Felix A. Diawuo, Roland Teye Amanor, Chapter 2 - Need for pumped hydro energy storage systems, Editor(s): Amos T. Kabo-Bah, Felix A. Diawuo, Eric O. Antwi, Pumped Hydro Energy Storage for Hybrid Systems, Academic Press, 2023, Pages 23-41, ISBN 9780128188538

Miguel Amado, Francesca Poggi, Chapter 1 - Cities Evolution, Editor(s): Miguel Amado, Francesca Poggi, Sustainable Energy Transition for Cities, Elsevier, 2022, Pages 1-17, ISBN 9780128242773, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824277-3.00002-5.
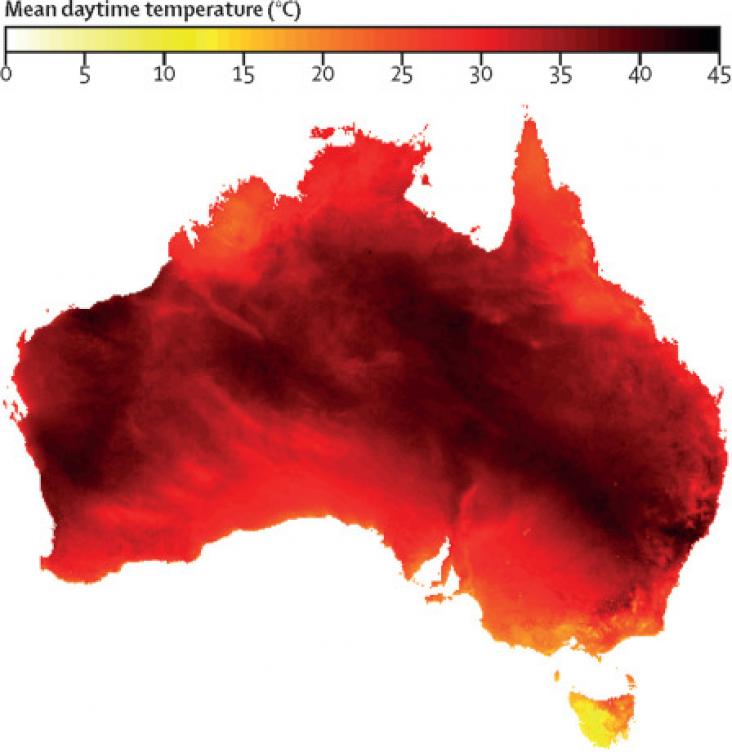
Background: Increasing air conditioner use for cooling indoor spaces has the potential to be a primary driver of global greenhouse gas emissions.
