Socioeconomic impact is an important consideration in the quest for sustainable development. It is inherently interwoven with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), 17 global objectives designed to enhance societal and environmental wellbeing. The interaction between socioeconomic factors and the SDGs is profound, multifaceted, and has significant implications for global progress. For example, SDG 1, 'No Poverty', directly addresses socioeconomic disparities, aiming to alleviate poverty in all its forms. The achievement of this goal has substantial effects on other SDGs, from SDG 2 'Zero Hunger', to SDG 3 'Good Health and Well-being'. It further influences SDG 4 'Quality Education' as socioeconomic status often dictates access to quality education, impacting people's ability to escape the poverty cycle. Similarly, SDG 8 'Decent Work and Economic Growth' and SDG 10 'Reduced Inequalities' underscore the role of economic factors in promoting sustainable development. The nexus between socioeconomic status and the SDGs extends to environmental considerations too. SDG 13 'Climate Action', for instance, is significantly affected by economic factors, such as industrial policies and investments that can either hinder or support green transitions. Moreover, it is recognized that climate change has disproportionate impacts on socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, revealing a clear interlinkage with SDG 1. Lastly, the implementation and success of SDGs are contingent upon the existing socioeconomic infrastructure of nations, highlighting the indispensable role of national and international policy frameworks, economic incentives, and robust institutions, as emphasized in SDG 16 'Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions' and SDG 17 'Partnerships for the Goals'. In conclusion, understanding and addressing socioeconomic impact is a fundamental necessity for realizing the ambitious vision of the SDGs.
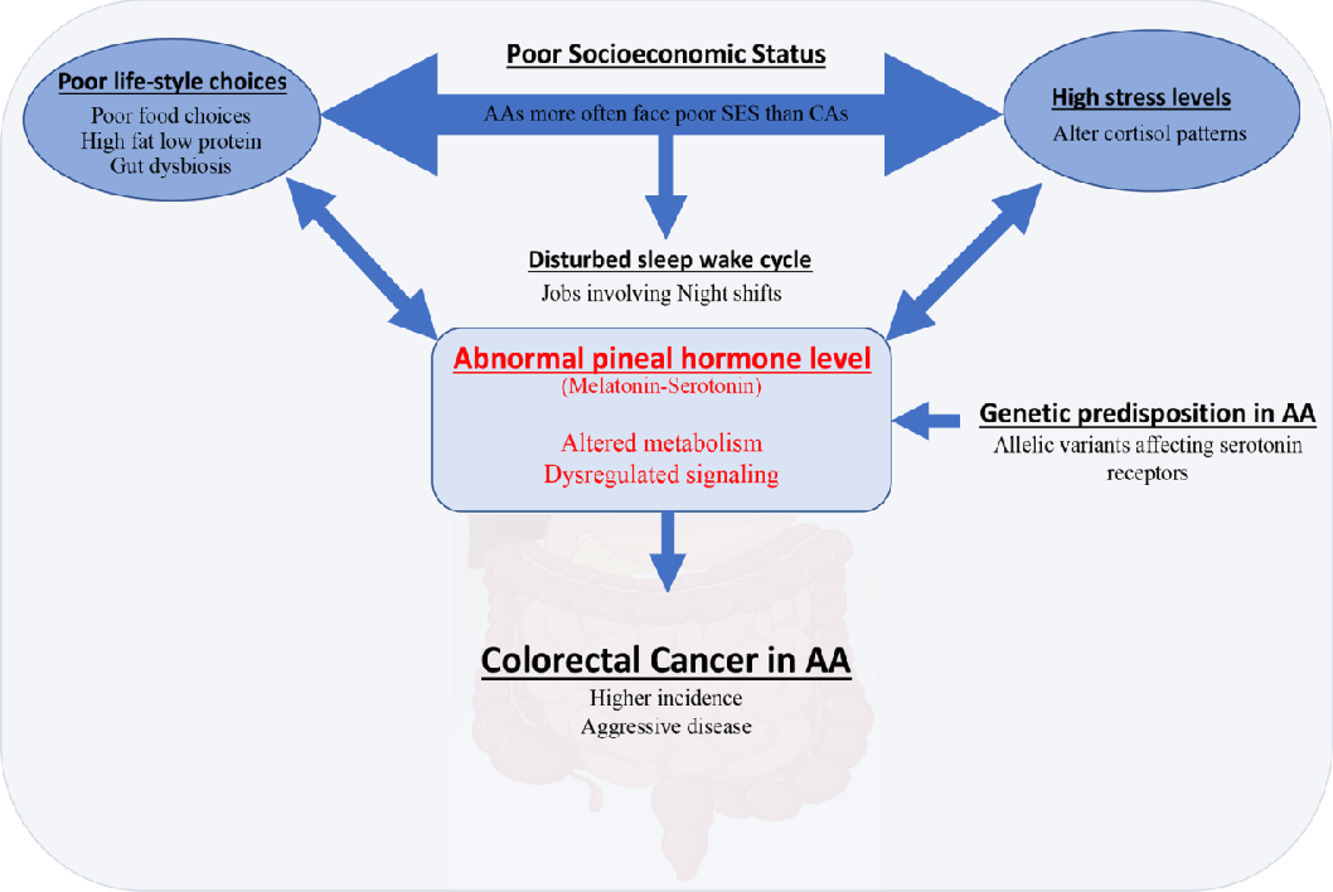
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Despite increased screening options and state-of-art treatments offered in clinics, racial differences remain in CRC. African Americans (AAs) are disproportionately affected by the disease; the incidence and mortality are higher in AAs than Caucasian Americans (CAs). At the time of diagnosis, AAs more often present with advanced stages and aggressive CRCs, primarily accounting for the racial differences in therapeutic outcomes and mortality.
Pathways towards a defossilated sustainable power system for West Africa within the time horizon of 2015–2050 is researched, by applying linear optimisation modelling to determine the cost optimal generation mix to meet the demand based on assumed costs and technologies in 5-year intervals. Six scenarios were developed, which aimed at examining the impact of various policy constraints such as cross-border electricity trade and greenhouse gas emissions costs.
A review of electricity access projects in rural areas reveals a number of unsustainable features. Each rural area can be very different with regard to the socioeconomic conditions and the dynamics between society and technology. This research is a comparative study to assess the impact of techno socioeconomic factors on the sustainability of two microhydro power projects. The assessment of sustainability projects was based on sustainable development indicators for rural electrification, considering technical, economic, social, environmental and institutional sustainability.