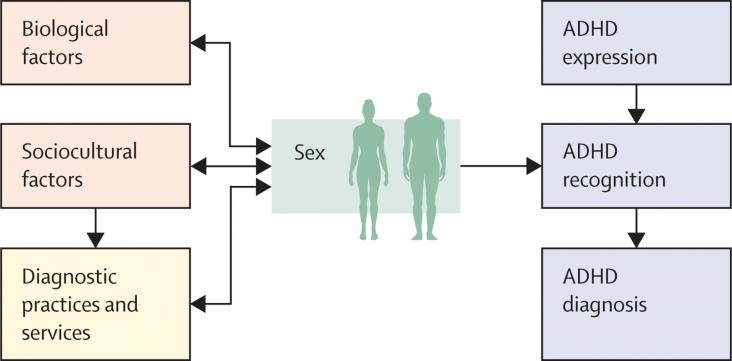
This Viewpoint looks at the reasons that females tend to be less likely to be diagnosed with ADHD, are diagnosed later in life, and are less likely to be prescribed medication. It considers potential biological factors including genetic factors, the influence of diagnostic factors such as diagnostic overshadowing, and sociocultural explanations including sex differences in presentation and compensatory behaviour.
The latest global prison trends from Penal Reform International suggest that approximately 740 000 women are in prison and that the number is rising in most regions. Neither the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development7 nor the UN definition of vulnerability make explicit reference to human rights of people deprived of their liberty.
This Article supports SDG 3 by showing that children with disabilities have fewer opportunities for play compared with children without disabilities (around 9% less), which is important because play is important for child development. Strategies to overcome barriers to participation in play are needed.
This Article supports SDG 3 by examining whether rehabilitation with hearing aid use in people with hearing loss is associated with lower mortality.
Proper regulation is essential to ensure that such a system benefited those in need, and that those who provided organs are properly compensated. Without significant policy changes, however, far too many patients will continue to languish on waiting lists until they run out of time. The goal of SDG3 is that everyone should have a good health and well-being.
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health. Hepatitis C is a common cause of chronic hepatitis associated with a significant global burden.
Elsevier,
Computational Intelligence and Deep Learning Methods for Neuro-rehabilitation Applications, 2024, Pages 121-148
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health by focusing on neurorehabilitation as a means to facilitate recovery from nervous system damage and enhance functional independence for individuals affected by conditions such as stroke or brain trauma. By incorporating advanced assistive technologies and machine learning into rehabilitation practices, the chapter highlights innovative approaches that can improve the effectiveness of interventions, ultimately promoting better health outcomes and quality of life for patients. Additionally, it supports Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by emphasizing the importance of accessible and adaptive technologies that provide all individuals, regardless of their disabilities or socioeconomic status, with the tools necessary to achieve greater independence and participate fully in society.
This study including 3173 Ukrainians assessed the levels of stress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) prevalence in not displaced persons (NDPs), internally displaced persons (IDPs), and refugees abroad. It found being forcibly displaced from the previous living area and, especially, entering a new cultural environment significantly contributes to the mental health issues caused by war exposure and witnessing.
The findings of this study that analyzes serious suicide attempts provide valuable insights for suicide prevention strategies and informing treatment approaches.
