Restoration thinking provides a new paradigm for charting a bold future that prevents further loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction, avoids catastrophic climate change, and promotes the well-being and safety of all people. Ten paths guide actions to restore and care for Earth and all its living creatures.
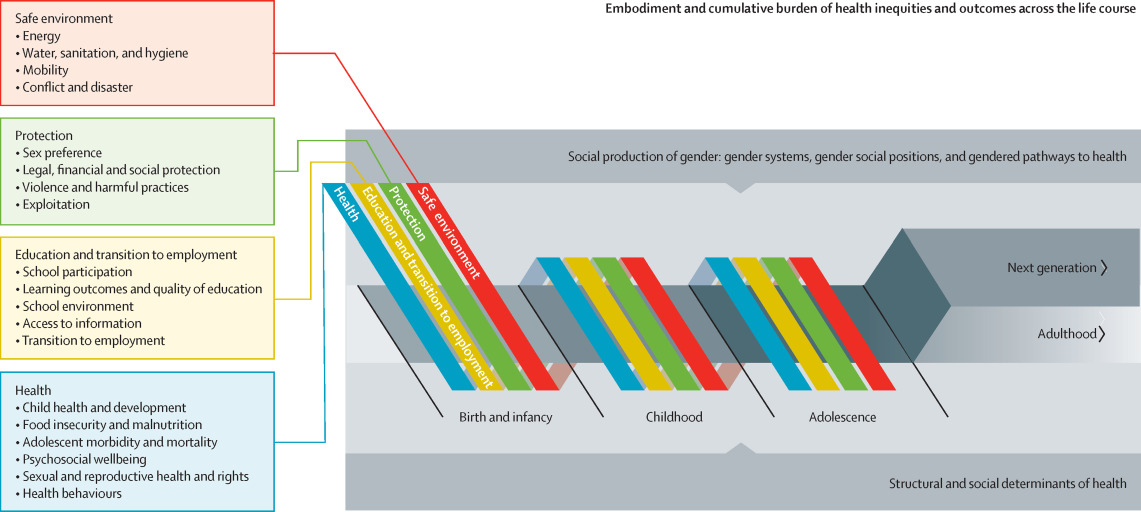
Background: By adulthood, gender inequalities in health and wellbeing are apparent. Yet, the timing and nature of gender inequalities during childhood and adolescence are less clear. We describe the emergence of gender inequalities in health and wellbeing across the first two decades of life. Methods: We focused on the 40 low-income and middle-income countries in Asia and the Pacific. A measurement framework was developed around four key domains of wellbeing across the first two decades: health, education and transition to employment, protection, and a safe environment.
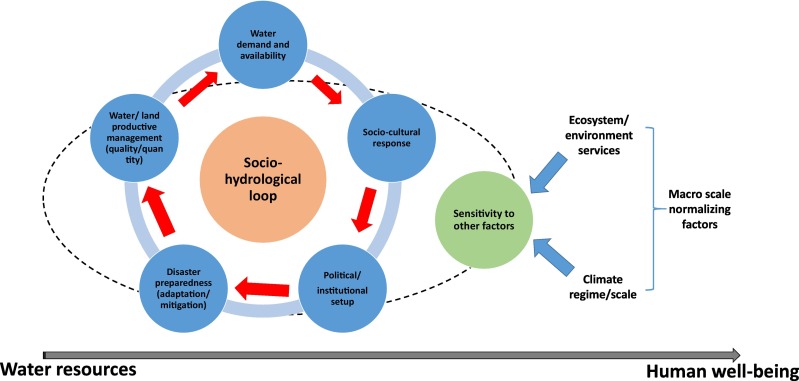
This paper presents challenges for water security in the three largest riverine islands in Asia, a socio-hydrology approach to manage water scarcity and human well-being, and an adaptive management cycle to implement socio-hydrology in the field.
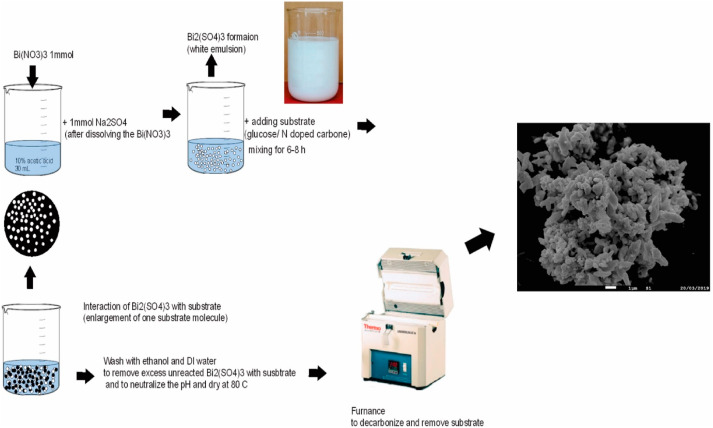
Iodide and bromide ions in surface and ground waters can react with natural organic matters and produce toxic disinfectant by-products. A novel bismuth composite material has been developed for the removal of iodides and bromides at parts per million concentrations.
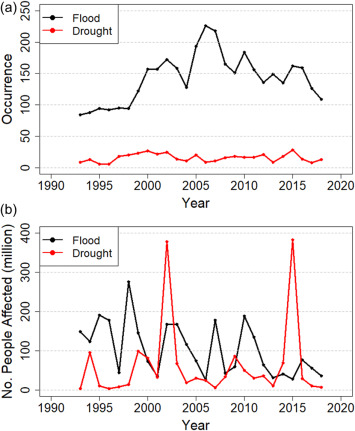
This paper examines the global trends and main health impacts of these events based on databases and case studies, identifies gaps in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) indicator framework for monitoring health impacts of disasters and suggests recommendations to address these gaps.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 by explaining how water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) essentially address healthy living through intelligent management of human behaviour and the production of wastes so that the environment and ecosystems are not negatively impated. This chapter describes WASH in low resource countries and the role of the engineer in enabling the approach.
This chapter addresses SDG 10 and SDG 3 through an examination the critical dimensions of cyberbullying in relation to hate speech and online harassment, connecting it with racial and ethnic discrimination.
This Personal View addresses SDGs 2, 3, 10, and 12 by exploring the potential consequences of food system innovations in relation to the SDGs. The authors highlight the negative consequences that standalone innovations can have for some sustainability goals, particularly for reducing inequalities and improving social justice. They identify ways in which technical innovations could be embedded in systemic changes to address trade-offs between positive and negative outcomes of their implementation.
Background: Circadian disturbances are commonly seen in people with Alzheimer's disease and have been reported in individuals without symptoms of dementia but with Alzheimer's pathology. We aimed to assess the temporal relationship between circadian disturbances and Alzheimer's progression. Methods: We did a prospective cohort study of 1401 healthy older adults (aged >59 years) enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA) who had been followed up for up to 15 years.
This chapter aligns with the SDG goal 3 of good health and wellbeing by examining the properties of the enzyme, hepatitis C NS2/3 protease, with special emphasis on the catalytic components of its active site, and the mechanism by which it hydrolyzes peptide bonds.